* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cisco Voice Programs - In Search of a Strategy
SIP extensions for the IP Multimedia Subsystem wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
Multiprotocol Label Switching wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
Real-Time Messaging Protocol wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Asynchronous Transfer Mode wikipedia , lookup
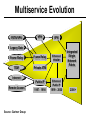
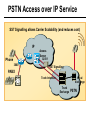
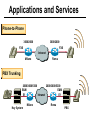
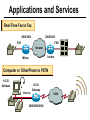
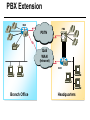
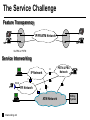
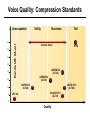
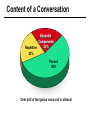
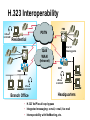
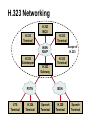
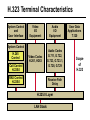
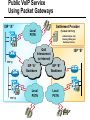
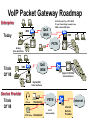
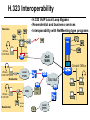
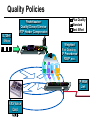
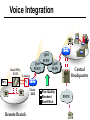
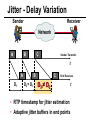
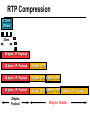
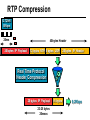
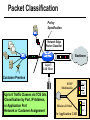
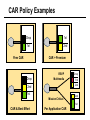
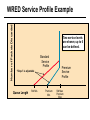
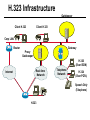
CS690b Presentation Multimedia Network Implementation - Data/Voice Convergence Xianfeng Zeng ( [email protected] ) Department of Computer Sciences Purdue University April 1,1999 Agenda • Overview • Data/Voice Convergence Technologies • Problems • Summary Why Voice/Data Convergence ? • Huge growth of Data/IP WAN traffic • Integrated Networks is cheaper to manage • Shared infrastructure - redundancy • Voice Processing is now economical – Voice compression algorithms give good quality at 8Kbps and DSPs have come down in price – Potential for reducing WAN costs integrating Voice and Data • Standards and Deregulation are here or are close – Voice over ATM, Voice over Frame Relay, Voice over IP – Voice compression, echo, jitter, etc.... Multiservice Evolution PSTN/VPN VPN VPN Legacy Data Frame Relay Frame Relay TDM Private ATM Internet Remote Access Source: Gartner Group Enhanced FR/ATM Public IP Enhanced Public IP 1997 - 1998 1999 - 2000 Integrated Single Network Fabric 2000+ PSTN Access over IP Service SS7 Signalling allows Carrier Scalability (and reduces cost) IP Access Server Q.931 Phone 3600 SS7 Signalling PABX Local Exchange Trunk Interface Trunk Exchange PSTN Applications and Services Phone-to-Phone 3600/2600 3600/2600 FXS FXS Intranet Milano Roma PBX Trunking 2600/3600/5300 2600/3600/5300 E&M E&M E1 E1 Intranet Key System Milano Roma PBX Applications and Services Real-Time Fax to Fax 2600/3600 2600/3600 FXS FXO Intranet Londra Milano Computer or EtherPhone to PSTN H.323 Software H.323 Gateway Ethernet 2600/3600/5300 PSTN Applications and Services Toll Bypass Milano Roma QoS IP Wan PSTN PSTN Local Calls Residential & Business Local Calls Residential & Business PBX Extension 3640 PBX V PSTN QoS WAN (Intranet) V 3640 Branch Office Headquarters Challenge • Have to understand both Voice networking and Data networking • Developing QoS networks and functionality • Voice quality is hard to guarantee • Need solutions (architecture) to move Voice from analog