* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 3 Telescopes
Hubble Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Lovell Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Allen Telescope Array wikipedia , lookup
James Webb Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
CfA 1.2 m Millimeter-Wave Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Optical telescope wikipedia , lookup
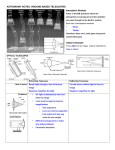
Telescopes Notes History •Hans Lippershey Middleburg, Holland –invented the _____________ telescope in 1608 •________________ –the ____________ to use a telescope in __________________. Galileo's designs used a combination of convex and concave lenses. •___________________ –___________________ the __________________ to have two convex lenses, which made the image upsidedown. Kepler's design is still the major design of refractors today, with a few later improvements in the lenses and the glass to make them. Why can’t you see an object that is far away? The answer is simple: ~ the object does not take up much space on your eye’s screen (retina). ~Using a digital camera analogy, at 150 feet the writing on a dime does not cover enough pixels on your retinal sensor for you to read the writing. ~This can be corrected by _______________ the light with lenses. Lenses •The lens in your eyes works like a glass lens. The ____________ ____________ as it goes through a ____________ _______________. •Light rays are bent when they intersect glass; a curved surface can produce an image. •In your _________, the ___________ is then ___________ at the ____________. How does this apply to telescopes? •If you had a _____________ ____________, you could _____________ _________ ____________ from the object. This image could be magnified so it stretches out over more pixels in your retina. This is also know as the collecting power. •In a telescope, two pieces make this possible: •the ____________ _______________ (refractor telescopes) or ___________ _____________- (reflecting telescopes) •the ___________ ___________ ~ When you combine the objective lens or primary mirror with the eyepiece, you have a telescope. ~ Again, the basic idea is to collect lots of light to form a bright image inside the _______________, and then use something like a magnifying glass to magnify (enlarge) that bright image so that it takes up a lot of space on your retina. A telescope has two general properties •how well it can collect the light (the ______________________) •how much it can magnify the image (the ___________________) The Aperture •A telescope's ability to ___________________ light is directly related to the diameter of the lens or mirror -- the _______________________ -- that is used to gather light. Generally, the larger the aperture, the more light the telescope collects and brings to focus, and the brighter the final image. Magnification •The telescope's _________________________, its ability to enlarge an image, depends on the combination of lenses used. The eyepiece performs the magnification. Since any magnification can be achieved by almost any telescope by using different eyepieces, aperture is a more important feature than magnification A closer look at eyepieces The purposes of the eyepiece are to: •produce and allow you to change the telescope's magnification •produce a ______________ ________________ •provide comfortable ______________ _____________ (the distance between your eye and the eyepiece when the image is in focus) •determine the telescope's field of view: –___________________ - how much of the sky, in degrees, is seen edge-to-edge through the eyepiece alone (specified on the eyepiece) –_____________ or real - how much of the sky can be seen when that eyepiece is placed in the telescope (true field = apparent field/magnification) Filters _______________ are pieces of glass or plastic that you can place in the barrel of an eyepiece to restrict the wavelengths of light that come through in the image. Set of filters for viewing, including a light pollution filter (left) and _________________ filters for enhancing contrast in ______________ images. Filters can be used to: •_______________ the _______________ of faint sky objects in light-polluted skies •enhance the _____________ of _______________ features and details on the moon and planets •____________ view the _______________ There are 2 main types of Telescopes •____________________ telescopes, which use ____________ ________________ •___________________ telescopes, which use _____________ instead of lenses. Both types accomplish exactly the same thing, but in completely different ways. Refractor Telescopes •Refractors are the type of telescope that most of us are familiar with. They have the following parts: –a _____________ _____________, made of metal, plastic, or wood –a glass combination lens at the front end (______________ lens) –a second glass combination lens (___________________) •Refracting telescopes focus light rays by ___________ them with _______________. Advantages and Disadvantages •Easy to _____________ and _________________ •Excellent for _______________, ________________ and binary star observing especially in larger apertures. •_____________ ______________ images with no secondary mirror or diagonal obstruction. •Sealed optical tube reduces image degrading air currents and protects optics. •________________ ______________ per inch of aperture •Heavier, longer and bulkier than equivalent aperture Newtonians and catadioptrics. •Small apertures •__________ ___________ for viewing small and ____________ deep sky _______________ •Color aberration due to colors of light bending different amounts. Reflecting Telescopes •History: –Isaac Newton developed the _______________ about 1680, in response to the chromatic aberration (rainbow halo) problem that plagued refractors during his time. Instead of using a lens to gather light, Newton used a curved, metal mirror (primary mirror) to collect the light and reflect it to a focus. Because the mirror reflected light back into the tube, he had to use a small, flat mirror (secondary mirror) in the focal path of the primary mirror to deflect the image out through the side of the tube, to the eyepiece; otherwise, his head would get in the way of incoming light. –In 1722, John Hadley developed a design that used parabolic mirrors, and there were various improvements in mirror-making. The __________________ reflector was a highly successful design, and remains one of the most popular telescope designs in use today. Reflecting telescopes ___________ light by ______________ them with ` _______________ Advantages and disadvantages •_______________ __________________ per inch of aperture •________________ ________________ and _______________ up to focal lengths of 1000mm. •_____________ for faint _____________ ____________ ___________ such as remote galaxies, nebulae and star clusters. •______________ _____________ for ____________ and planetary ______________. •___________ in ______________ _______________. •Open optical tube design allows image-degrading air currents and air contaminants •___________- ____________ •Large apertures (over 8") are bulky, heavy and tend to be expensive. •Slight light loss due to secondary obstruction when compared with refractors. Not everything is visible… •Many modern day telescopes do not use visible light to collect images. •Radio telescopes, x-ray telescopes and infrared (IR) telescopes have become a staple of modern day astronomy, producing some amazing images. Problems with earth-based telescopes •Earth’s atmosphere ___________ ____________ _____________ –x-rays, gamma rays and most UV light is not transmitted by our atmosphere •Earth’s _____________ _____________ images –the bending of light by the atmosphere depends on the temperature of the “air” –“twinkling” (shimmering) effect •“____________ _________________” •Solution? Put the telescope in space. Disadvantages of space-based telescopes •___________________ to launch and maintain •_______________ to ___________ •_____________ _______________