* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download IPTV
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Remote Desktop Services wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.1aq wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
TV Everywhere wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
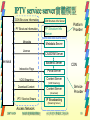
Real-Time Messaging Protocol wikipedia , lookup
Streaming media wikipedia , lookup
Peer-to-peer wikipedia , lookup
IPTV (Internet Protocol Television) Speaker : Chi-Wen Yang Advisor : Kai-Wei Ke Date : 2007/10/29 2007/10/29 無線與寬頻網路實驗室 台北科技大學資訊工程系所 1 Reference • Jian-Guang Luo, Yun Tang, Meng Zhang, Li Zhao, Shi-Qiang Yang. "Design and Deployment of a Peerto-Peer Based IPTV System over Global Internet." Department of Computer Science and Technology Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China. • Francis E. Retnasothie*, M. Kemal Ozdemir*, Tevfik Yiicektt, Hasari Celebitt, Joseph Zhang*, and Ranesh Muththaiah*. "Wireless IPTV over WiMAX: Challenges and Applications." University of South Florida, Department of Electrical Engineering 4202 E. Fowler Avenue, Tampa, FL, 33613. 2007/10/29 無線與寬頻網路實驗室 台北科技大學資訊工程系所 2 Outline • • • • IPTV Introduction P2P IPTV System over Global Internet Wireless IPTV over WiMax Conclusion 2007/10/29 無線與寬頻網路實驗室 台北科技大學資訊工程系所 3 Outline • IPTV Introduction 2007/10/29 無線與寬頻網路實驗室 台北科技大學資訊工程系所 4 IPTV • IPTV (Internet Protocol Television) is a system where a digital television service is delivered by using Internet Protocol over a network infrastructure, which may include delivery by a broadband connection. A general definition of IPTV is television content that, instead of being delivered through traditional broadcast and cable formats, is received by the viewer through the technologies used for computer networks. 2007/10/29 無線與寬頻網路實驗室 台北科技大學資訊工程系所 5 IPTV characteristic • • • • • • • • • • • • • 完善的互動介面 電視不再是單向的資訊提供 可針對收視戶的需要提供一對一的服務 高畫質(HD)影像 H.264 高畫質影像播放 資訊傳遞快速 與網際網路(Internet)資訊互通 資訊取得容易、迅速 通信運用 網路電話(IP Phone) 視訊會議( Video Conference ) 延伸性(跨國界) 無遠弗屆 2007/10/29 無線與寬頻網路實驗室 台北科技大學資訊工程系所 6 IPTV application(1) • 電視(TV) • 從DVBT 信號接收機上盒將發展到重於高畫質電視(HDTV)播 放。 • DVB-T、DVB-C、DVB-S、DVB-H • IP-TV • 節目表查詢(EPG) • 節目錄影(PVR) • Time Shift(時移) • 隨選影視(VOD) • 結合電子商務機制,收視戶可透過電視隨時挑選付費收看HD Video(high definition Video)影片。 • 透過DRM 技術,提供影片線上即時收看(Streaming)或下載後 收看(Download),保護影片盜看或複製。 2007/10/29 無線與寬頻網路實驗室 台北科技大學資訊工程系所 7 IPTV application(2) • 電視購物(TV Shopping) • 結合電子商務機制,營造出多媒體(廣告影片、商片相片、圖片、 文字介紹)互動購物環境。 • 付款方式提供收視戶以信用卡刷卡付費或晶片金融卡轉帳付費。 • 透過互動特性,容易收集收視戶對商品喜好程度,並可針對收視 戶背景做交叉分析,以利未來行銷計畫。 • 開創另一商品銷售強勢通路。 • 生活資訊 • 網際網路資訊取得迅速。 • 運用互動的特性,收視戶可快速的查找食、衣、住、行相關資訊。 • 新聞報導;氣象報導;航班、火車、捷運班次查詢;路況報導; 樂透、統一發票獎號查詢;旅遊資訊查詢……. 2007/10/29 無線與寬頻網路實驗室 台北科技大學資訊工程系所 8 IPTV application(3) • 金融理財 • 家庭銀行 • 晶片金融卡轉帳、繳費、繳稅、帳戶餘額查詢、更改提款卡密碼, 將銀行搬到家庭中。 • 股市、期貨 • 股市、期貨資訊查詢、分析(圖表分析、股市分析師即時解盤影 片)。 • 即時下單。 • 教育學習 • 互動學習 • 營造多媒體互動學習環境,收視戶可選擇所要學習的科目、課程, 並透過知識庫提問,線上模擬測驗。 • 遠距教學 • 即時廣播教學,收視戶可透過電視與實體教學教室學習及互動。 2007/10/29 無線與寬頻網路實驗室 台北科技大學資訊工程系所 9 IPTV application(4) • • • • • • • • • • • • 視訊電話 單方通話、多方視訊會議 視訊、語音信箱 通訊即時錄影、錄音 家庭自動化環境控制 室內照明控制 室內溫度控制 影像監控系統 室內紅外線、瓦斯預警 居家保全預警 居家看護 結合家用醫療檢測器材,系統儲存及分析檢測結果數據,並自動 透過網路傳輸至醫療院所,進行醫療諮詢建議或緊急送醫。 • 醫療檢測可包括:血壓、血脂、體溫、血糖、體重、尖峰流量(氣 喘)、心電圖及血氧含量等。 