* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Metro Ethernet - Blog of FX Ari Wibowo
Survey
Document related concepts
Net neutrality law wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Registered jack wikipedia , lookup
Passive optical network wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Asynchronous Transfer Mode wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.1aq wikipedia , lookup
Multiprotocol Label Switching wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
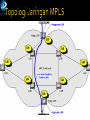
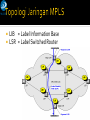
SC441 Computer Networks – Independent Study Boston University Metropolitan Ethernet Networks Estella Kang Matt Powers Typically covers several hundred miles of concentrated metropolitan areas Explosion of Internet traffic and IP services demand for rapid scalability and dynamic functionality Service and operational cost reduced Scalable – up to 100Gbps Simple – fewer protocol conversion Full suite of carrier-class Ethernet services Ethernet switching Statistical multiplexing functionality Bandwidth-on-demand service Service and management Scalability Network Reliability Co-existence with existing infrastructure Topological flexibility Reduction in operational and network costs A Metro Ethernet is a computer network based on the Ethernet standard and which covers a metropolitan area. It is commonly used as a metropolitan access network to connect subscribers and businesses to a Wide Area Network, such as the Internet. Large businesses can also use Metro Ethernet to connect branch offices to their Intranet. A typical service provider Metro Ethernet network is a collection of Layer 2 or 3 switches or routers connected through optical fiber. The topology could be a ring, hub-and-spoke (star), or full or partial mesh. The network will also have a hierarchy: core, distribution and access. The core in most cases is an existing IP/MPLS backbone, but may migrate to newer forms of Ethernet Transport in the form of 10G or 100G speeds. Ethernet on the MAN can be used as pure Ethernet, Ethernet over SDH, Ethernet over MPLS or Ethernet over DWDM SM341073 Pengenalan Teknologi dan Jasa Telekomunikasi Semester Ganjil Tahun Ajaran 2009 - 2010 6 The main advantages of an MPLS-based Metro Ethernet against a pure Ethernet are: Scalability: pure Ethernet MAN are limited to a maximum of 4,096 VLANs for the whole network, when using MPLS, Ethernet VLANs have local meaning only (like Frame Relay PVC). Resiliency: pure Ethernet network resiliency relies on STP or RSTP (30 to 1 sec convergence) while MPLS-based MANs use MPLS-based mechanism Multiprotocol convergence: with the maturity on pseudowires standards (ATM VLL, FR VLL, etc.) an MPLS-based Metro Ethernet can backhaul not only IP/Ethernet traffic but virtually any type of traffic coming from customer networks or other access networks (i.e. ATM aggregation for UMTS). End to End OAM: MPLS-based MAN offers a wider set of troubleshooting The Metro Ethernet Forum (MEF) has defined two types of services that can be delivered through Metro Ethernet: E-Line also known as Virtual Leased Line and Point-to-Point. E-LAN also known as Virtual Private LAN Services, Transparent LAN Services and MultiPoint-to-MultiPoint. SM341073 Pengenalan Teknologi dan Jasa Telekomunikasi Semester Ganjil Tahun Ajaran 2009 - 2010 7 Ethernet Private Line Dedicated UNIs for Point-to-Point connections Ethernet UNI Ethernet UNI CE Ethernet UNI OC-3 DS1 CE MEN Ethernet UNI Ethernet Private Line using E-Line Service type Internet CE MEN CE ISP POP CE Storage SP Dedicated TDM circuits Storage SP Point-to-Point EVCs (dedicated BW) ISP POP DS3 OC-3 CE Private Line Analogy to E-Line Service Internet Ethernet Virtual Private Line Supports Service Multiplexed UNI Point-to-Point VPN for site interconnectivity Point-to-Point EVCs Ethernet UNI Point-to-Point FR PVCs Service Multiplexed Ethernet UNI FR UNI FR UNI CE MEN CE CE Ethernet UNI Ethernet Virtual Private Line using E-Line Service type FR CPE FR CPE MEN FR CPE FR UNI Frame Relay Analogy to E-Line Service Metro core and metro access ring topology ADM DACS TDM Complex, multi-tiered, hierarchical network Limited Scalability Expensive Label switching to forward data by mapping VLAN tags to label switched paths (LSPs) Load sharing by switching path around bottlenecks to less congested links Dedicated backup LSP and fast reroute when a connection failure occurs Pada kecepatan tinggi IP terlalu komplek. Pada kecepatan tinggi IP terlalu memakan resource CPU. Operator perlu teknologi yang effisien. Tujuan direct hanya terbatas. Misalnya Lampung --> Jakarta, Medan, Surabata dan Internet. Sangat terbatas, tidak banyak tujuan kecuali Internet. Aplikasi pelanggan juga terbatas. E-mail, web, sekali-sekali video conference. Perlu customisasi per pelanggan yang mudah. Label Switch – jauh lebih sederhana & effisien. TCP/IP – kompleks & tidak effisien. Label Switch – jauh lebih baik untuk backbone daripada IP. LIB = Label Information Base LSR = Label Switched Router LSR, Label Switched Router – router yang mampu melakukan switching dengan label. LIB, Label Information Base – kira-kira tabel routing label tempat melihat outbound Interface & label yang digunakan utk mengirim paket.