to data network quicker The Service Challenge Feature Transparency IP/FR/ATM Network Via PBX or PSTN Service Interworking PSTN & PBX Network B IP Network F E FRAD FR Network C A ATM Network Interworking unit D Billing System Packet to PSTN Gateway Forecast Total Internet Telephony Gateway Market: WW Unit Shipment & Revenue Forecasts 2,000 3,000 Revenue ($M) 1,800 Port Units (K) 2,500 1,600 2,000 1,200 1,000 1,500 800 1,000 600 400 500 200 0 0 1996 1997 1998 1999 Year Source: Frost & Sullivan; Internet Telephony Product Markets; #5637-60 2000 2001 Port Units (K) Revenue ($M) 1,400 Voice Quality: Compression Standards Unacceptable Utility Business Toll 64 48 40 32 Bandwidth (kbps) 56 Cellular Voice ADPCM 32 (G.723) ASPCM 24 (G.725) 24 ADPCM 16 (G.726) 16 8 LPC 4.8 PCM LDCELP 16 (G.728) CS-ACELP 8 (G.729) 0 Quality Quality/Delay Issue One Way Delay (msec) Description 0–150 Acceptable for Most User Applications 150–400 Acceptable Provided that Administrations Are Aware of the Transmission Time Impact on the Transmission Quality of User Applications 400+ Unacceptable for General Network Planning Purposes; However, it Is Recognized that in Some Exceptional Cases this Limit will Be Exceeded ITU G.114 Recommendation Voice over ATM/FR/IP - 1997 Scalability/ Performances ATM IP IP Campus TDM MAN Infrastructure Access FR Voice over ATM/FR/IP - 1999 Scalability/ Performances ATM IP FR TDM Campus MAN Infrastructure Access Standards & Organizations • ITU-T—H.323 • IMTC—VoIP ( International Multimedia Teleconferencing Consortium) • IETF—RSVP,WFQ, RED, RTP • FRF—VoFR FRF.11 FRF.12 Voice Technologies/Standards Status G.711 ITU-T recommendation (1988)— Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) of voice frequencies G.723.1 ITU-T recommendation (3/96)—Dual Rate Speech encoder for multimedia connections transmitting at 5.3 and 6.3 kbit/s G.729 ITU-T recommendation (3/96)—Coding of speech at 8 kbit/s using conjugate-structure algebraic-code-excited linearprediction Q.931 ITU-T recommendation (3/93)—Digital Subscriber signalling System No. 1 (DSS 1)—ISDN user network interface Layer 3 specification for basic call control Q.931 bis ITU -T recommendation (2/95)—PICS and abstract test suite for ISDN DSS 1 Layer 3—Circuit and Circuit mode, basic call control conformance testing 72 Voice over IP Protocols Presentation Session G.729(A)/G.723(.1)/G.711 H.323/H.323Gateway/SIP/SDP Transport RTP/UDP/RSVP Network IP/WFQ/IP-prec Link Physical MLPPP/FR/ATM AAL1 ––– Content of a Conversation Essential Components 22% Repetitive 22% Pauses 56% Over half of the typical voice call is silence! VoIP Technologies/Standards Status H.323 ITU-T Recommendation (11/96)—Visual Telephone Systems and Equipment for Local Area Networks Which Provide a Non-Guaranteed Quality of Service H.245 ITU-T Recommendation (3/96)—Control Protocol for Multimedia Communications RFC 1889 IETF RFC 1889 RTP: A Transport Protocol for Real-Time Applications RFC 1717 IETF RFC 1717 MP: The PPP Multilink Protocol RFC 1990 IETF RFC 1990 MP: The PPP Multilink Protocol Obsoletes RFC 1717 IETF Draft RSVP - Resource ReSerVation Protocol (RSVP)— Version 1 Functional Specification 0090_08F8_c1 873301-01 75 RTP - RFC 1889 • RTP “ Real-time Transfer Protocol “ – Small, real time data packets - Connectionless environment • RTCP “ Real-time Transfer Control