2007/10/29 無線與寬頻網路實驗室 台北科技大學資訊工程系所 10 IPTV application(5) • • • • • • • 個人化服務 晶片會員卡加值服務 加值服務 付費頻道、付費互動服務 點數消費 網路部落格 與網際網路Blog 結合,文章、相片、影片可透過IPTV 分享給親 朋好友。 • E-Mail 收發 • 與網際網路E-Mail 系統結合 2007/10/29 無線與寬頻網路實驗室 台北科技大學資訊工程系所 11 IPTV業務發展情况 • IPTV業務發展情况: – – – – 1999年-英國Video Networks率先推出 2004年-歐洲、亞洲及北美等國家進行規模試驗和建置 2006年-33個電信營運商推出業務,800萬用户 預估 -2008年用户2600萬用户、收入150億美元 2007/10/29 無線與寬頻網路實驗室 台北科技大學資訊工程系所 12 IPTV結構層---ITU標準組織之觀點 Other Telecom aspects (SG13) Mobile aspects (SG19) SG2+SG16 Overall Architecture Service (Server) Service (User) Service (User) Charging/ Accounting (SG3) OAM/Manag. (SG4) Security (SG17) Middleware ? QoS/QoE/NP (SG12 + SG13) Traffic/NNAR (SG2) Control (SG11) Cable aspects (SG9) Transport Home Access Core Access Home FTTx, xDSL, Cable, Satellite, WLAN, WiMax, DMB etc. SG9 (Cable), SG15 (Transport), SG19 (mobile), other SODs 2007/10/29 無線與寬頻網路實驗室 台北科技大學資訊工程系所 13 IPTV平台分層架構 與其他支援系統連結(可選) 業務支援 相關營運系統 業務管理 內容管理 營運服務平台 營 運 支 援 系 統 加值業務平台 內容製作平台 串流媒體服務平台 EPG系統 骨幹網絡 傳輸網路 區域網絡 ADSL / LAN / WLAN接取 終端用戶 2007/10/29 IPTV終端 無線與寬頻網路實驗室 台北科技大學資訊工程系所 14 IPTV service server 實體模型 CDN Structure Information CDN Structure Info Server PF Structure Information PF Structure Info Server Metadata Metadata Server License Terminal CAS/DRM Server Backend Server Interactive Page VOD Streaming Platform Provider CDN Portal Server Content Server (VOD Streaming) Download Content Content Server (Download) IPTV Service Stream Service Provider IP Broadcasting (Streaming Server) Access Network 2007/10/29 無線與寬頻網路實驗室 台北科技大學資訊工程系所 15 IPTV --DRM技術 目前,DRM成熟的產品 主要是WMV-DRM、 Real-DRM,對Mpeg- 4和H264兩種格式的 DRM尚無成熟的產品 原 始 內 容 內 容 製 作 MPEG-4 加密系統 金鑰生成 Key 內容傳 送系統 加密 H.264 Key 節目信息 金鑰管理系統 2007/10/29 無線與寬頻網路實驗室 台北科技大學資訊工程系所 版權發 佈中心 16 IPTV編碼技術 • 視訊編碼技術 • 目前的標準有MPEG-4ASP、H.264、VC-1和AVS幾種 • VC-1︰ • 支援的廠商不多 • AVS︰ • 中國自己開發的標準,其具體發展趨勢尚須觀察 • MPEG-4︰ • 應用廣泛,在1.5M~2M的bit rate下,可以達到接近 DVD的畫質效果 • H.264 ︰ • 編解碼效率比MPEG4的效率高5%~15%,從技術的演 進來看H.264視訊編碼標準,被認為是下一階段的必然選 擇 2007/10/29 無線與寬頻網路實驗室 台北科技大學資訊工程系所 17 Outline • P2P IPTV System over Global Internet 2007/10/29 無線與寬頻網路實驗室 台北科技大學資訊工程系所 18 P2P based file sharing system • • • • Napster Gnutella KazaA BitTorrent 2007/10/29 無線與寬頻網路實驗室 台北科技大學資訊工程系所 19 P2P based live streaming system • • • • • PPLive PPStream TVAnts FeiDian Gridmedia 2007/10/29 無線與寬頻網路實驗室 台北科技大學資訊工程系所 20 The structure of Gridmedia system 2007/10/29 無線與寬頻網路實驗室 台北科技大學資訊工程系所 21 Elements of Gridmedia system • Rendezvous Point(RP)server – The RP server is used to facilitate the login process of new arriving peers. • Streaming server – The streaming server in Gridmedia is almost the same to traditional C/S servers. When it is connected to by a peer, it will send the live content to the peer. • Peers – The peers mainly comprises two parts of the unstructured overlay organization and push-pull streaming schedule. 2007/10/29 無線與寬頻網路實驗室 台北科技大學資訊工程系所 22 Unstructured Overlay Organization • In Gridmedia, end nodes are organized into an unstructured overlay networks. • On each node, there is an overlay manager component to take charge of finding appropriate neighbors by gossip protocol so that the application layer network can be successfully built up. • A new arriving node firstly contacts the RP server to get a list of the nodes already in the overlay (candidates list), which could be regarded as the login process. • The newly participating node will select several nodes from the candidates list as its initial neighbors as follows: – It measures the Round-Trip Time (RTT) to each candidate. – it chooses some nodes with the minimum RTT as one part of its initial neighbors. 