* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AP U - Uplift Community High School
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
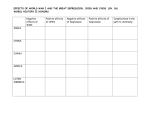
AP U.S. History 3rd Quarter Exam Chapters 23-34 March 24, 2009 Part 1: Multiple-Choice: Mark the one best answer for each of the following questions. (1 pt. each, loss of a ¼ pt. for wrong answers) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Andrew Carnegie’s use of the vertical integration was significant in that it: a. Synthesized the various immigrant labor groups into one cohesive productive force b. Led to substantial cooperation between industry and banking c. Stimulated competition in the steel industry d. Allowed a capitalist to control all aspects of the production process e. Ultimately led to the construction of massive steel factories in Pittsburgh William Jennings Bryan became the presidential candidate of both the Democrats and Populists in 1896 because of his support for: a. High protective tariffs to protect domestic industries b. Unlimited and free coinage of silver c. Nationalizing the railroad industry d. Policies that would unite poor black and white farmers e. A single six-year term for presidents Which of the following groups was NOT identified with the Populist Party? a. Supporters of the gold standard b. Anarchists c. Knight of Labor d. Grangers e. Greenback Party This muckraking novel addressed the abuses that occurred in Chicago’s meatpacking industry. a. The Octopus b. How the Other Half Lives c. Shame of the Cities d. The Jungle e. The History of the Standard Oil Company Which term best characterizes Woodrow Wilson’s approach to American foreign policy diplomacy? a. Imperialistic b. Idealistic c. Realistic d. Balance-of-power e. Isolationist The Populist Party’s presidential candidate in 1892 was: a. James B. Weaver b. William Jennings Bryan c. Mary Elizabeth Lease d. Adlai Stevenson e. William “Coin” Harvey All of the following became possessions of the U.S. under the provision of the Treaty of Paris with Spain (at the end of the Spanish-American War) EXCEPT: a. Puerto Rico b. Guam c. The Philippine Islands d. Hawaii e. Manila In the 1896 case of Plessy v. Ferguson, the Supreme Court ruled that: a. African Americans could be denied the right to vote b. Segregation was unconstitutional c. “separate but equal” facilities were constitutional d. the 14th Amendment did not apply to African Americans e. literacy tests for voting were constitutional President Taft’s foreign policy was dubbed: a. Big-stick diplomacy b. The Open Door policy c. The Good Neighbor policy 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. d. Dollar diplomacy e. Sphere-of-influence diplomacy William Jennings Bryan gained the presidential nomination of the Democratic party primarily because he: a. Had already gained the nomination of the Populist Party b. Had the support of urban workers c. Possessed a brilliant political mind d. Eloquently supported the farmers’ demand for the unlimited coinage of silver e. Was backed by the Democratic Party establishment A scarcity of gold in the U.S. in the late 19th century contributed to: a. Inflation b. the use of other medals to back up the U.S. currency c. a devaluation of U.S. currency d. deflation e. a rise in prices on farm commodities The legal codes that established the system of segregation were: a. Found only in the North b. Called Jim Crow laws c. Overturned by Plessy v. Ferguson d. Undermined by the crop lien system e. Passed during Reconstruction The “Gospel of Wealth,” which associated godliness with riches, a. Based its theology on the sayings of Jesus b. Held that the wealthy should display moral responsibility for their God-give money c. Stimulated efforts to help minorities d. Was opposed by most clergymen e. Encouraged many millionaires to help the poor During WWI, the Triple Entente included all of the following EXCEPT: a. France b. Russia c. Serbia d. Great Britain e. Germany All of the following were causes of World War I EXCEPT: a. European Imperialism b. Militarism c. The Stock Market Crash d. Military Alliances e. Assassination of Francis Ferdinand Disillusioned by war and peace, Americans in the 1920s did all of the following EXCEPT: a. Denounce “radical” foreign ideas b. Condemn “un-American” life-styles c. Enter a decade of economic difficulties d. Shun diplomatic commitments to foreign countries e. Restrict immigration The spark that ignited World War I was the assassination of Francis Ferdinand. War was first declared by: a. The Austria-Hungarians against Serbia b. The Russians against Serbia c. The Germans against France d. The Austria-Hungarians against Russia e. The Italians against the British During World War I, civil liberties in America were: a. Protected by the Espionage Act b. Limited, but no one was actually imprisoned for his or her convictions c. Extended to everyone in this country, because the war was fought for democracy d. Protected for everyone except German Americans e. Denied to many, especially those suspected of disloyalty During WWI, the