* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lesson Plan Format
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Noether's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Brouwer fixed-point theorem wikipedia , lookup
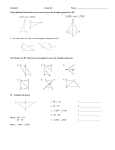
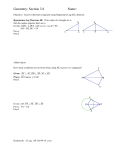
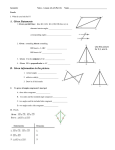
HW- pg. 113 (1-5) Ch. Test THURSDAY 10-10-13 www.westex.org HS, Teacher Website 10-4-13 Warm up—Geometry CPA Determine whether each statement is true or false. If false, give a counterexample. 1. If two angles are complementary, then they are not congruent. 2. If two angles are congruent to the same angle, then they are congruent to each other. GOAL: I will be able to: 1. write two-column proofs. 2. prove geometric theorems by using deductive reasoning. HW- pg. 113 (1-5) Ch. Test THURSDAY 10-10-13 www.westex.org HS, Teacher Website Name _________________________ Geometry CPA 2-6 Geometric Proof GOAL: I will be able to: 1. write two-column proofs. 2. prove geometric theorems by using deductive reasoning. Date ________ When writing a proof, it is important to justify each logical step with a reason. You can use symbols and abbreviations, but they must be clear enough so that anyone who reads your proof will understand them. Example 1: Writing Justifications Write a justification for each step, given that A and B are supplementary and mA = 45°. STATEMENT REASON 1. A and B are supplementary 1. mA = 45° 2. mA + mB = 180° 2. 3. 45° + mB = 180° 3. 4. mB = 135° 4. YOU TRY: Write a justification for each step, given that B is the midpoint of AC and AB EF. STATEMENT REASON 1. B is the midpoint of AC. 1. 2. AB BC 2. 3. AB EF 3. 4. BC EF 4. A _______________ is any statement that you can prove. Once you have proven a theorem, you can use it as a reason in later proofs. Example 2: Linear Pair Theorem If two angles form a linear pair, then they are supplementary. Given: 1 and 2 are a linear pair Prove: 1 and 2 are supplementary Statements 1. 1 and 2 are a linear pair 2. and form a line. Reasons 1. 2. Def. of linear pair 3. mABC = 180° 3. 4. m1 + m2 = mABC 4. Angle addition post. 5. 5. Subst. steps 3, 4 6. 1 and 2 are supplementary 6. A geometric proof begins with Given and Prove statements, which restate the hypothesis and conclusion of the conjecture. In a _________________ __________, you list the steps of the proof in the left column. You write the matching reason for each step in the right column. Example 3: Congruent Supplements Theorem Given: 1 and 2 are supplementary, and 2 and 3 are supplementary. Prove: 1 3 Example 4: Congruent Complements Theorem If two angles are complementary to the same angle (or to two congruent angles), then the two angles are congruent. Given: ∠1 and ∠2 are complementary and ∠2 and ∠3 are complementary. Prove: ∠1 ∠3 Statements Reasons 1. 1. 2. 2. 3. 3. 4. 4. 5. 5. 6. 6.