2007/10/29 無線與寬頻網路實驗室 台北科技大學資訊工程系所 23 Unstructured Overlay Organization • Each node should maintain a list of neighbor nodes. • Due to the frequent come and leave of peers, the list should be updated from time to time. • The member tables is then encapsulated into a message and exchanged among neighbors periodically. After receiving the message, the node will update its member table accordingly. • Each node delivers an "alive message" to all its neighbors periodically to declare its existence. • Once a node quits, it will broadcast a "quit message" to all its neighbors. This message will be flooded within a limitation of hop count. 2007/10/29 無線與寬頻網路實驗室 台北科技大學資訊工程系所 24 Push-Pull Streaming Schedule • Pull mode in DONet/CoolStreaming. • Every peer in DONet periodically exchanges buffer map of video packets with partners, and then retrieves the absent packets from partners which reported to have the packets. 2007/10/29 無線與寬頻網路實驗室 台北科技大學資訊工程系所 25 Push-Pull Streaming Schedule • Peer B fetching a packet from peer A: – A sends information to tell B that the packet is in its local buffer. – If B needs this packet, it sends request to A about the packet. – A sends the packet to B after it received the request from B. • The time used to get a packet is at least 3 times to the end-to-end delay (EED) between A and B assuming the EED is symmetric. • To reduce the overhead of information exchanged between peers, the buffer map and requests will only be sent periodically. 2007/10/29 無線與寬頻網路實驗室 台北科技大學資訊工程系所 26 Push-Pull Streaming Schedule • Use a push-pull streaming mechanism in Gridmedia in which the pull mode of receiver and push mode of sender are used alternatively between partners. • Each node uses the pull method as a startup, and after that each node will relay a packet to its neighbors as soon as the packet arrives without explicit requests from the neighbors. • A pulling packet of a node is delivered by a neighbor only when the packet is requested. • A pushing packet is relayed by a neighbor as soon as it is received. 2007/10/29 無線與寬頻網路實驗室 台北科技大學資訊工程系所 27 Push-Pull Streaming Schedule • Each node works under pure pull mode in the first time interval when just joining. • Based on the traffic from each neighbor, the node will subscribe the pushing packets from its neighbors accordingly at the end of each time interval. • The lost packets induced by the unreliability of the network link or the neighbors quit will be pulled as well from the neighbors at the same time. 2007/10/29 無線與寬頻網路實驗室 台北科技大學資訊工程系所 28 Experiments on PlanetLab • PlanetLab is an open platform for experimenting, developing, deploying, and accessing planetary-scale services. • It had about 500 nodes over about 250 sites all over the world, only around 350 nodes are available online at the same time. 2007/10/29 無線與寬頻網路實驗室 台北科技大學資訊工程系所 29 Experiments on PlanetLab • DEDICATED NODES IN OUR EXPERIMENTS ON PLANETLAB 2007/10/29 無線與寬頻網路實驗室 台北科技大學資訊工程系所 30 Experiments on PlanetLab • A packet generator runs on the root node to simulate the media streaming and transmits the packets to the local peer directly. • RP helps new nodes to participate the overlay. • Log collecting server is deployed to gather log report packets sent by all the peers, such as control overhead, neighbor information, delivery ratio, traffic distribution, etc. • The control node is responsible for commanding the active nodes on PlanetLab to participate or depart the overlay. 2007/10/29 無線與寬頻網路實驗室 台北科技大學資訊工程系所 31 Experiments on PlanetLab • PARAMETERS IN EXPERIMENTS 2007/10/29 無線與寬頻網路實驗室 台北科技大學資訊工程系所 32 Experiments on PlanetLab • Comparison between pull and push-pull method in both static and dynamic environment without upload bandwidth limitation • • • • • • • 2007/10/29 無線與寬頻網路實驗室 台北科技大學資訊工程系所 33 Experiments on PlanetLab • Comparison between pull and push-pull method in both static and dynamic environment with upload bandwidth limitation to 500 Kbps for each node • • • • • • • • 2007/10/29 無線與寬頻網路實驗室 台北科技大學資訊工程系所 34 PRACTICAL IS SUES OF SYSTEM IMPLEMENTATION • Revise the developing codes to make system reliable, other practical issues includes NAT and firewall traversal, system monitoring, and user management. • In Gridmedia, use STUN(Simple Traversal of UDP through NAT)to traversal the NATs. • To traversal the firewalls, Gridmedia allows the peer to fetch data from other peers through HTTP connections. 2007/10/29 無線與寬頻網路實驗室 台北科技大學資訊工程系所 35 PRELIMINARY STATISTICAL RESULTS • 2007/10/29 Number of concurrent online users over time 無線與寬頻網路實驗室 台北科技大學資訊工程系所 36 Outline • Wireless IPTV over WiMax 2007/10/29 無線與寬頻網路實驗室 台北科技大學資訊工程系所 37 Wireless IPTV over WiMAX • Since WiMAX PHY supports varying frame sizes and scalable bandwidth, WiMAX is an ideal choice for IPTV applications. • WiMAX base stations (BSs), subscriber and mobile stations (SSs/MSs) are ideally suited for the delivery of IP based services; (triple play) VoIP, IPTV, internet multimedia over wireless MAN. • This makes WiMAX a superior choice over conventional cable, DSL, and satellite solutions. 2007/10/29 無線與寬頻網路實驗室 台北科技大學資訊工程系所 38 System model for IPTV applications 2007/10/29 無線與寬頻網路實驗室 台北科技大學資訊工程系所 39 Protocol Stack for IPTV Transmission 2007/10/29 無線與寬頻網路實驗室 台北科技大學資訊工程系所 40 Wireless IPTV over WiMAX • IPTV transmission requires higher payload capacity, therefore, it poses a challenge in providing maximum service, efficient delivery of IP based payload including voice, video, multimedia and Internet over wireless. • For real time streaming video services, UDP ports can be used and for video on demand (VoD), TCP ports can be used. • Broadcast, multicast or unicast services are also supported. • There can be multiple packets from various sources that must be delivered to targeted users with different QoS parameters making it a challenging task. 2007/10/29 無線與寬頻網路實驗室 台北科技大學資訊工程系所 41 Medium Access Control (MAC) Layer (1) • The IEEE 802.16 MAC is logically divided into three sublayers: – convergence sublayer (CS) • IPTV packets over Ethernet are received from the network as MAC SDUs. Received packets are then classified based on their TCP/UDP port, source/destination, IP, MAC address etc. Each packet is then assigned to a connection for transmission over the air. 2007/10/29 無線與寬頻網路實驗室 台北科技大學資訊工程系所 42 Medium Access Control (MAC) Layer (2) – common part sublayer (CPS) • The packets are fragmented and/or packed for the efficient use of available bandwidth. Fragmentation also enables automatic request (ARQ) services to minimize retransmission. MAC PDUs are constructed in this sublayer. Packets are scheduled based on service level agreements (SLA) and quality of service (QoS) requirements for both DL and UL. Ultimately, the frame in which IPTV packets will be transmitted is prepared in this layer. 2007/10/29 無線與寬頻網路實驗室 台北科技大學資訊工程系所 43 Medium Access Control (MAC) Layer (3) – security sublayer (SS) • The packets are encoded to prevent theft of service. Key exchanges between SSs and for secure authenticated transmission, the use of cyclic redundancy check (CRC) are also implemented in this sublayer. 2007/10/29 無線與寬頻網路實驗室 台北科技大學資訊工程系所 44 MAC scheduler for IPTV Applications • 2007/10/29 MAC QoS architecture 無線與寬頻網路實驗室 台北科技大學資訊工程系所 45 IEEE 802.16 QoS Service Classes 2007/10/29 無線與寬頻網路實驗室 台北科技大學資訊工程系所 46 MAC scheduler for IPTV Applications • Scheduling services represent the data handling mechanisms supported by the MAC scheduler for data transport on a connection. • Packet Classifier block will send the packet header's information to Connection Control component. • Connection Control assigns CID and service flow ID (SFID) to the corresponding packet or flow. • Each SFID will be related to a set of QoS parameters stored in QoS Policy component. • MAC management component handles dynamic service access/change (DSA/DSC)'s transaction and dynamically change QoS parameters. 2007/10/29 無線與寬頻網路實驗室 台北科技大學資訊工程系所 47 Outline • Conclusion 2007/10/29 無線與寬頻網路實驗室 台北科技大學資訊工程系所 48 The Future of IPTV • • • • • • • • • • • • Standard Def. Television(SDTV) High Def. Television (HDTV) Video-on-Demand (VOD) Interactive program guide calling/conferencing Web browsing on TV Music channels place + Local programming Voice services Emergency services Information services Personal Video Recorder (PVR) Integration 2007/10/29 無線與寬頻網路實驗室 > Interactive information > Content portability > Video clips on-demand > Video > Video messaging > Network based time & shifting > Peer-to-Peer Video > Home automation > On-line dating > Personalized advertising > Wireless/Wireline 台北科技大學資訊工程系所 49 Conclusion • A peer-to-peer (P2P) based IPTV system in global Internet : Gridmedia. • It reduce the playback latency at end users as well as offer resilience to high chum rate in peer community, and hence organizes end users into an unstructured overlay while proposes an efficient push-pull streaming mechanism to distribute video segments among partner nodes. • The practical issues when perfecting a prototype on testbed to a publicly released platform. – Improve system performance in terms of startup delay and streaming quality of service. 2007/10/29 無線與寬頻網路實驗室 台北科技大學資訊工程系所 50 Conclusion • With WiMAX offering high data rates to both mobile and fixed users, and the desire of users to watch real-time TV or VoD services make the implementation of IPTV over WiMAX an exciting killer application. • Broadcast IPTV packets are in general unpaid services, while unicast IPTV packets are paid services. Hence the delivery of unicast packets is more critical than the broadcast packets, requiring different QoS parameters. 2007/10/29 無線與寬頻網路實驗室 台北科技大學資訊工程系所 51