Central Powers included all of the following EXCEPT: a. Japan 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. b. Germany c. Austria-Hungarian Empire d. Bulgaria e. Ottoman Empire Two constitutional amendments adopted in part because of wartime influences were the 18th, which dealt with _______________ and the 19th, whose subject was _______________. a. Prohibition; an income tax b. Direct election of senators; women suffrage c. Prohibition; woman suffrage d. An income tax; direct election of senators e. Women suffrage; prohibition All of the following helped to make the prosperity of the 1920s possible EXCEPT: a. Government stimulation of the economy b. Rapid expansion of capital c. Increased productivity of workers d. Perfection of assembly-line production e. Advertising and credit buying The prosperity that developed in the 1920s: a. Was accompanied by a cloud of consumer debt b. Led to a growing level of savings by the American public c. Enabled labor unions to gain strength d. Was concentrated primarily in agriculture e. Closed the gap between rich and poor During Coolidge’s presidency, government policy was set largely by the interests and values of: a. Farmers and wage earners b. The business community c. Racial and ethnic minorities d. Progressive reformers e. Conservative New Englanders Which of the following was NOT a consequence of the American policy of raising tariffs in the 1920s? a. European nations raised their own tariffs b. The postwar chaos in Europe was prolonged c. International economic distress deepened d. American foreign trade declined e. The American economy slipped into recession As a result of America’s insistence that is Allies’ war debts be repaid in full, a. The French and British demanded enormous reparations payments from Germany b. The German mark was ruined by drastic inflation c. The Allies borrowed money from Switzerland to repay the loans d. The United States bean threatening renewed military intervention in Europe e. The allies insisted on lower U.S. tariffs A market that is optimistic, growing and confident is called a: a. Bear Market b. Dog Market c. Bull Market d. Cheetah Market e. Lion Market All of the following were true of Al Capone EXCEPT: a. He was Italian b. He operated a large, underground, illegal network of alcohol sales during Prohibition c. He was responsible for the St. Valentine’s Day Massacre d. He was busted by the FBI for violating the 18th Amendment of the Constitution e. He was busted by the IRS for not reporting his full income to the Federal Gov’t for taxes President Herbert Hoover believed that the Great Depression could be ended by doing all of the following EXCEPT: a. Providing direct aid to the people b. Directly assisting businesses and banks c. Keeping faith in the efficiency of the industrial system d. Continuing to rely on the American tradition of rugged individualism e. Lending federal funds to feed farm livestock 29. The Agricultural Adjustment Act (AAA) proposed to solve the “farm problem” by: a. Reducing agricultural production b. Subsidizing American farm exports overseas c. Encouraging farmers to switch to industrial employment d. Helping farmers to pay their mortgages e. Creating farm cooperatives 30. The federally-owned Tennessee Valley Authority was seen as a particular threat to: a. The entire capitalist system b. The Republican party c. The automobile industry d. The private electrical utility industry e. White southern racial practices 31. The economic policies of FDR’s New Deal for America were based upon the economic philosophy of: a. Laissez Faire capitalism b. Neoliberalism c. Keynesianism d. Supply-side economics e. socialism 32. The FDIC (Federal Deposit Insurance Commission) was and example of a New Deal______________ policy. a. Recovery b. Reform c. Revolution d. Relief e. Reaction 33. Most Dust Bowl migrants headed to: a. Oklahoma b. Arizona c. Nevada d. Oregon e. California 34. The economic policy that believes that gov’t should keep its hands off of the economy and let it regulate itself; gov’t involvement only makes economy worse and violates free enterprise: a. supply-side b. Keynesian c. laissez faire d. socialism e. neoliberalism 35. The economic policy of FDR and New Deal; gov’t should actively regulate economy to prevent economic collapse; capitalism is best system, but not perfect; gov’t must protect interests of workers and middle class w/ safety net programs: a. supply-side b. Keynesian c. laissez faire d. socialism e. neoliberalism 36. All of the following contributed to the Dust Bowl of the 1930s EXCEPT: a. Dry-farming techniques b. Drought c. Farmers’ failure to use tractors and other modern equipment d. The cultivation of marginal farmlands on the Great Plains e. Soil erosion 37. The AAA (Agricultural Adjustment Act) was an example of a New Deal _____________ policy. a. Reform b. Recovery c. Revolution d. Relief e. Reaction 38. British economist John Maynard Keynes believed all of the following EXCEPT: 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. a. Gov’t needs to be the spender to get the economy