* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Vocabulary for Probability
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
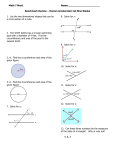
Vocabulary for Probability 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. Combination: (Simple) Event: Experiment: Experimental probability: Factorial: Outcomes: Permutation: Probability: Theoretical Probability: Tree Diagram: Independent Events: Dependent Events: Random sample: Sample space: Biased sample/Unfair: Examples: 1. Combination: 2. (Simple) Event: 3. Experiment: 4. Experimental probability: 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. An arrangement of items or events in which order does not matter. (p. 564) An outcome or set of outcomes of an experiment or situation. (p. 522) In probability, any activity based on chance (such as tossing a coin). (p. 522) The ratio of the number of times an event occurs to the total number of trials, or times that the activity is performed. (p. 527) The product of all whole numbers except zero that are less than or equal to a number. (p. 563) A possible result of a probability experiment. (p. 522) An arrangement of items or events in which order is important. (p. 563) A number from 0 to 1 (or 0% to 100%) that describes how likely an event is to occur. (p. 522) The ratio of the number of equally likely outcomes in an event to the total number of possible outcomes. (p.540) A branching diagram that shows all possible combinations or outcomes of an event. (p. 522) Events for which the outcome of one event does not affect the probability of the other. (p. 545) Events for which the outcome of one event affects the probability of the other. (p. 545) A sample in which each individual or object in the entire population has an equal chance of being selected. (p. 462) All possible outcomes of an experiment. (p. 522) A sample that does not fairly represent the population. (p. 463) For objects A, B, C, and D, there are 6 different combinations of 2 objects: AB, AC, AD, BC, BD, CD. When rolling a number cube, the event “an odd number” consists of the outcomes 1, 3, and 5. Tossing a coin 10 times and noting the number of “heads”. Kendra attempted 27 free throws and made 16 of them. Her experimental probability of making a free throw is Number made = 16 = 0.59 Number attempted 27 4 factorial = 4! = 4*3*2*1 = 24 When rolling a number cube, the possible outcomes are 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6. For objects A, B, and C, there are 6 different permutations: ABC, ACB, BAC, BCA, CAB, CBA. A bag contains 3 red marbles and 4 blue marbles. The probability of randomly choosing a red marble is3/7. When rolling a number cube, the theoretical probability of rolling a 4 is 1/6. Factorial: Outcomes: Permutation: Probability: Theoretical Probability: Tree Diagram: Independent Events: A bag contains 3 red marbles and 2 blue marbles. Drawing a red marble, replacing it, and then drawing a blue marble is an example of independent events. Dependent Events: A bag contains 3 red marbles and 2 blue marbles. Drawing a red marble and then drawing a blue marble without replacing the first marble is an example of dependent events. Random sample: Sample space: When rolling a number cube, the sample space is 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6. Biased sample/Unfair: