* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit-7-Key-Concepts-Master-Copy
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
German–Soviet Axis talks wikipedia , lookup
World War II and American animation wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
European theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
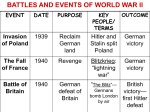
Key Concepts Chart Key Concepts Chart (World War II) Key Concepts + √ - Explanation Extra Information The treaty that ended the “war to end all wars” did not create a “just and secure peace.” Hitler and Mussolini both subscribed to this philosophy and used to consolidate control over their respective countries. Fascism is an very conservative ideology Treaty of Versailles Treaty that ended WWI. fascism political philosophy that emphasizes the importance of the nation or an ethnic group, and the supreme authority of the leader over that of the individual Nazism an extreme form of fascism shaped by Hitler’s fanatical ideas about German nationalism and racial superiority Hitler used propaganda, parades, rallies, and regalia in order to restore German pride and manipulate the German people into supporting his policies Totalitarianism A government that exerts total control over the nation and citizens’ lives Not necessarily evil, but usually is. Government uses terror and restricts individual rights. Importance of the group (nation) over the individual Axis power aggression Germany – Austria, Czechoslovakia, Sudetenland, Poland, Belgium, France Aggressors typically receive the most punishment. Axis powers clearly the aggressors in the war. Japan – China, Manchuria Italy - Ethiopia Munich Conference Meeting between Neville Chamberlain, Adolf Hitler, and Benito Mussolini in September 1938. Britain and France give the Sudetenland to Hitler in order to appease him. Seen as one of the biggest mistakes of the war for the Allies. It does not work, Hitler never intended to stop taking territory. Appeasement giving into a competitor’s demands in order to keep the peace Usually associated with the Munich Conference, fails to prevent World War II. Neville Chamberlain claimed “Peace in our time” yet it only delayed the inevitable NonAggression Pact Signed between Hitler and Stalin, said that Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union would not fight each Stalin thought Hitler had no plans to invade the Soviet Union. The pact will cease when Hitler eventually invades the USSR in Key Concepts Chart other when war broke out between the Allies and the Axis Powers 1941 U.S. isolationism U.S. is focused on getting out It was clear that we supported the of the Depression. Benefitted Allies, yet FDR stressed neutrality us more to make money off the war and stay out of the fighting. Neutrality Acts Several acts, which banned U.S. from providing weapons to warning nations, loans to warring nations. “Four Freedoms” speech FDR 1) Freedom of speech 2) Freedom of worship We were using “cash and carry” European powers like France and Britain would sail to U.S. ports, pay cash for what they purchased, and ship it back out using their own ships (we assume little risk this way) Promoted democratic ideals for world peace and prosperity, dealt mainly with U.S. national security though 3) Freedom from want 4) Freedom from fear Lend-Lease Act Authorized FDR to aid any nation whose defense he thought was vital to American security Sent aid to Britain at first, then the Soviet Union after Germany invades. We gave aid to other minor nations Pearl Harbor December 7, 1941 The last time that we have officially declared war was World War II. The Japanese were angry at the U.S. because we froze their financial assets in the U.S. and cut off oil shipments. We wanted to check their expansion In less than 2 hours, 2,400 Americans had been killed. Many warplanes destroyed, 18 warships sunk or damaged, including 8 out of 9 of the Pacific fleet’s battleships Office of War Mobilization Centralized resources for the war effort under James F. Byrnes, who had such broad authority he was often called the “assistant president” Led to record production numbers. We produced twice as much as the Axis nations combined Office of Price Administration Tried to control inflation by limiting prices and rents Also oversaw rationing in order to fairly distribute scarce items. deficit When spending exceeds Spending will go from $8.9 billion Key Concepts Chart spending revenue aka you’re spending more money than you’re making and going into debt. Propaganda Attempting to sway public opinion and stir emotion based on