going again, even if it means a deficit budget b. The Gov’t should provide aid in the form of tax cuts to the large businesses to stimulate economic growth c. Gov’t spends money to create jobs; with jobs, consumers have money to spend d. As consumers spend, the wheels of the economy start moving again e. It’s the Gov’t role, through deficit spending and job provisions, to “grease the wheels” of the economy All of the following were effects of the Great Depression EXCEPT: a. Prosperity for farmers on the Great Plaines b. High unemployment c. Personal and business bankruptcies d. Fear of investing e. Bank failures All of the following were effects of the New Deal EXCEPT a. A transition from Keynesian economic policy to Laissez Faire economic policy b. Creation of economic safety net programs like welfare and social security c. Creation of job programs like the CCC and PWA d. Government became involved in previously private enterprises, such as supplying electricity e. Government took more active role in regulating the economy Franklin Roosevelt’s New Deal was most notable for: a. Ending the Great Depression b. Providing moderate social reform without radical revolution or reactionary fascism c. Undermining state and local governments d. Aiding big cities at the expense of farmers e. Attacking the American capitalist system America’s neutrality during the Spanish Civil War of 1936-1939 allowed: a. Hitler to conquer Spain b. The Loyalists to win the war c. Roosevelt and Franco to become personal friends d. The Soviets to aid the Spanish Republic e. Spain to become a fascist dictatorship All of the following are true of Communism EXCEPT: a. a political and economic system the believes that capitalism is fundamentally unjust because it allows the wealthy to exploit the poor and working class; b. working class needs to rise up and seize the government c. all property and wealth needs to be redistributed to create a classless society d. seeks a society that is culturally, racial, and ethnically the same e. seeks a society that is economically equal All of the following are true of Fascism EXCEPT: a. Requires the armed revolution of the working class b. a political system that emphasizes government power / control c. seeks to create a single national identity or a homogenous society; d. seeks a society that is culturally, racially and ethnically the same e. emphasizes intense nationalism, militarism and the growth of Empire Fascist aggression in the 1930s included Mussolini’s invasion of ___________, Hitler’s invasion of ___________, and Franco’s overthrow of the Republic of ____________. a. Egypt, France, Poland b. Albania, Italy, Austria c. Ethiopia, Czechoslovakia, Spain d. Belgium, the Soviet Union, France e. Ethiopia, Norway, Portugal All of the following were causes leading to the rise of totalitarianism in the 1930s EXCEPT: a. The devastation of Europe after WWI b. The shame and reparations forced upon Germany c. The prosperity and wealth that came to Europe during the early 1930s d. The failure of democracy in the midst of economic collapse e. The harsh consequences of the Treaty of Versailles upon Germany All of the following are true of totalitarianism EXCEPT: a. the practice of a government where the dictator or party has complete control b. deep respect for freedom of the press, freedom of speech, freedom of religion, freedom of assembly and freedom to protest the government c. government controls all the media, information, education, military, police, economy, religion, etc. d. historically, it was the practice of both communist and fascist countries e. involves an intense use of propaganda 48. Shortly after Adolf Hitler signed a nonaggression pact with the Soviet Union, a. Britain and France signed a similar agreement b. The Soviets attacked China c. Germany invaded Poland and started World War II d. Italy signed a similar agreement with the Soviets e. The Germans invaded Finland 49. One of the 1st signs that the Nazis were building a military designed for aggression in Europe was: a. When Germany attacked and conquered Ethiopia b. When Germany attacked and conquered Manchuria in northern China c. When Germany attacked Pearl Harbor d. When Germany reoccupied the Rhineland e. When Germany invaded Austria 50. All of the following are true of Nazism EXCEPT: a. Desire to create the Third Reich b. A form of Fascism c. Desire for a multicultural society d. Belief in superiority of “Aryan Race” e. Intense anti-Semitism Part 2: Paragraph Answer: Choose two the following questions and answer each in a well-written paragraph. Questions: 1. Discuss the various causes of the Great Depression. 2. Analyze the economic policy beliefs behind Franklin Roosevelt’s New Deal during the 1930s? How did these beliefs differ from the economic policy beliefs of the previous decade? 3. Explain the ideological beliefs of Communism and Fascism. How did the two relate to each other and how have they each been considered totalitarian? 4. Discuss the factors that contributed to the rise of totalitarianism in various countries during the 1930s.