* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download INTRODUCTION TO INFORMATION SYSTEMS TECHNOLOGY
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
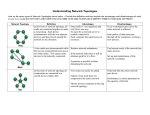
NETWORKING TECHNOLOGIES (Tuesday 3/4/2008) BUS3500 - Abdou Illia, Spring 2008 1 LEARNING GOALS Identify the major hardware components in networks. Identify and explain the various types of computer networks. Identify the various types of transmission media Describe the role of software used in networks. 2 Why Networking ? Resource sharing High reliability Same resources at different places Fault tolerance Cost saving Communication tool 3 Computer Network Once connected to the network, the computer (or another device) becomes a network node An interconnection of computers and computing equipment using either wires or radio waves over small or large geographic distances GHI DEF ABC MNO “Connect to GHI” JKL 4 Network scope Local area network (LAN): computer network where the nodes are all in close proximity spanning a room, building, or campus Metropolitan area network (MAN): network that serves an area of 3 to 30 miles - approximately the area of a typical city. Wide area network (WAN): a large network that encompasses parts of states, multiple states, countries, and the world 5 Physical Transmission Media Physical media Wireless Transmission media used to physically connect nodes in to the network Transmits electrical or optical signals Could be cooper wire or fiber optic cable 6 Transmission Media (Continued) Twisted Pair Category Use Signal Data rate Distance Problem Category 1 Telephone Analog/Digital <100Kbps 3-4 miles Security, noise Category 2 T1, ISDN Digital <2 Mbps 3-4 miles Security, noise Category 3 LANs Digital 10 Mbps 100 m Security, noise Category 4 LANs Digital 20 Mbps 100 m Security, noise Category 5 LANs Digital 100 Mhz 100 m Security, noise Category 6 LANs Digital 250 Mhz 100 m Security, noise Category 7 LANs Digital 600 Mhz 100 m Security, noise Fiber optic Source Thin glass fibers surrounded by coating Uses lasers or light for data transmission Very fast (10+ Gbps, 100 miles without any repeater) Very secure Photo diode (LED or LD) Photo receptor Fiber optic cable (LED or LD) Destination 7 Wireless Media Uses electromagnetic waves or electromagnetic radiation for data transmission Propagation through space, and indirectly, through solid objects Two kinds of wireless media used Radio waves (radio Frequency) Infrared light Affected by Multipath interference Highly vulnerable to snooping Limited distance Blocked by thick objects Close proximity and “line of sight” location required Laptop Comm. Tower 8 Computing Equipment Network interface card (NIC): Device that provides a computer with unique address Converts data into signal for transmission Hub / Switch: Central collection point for transmission media that interconnect computers Modem Router Converts digital data into analog signal and back again special hardware that determines optimal routing path for data packets Usually used to connect a LAN to a WAN Bridge Forwards messages between LANs 9 Small Network illustrated Hub or Switch Wide Area Network Router Media 10 Network Software Network operating system Workstation operating system Used on servers Used for managing network resources Examples: Novell NetWare, Windows Server 2003 Used on client PCs Used to manage local resources & access network resources Network monitoring software Packet sniffers – allow seeing data as it moves over network Keystroke monitors – allow seeing what users are typing 11 Network Topologies The configurations of network components How physically the network looks like How logically data is transferred on the network Types of network topologies: Bus Star Ring Mesh 12 Bus Network Topology Most simple network topology All devices connected to a common central cable called a “bus” Inexpensive If cable fails, the entire network will shut down 13 Star Network Topology Centered around central device called a hub or a switch All network nodes connect to the hub/switch Easy to install and update If hub fails, network fails 14 Ring Topology Node connected to a logical ring in a central device called MAU More reliable than bus or star Only one node sends at a time (no collisions) Expensive and limited speed 15 Mesh Network Topology Every node connected to every other node Reliable Expensive If one device goes down, it is the only node affected Every node must be wired to every other node Difficult to add nodes If 32 nodes in a mesh network and wish to add a new node, how many new cables? 16 Network Architecture Defines how the processing takes place on the network Two primary types Client-server Peer-to-peer (P2P) 17 Client-server Network Architecture Nodes are either clients or servers Clients use services Servers provide services File service E-mail service Printing service Database service Client software on client node cooperates with server software on server node The WWW is the largest client server application 18 Client-server Network Architecture Collaboration between Client and Server program 19 Client-server Network Architecture Division of Labor Client program handles lighter work, such as user interface chores and light processing chores Server program handles heavy work, such as database retrieval Server Program Client Program Client Machine Server 20 Peer-to-Peer Network Architecture All nodes on the network are equal. Any node can be both a client and a server. 21 Summary Questions Book 1) Name categories of computer networks based on their scope; i.e. their range of operation Notes 5 2) Name one example of: (a) WAN, (b) LAN 3) Name physical and wireless media used in networking 4) What is the role of (a) a modem, (b) a router, (c) a bridge? 6-8 9 5) What is the difference between a Network operating system and a workstation operating system? 11 6) What is a network topology? 12 7) Distinguish between network topologies 13-16 8) Distinguish between Client-server and P2P networks 18-21 22