exaggerated “truths” Rationing Controlling and/or limiting the amount of resources that are consumed. Used during the war to ensure that as much could be sent overseas to the troops as possible victory gardens Backyard gardens that the government encouraged Americans to plant so they could feed themselves and not rely on factory production or agricultural production Idea was that we could send as much food to troops overseas as possible war bond drives Encouraged Americans to buy war bonds. Pay money now, get a return on your investment later If I buy a war bond for $20 in 1941, I could cash it in years later for more money, say $40 in 1951 for example Rosie the Riveter Meant to inspire women to take up the factory jobs that their husbands, brothers, and sons left behind and support the war effort. One of the most recognizable propaganda posters from the era. Double V Campaign Victory at home and abroad. Attempt by African Americans to achieve civil rights to $95.2 billion in 1945. We obviously have no reservations about deficit spending in modern American economics. The national debt is currently in the trillions. Used heavily in World War II to get Americans to conserve natural resources, buy war bonds, plant victory gardens, and in general support the war effort Americans had coupon books for certain items that they could use to purchase rationed goods. Key Concepts Chart progress at home during the war. Executive Order 8802 Opened jobs and job training programs in defense to all Americans “without discrimination because of race, creed, color, or national origin.” FEPC Fair Employment Practices Committee put in place to hear complaints about job discrimination Congress of Racial Equality A. Philip Randolph Use of nonviolent techniques to end racism. Used sit-ins. Paved the way for the Civil Rights Movement in the 1950s and 60s Tuskegee Airmen code talkers 1943 repeal of Chinese Exclusion Act Labor and civil rights leader during WWII and later on with MLK Thanks to his efforts, the government helped protect the rights of minorities in the workplace by cracking down on discrimination First African American flying African Americans got the unit in the U.S. military opportunity to fight due to large casualties Navajo Indians developed a Provided important secure secret code based on their communications link in several key language that the enemy could battles of the war. There’s even a not break 2002 movie about it called Wind Talkers. Shows that while China was also our ally in the war, discrimination was still and we want to stay favorable in practiced, the U.S. their eyes, at least until 1949 when government is starting to lax they fell to communism. some. Zoot-Suit Riots of 1943 Fights between sailors and Mexican Americans in LA. Sailors aid the Mexicans were not dressed “American” Police sided with the sailors, though they started the fights/riots Shows the racial prejudice that existed against Mexican Americans Japanese internment Forced relocation under Executive order 9066 of all Japanese Americans living on the West Coast Korematsu v. United States Fred Korematsu refused to relocate and was arrested. Korematsu appealed, saying his civil rights were violated Confined in remote areas far from the coast, in wooden shacks surrounded by barbed wire. Cramped living conditions that resembled concentration camps in Europe Supreme Court ruled that the relocation policy was not based on race and therefore justified. Years later in 1988, Congress passed a law rewarding any surviving Key Concepts Chart Battle of the Atlantic Allied warships used sonar to locate and attack German submarines (U-boats). Began using long range sub-hunting aircraft Battle of Stalingrad Considered the turning point of the war in Europe. The cold Russian winter stopped German advancement into USSR. The Soviets counterattack and lose approximately 1 million but take 350,000 Nazis with them North Africa Campaign Eisenhower vs. Rommel in the desert. Americans lose a key battle yet issue a counterattack and take over the area. D-Day member of the internment camps with a tax-free payment of $20,000. 