* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit One: Earth Dimensions Although the Earth appears to be a
Impact event wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial atmosphere wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
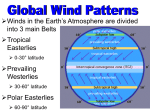
Unit One: Earth Dimensions Although the Earth appears to be a perfect sphere, by actual measurement, the Earth is an OBLATE SPHEROID, having a larger circumference around the equator than the poles. Circumferences of the Earth: At Equator- 40,076 kilometers At Poles- 40,008 kilometers Equatorial Diameter- 12,757 kilometers Polar Diameter- 12,714 kilometers ***Remember the Earth is slightly bulged at the equator and slightly flattened at the poles. Evidences of Earth’s Shape 1. Polaris, the North Star can be used to help determine the Earth’s shape According to the principle of the geometry of a sphere, the altitude of Polaris is equal to the latitude of the observer. Apparent counterclockwise motion of stars around the North Star Altitude- a celestial objects’ angular distance above the horizon Latitude- distance north or south of the equator measured in degrees 0o at the equator and 90o at the poles 2. Photographs of the Earth from Space 3. Law of Gravitation Gravity- the force of attraction between two objects Same objects weigh more at the poles than at the equator of the Earth because there is a greater gravitational pull at the poles than at the equator. 4. Sinking Ship Theory Earth’s “SPHERES” ATMOSPHERE Composed of materials that form a thin envelope surrounding the Earth held in place by gravitation The atmosphere is stratified into zones each having different temperature, pressure ranges, composition, and effects on Earth. They are the following: Mesosphere- 30 to 90 kilometers above Earth’s surface with a decreasing temperature from 100 C to -900C as altitude increases Stratosphere Above the troposphere and below the mesosphere with an increasing temperature as altitude increases due to the presence of ozone Troposphere Lowest region of the atmosphere with a decreasing temperatures altitude increases Thermosphere- Outermost shell of atmosphere where temperature continuously increases as altitude increases ***The atmosphere is the least dense of the Earth’s spheres (lithosphere, atmosphere, and hydrosphere) HYDROSPHERE Almost three quarters (71%) is covered with water Sphere is relatively thin as it is only 3.5 to 4.0 kilometers thick Hydrosphere includes salt-water (oceans) as well as freshwaters (lakes and rivers) LITHOSPHERE The most solid portion of the Earth is the rock near the Earth’s surface which includes mountains, valleys, and the ocean floor. The parallels of latitude is the equator that is located halfway between the North and South Poles Prime Meridian has a longitude of 00 and runs through Greenwich, England. LATITUDE- distance measured in degrees north or south of the equator (LINES RUN EAST AND WEST) LONGITUDE- lines RUN NORTH AND SOUTH but is measured in degrees east and west of the Prime Meridian ***How do we name the coordinates of a place using longitude and latitude??? We say latitude first, then longitude.