1988 was also the same year Die Hard came out, and the Japanese CEO in the film was an internment camp survivor Once the German U-boats were made less effective, it proved a key turning point in the European naval theater. The German offensive stalls, Russians begin to regain lost ground and push towards Germany. Casablanca Conference following the campaign, where Churchill and Roosevelt agree to: 1) Europe needed to be dealt with first 2) nothing but the unconditional surrender of the Axis Powers Largest amphibian invasion in Once Western France is taken, it world history on June 6, 1944. marks the beginning of the end for Allies invade Western Europe Hitler. Though a huge victory, by landing on the beaches of many Allied lives were lost in Normandy, France. taking Omaha beach Battle of Midway Huge naval victory for the Allies vs. Japan Considered the turning point in the Pacific Theater Battle of Okinawa One of the bloodiest battles of the Pacific theater. It was the last major stronghold before the invasion of Japan. island hopping U.S. strategy in the Pacific pursued by Douglas MacArthur. Also called “leapfrogging,” U.S. would The Japanese fight to the death, leading to heavy casualties on both sides. One of the reasons Truman drops the bombs is because he saw how fiercely the Japanese fought at Iwo Jima and Okinawa: they would fight equally as hard if the Allies invaded Japan. Called leapfrogging because of the way we jumped from one lily pad to the next on our way to Japan. Key Concepts Chart take islands one at a time in progression that they could use for bomber bases for planes to take off from to bomb Japan kamikaze pilots Pilots towards the end of the war that sacrificed themselves by crashing their planes into Allied ships. Many kamikaze planes were loaded with bombs in order to inflict as much damage as possible. Manhattan Project Top secret project to develop the atomic bomb the Big Three of WWII FDR, Churchill, and Stalin… and their respective countries. They meet at several conferences during the war to decide the fate of Europe after the war First bomb field tested in the New Mexico desert. Robert Oppenheimer, the chief architect behind the bomb, said “Now I am become Death, the destroyer of worlds.” Churchill and FDR became fast friends, but they did not trust Stalin, who used the war as an excuse to take up territory. Atlantic Charter Churchill and FDR agree: 1) No territorial expansion 2) Self determination for colonies These principles led to the founding of the United Nations. Unlike its predecessor, the League of Nations, the UN actually had teeth and could exert pressure on countries to behave. 3) World peace 4) Abandonment of the use of force Potsdam conference Truman tells Stalin that we Last conference of the war. have a new weapon to use in Truman, Stalin, Clement Atlee the war in order to intimidate him (atomic bomb). The future of Germany and Poland are also discussed Tehran conference Churchill and FDR promise Stalin that a cross-Channel invasion of Nazi-held Europe was coming, Stalin promised to enter the war against Japan Big Three also promise Chiang Kai-shek that all Chinese territories taken by Japan would be returned after the war. Key Concepts Chart upon Germany’s defeat Yalta conference Established the UN and the UN Security Council with the five permanent members U.S., France, U.K., U.S.S.R., and China Holocaust Systematic genocide of the Jews in Europe. German people looked for someone to blame for their problems. Nuremberg Trials A military tribunal composed of members selected by the Allies executed half of the 24 Nazi defendants Dwight D. Eisenhower Supreme Allied Commander in World War II. Very capable military commander and future president. Fought mainly in the European theater. 2/3 of Europe’s Jewish population would lose their lives in concentration camps. Other undesirables were homosexuals, Jehovah’s witnesses, Gypsies, and the homeless Established the precedent that individuals are responsible for their own actions. “we were only following orders” was no longer a viable excuse. Very good at judging his subordinates and delegating authority. Douglas MacArthur Commander of Allied forces in the Pacific Theater. Pursued the islandhopping strategy and would later command U.S. forces in the Korean War 1950-53 Called “American Caesar,” MacArthur had Supreme Command in the Pacific, answering to no one other than FDR. Adm. Chester Nimitz Admiral of the Allied fleet in the Pacific, oversaw key victories like Coral Sea and Midway A lesser known name, yet Nimitz scored several decisive Allied victories. Harry S. Truman FDR’s successor, was left to him to decide whether or not to drop the atomic bomb. He would be reelected to a second term Felt it would save American lives so he dropped it. Never regretted the decision, said Americans “should do their weeping at Pearl Harbor.” United Nations International peacekeeping community established after World War 2 Uses primarily economic sanctions to keep countries in line. NATO has more military might in reality. Key Concepts Chart