Protocol “ – Provides feedback on current network conditions H.323 Interoperability PBX I-Phone H.323 S/W PSTN Residential PBX 4 to 12 Analog ports QoS WAN (Intranet) 3620 V V 3640 I-Phone H.323 S/W I-Phone H.323 S/W Branch Office Headquarters • H.323 VoIP local loop bypass • Integrated messaging: e-mail, v-mail, fax mail • Interoperability with NetMeeting, etc. H.323 Networking H.323 MCU H.323 Terminal H.323 Terminal Scope of H.323 WAN RSVP H.323 Gatekeeper H.323 Terminal H.323 Gateway PSTN V.70 Terminal H.324 Terminal ISDN Speech Terminal H.320 Terminal Speech Terminal H.323 Terminal Characteristics System Control and User Interface Video I/O Equipment Audio I/O Equipment Video Codec H.261, H263 Audio Codec G.711, G.722, G.723, G.723.1, G.728, G.729 User Data Applications T.120 System Control H.245 Control Call Control H.225.0 RAS Control H.225.0 Receive Path Delay H.225.0 Layer LAN Stack Scope of H.323 Gatekeeper Functions • Mandatory services: – – – – Address translation Admissions control Bandwidth control Zone management • Optional services: – Call control signalling – Call authorization – Bandwidth management and reservation – Call management – Gatekeeper management information data structure – Directory services Public VoIP Service Using Packet Gateways ISP “A” Settlement Provider Local PSTN (Trusted 3rd Party) Authentication, Call Routing, Billing and Settlement Server V QoS Interconnect (or Internet) POP (i) ISP “A” Backbone V POP (ii) Local PSTN ISP “B” ISP “B” Backbone Local PSTN V VoIP Packet Gateway Roadmap G.729, Group 3 Fax, RTP, RSVP Enterprise QoS WAN 3600 Today IP over Frame Relay, Leased Lines, ISDN or other WAN links V V 3600 PSTN Analog Voice Interfaces Trials Q1’98 QoS WAN 3600 V V Digital (T1/E1/PRI) Voice Interfaces Digital (BRI) Voice Interfaces Service Provider Trials Q1’98 I-Phone POTS Phone Residential Residential PSTN Internet V H.323 Interoperability Internet Service Provider H.323 Interoperability - H.323 VoIP Local Loop Bypass - Resendential and business services - Interoperability with NetMeeting type programs Business PBX PSTN PBX I-Phone H.323 S/W V Router + VoIP Local PSTN I-Phone H.323 S/W QoS WAN POP Internet Residential xDSL I-Phone H.323 S/W Residential XDSL Modem 2nd line phone DSLA M Local PSTN V Central Office VoIP Voice Compression VAD etc. PCM CODER G.711 64Kbps FXS Voice Card G.729r8 8Kbps Quality Policies Packetizazion Quality/Class of Service RTP Header Compression Plus Quality Standard Best Effort G.729r8 8Kbps Weighted Fair Queuing, IP Precedence RSVP, ecc. IP WAN Link FXS Voice Card Voice Integration Small PBX, POTS 2 Analog Fax QoS WAN QoS WAN QoS WAN PBX V Cisco 3600 Remote Branch Plus Quality Standard Best Effort PSTN Central Headquarter Jitter - Delay Variation Sender Receiver Network B A C Sender Transmits t A D1 B D2 = D1 C Sink Receives D3 = D2 t • RTP timestamp for jitter estimation • Adaptive jitter buffers in end points Line Protocol Problem Voice Packet FTP Session Time to : • High Priority Queue Empty • The Router starts sending packet from another queue 1500 bytes take 187ms at 64K Jumbogram FTP Session Link IP WAN Line Protocol Problem Voice Packet FTP Session Time t1 : • New RTP Packets Come • It has to wait the FTP Jumbogram to be sent 1500 bytes take 187ms at 64K VoIP Link IP WAN Jumbogram FTP Session Multilink PPP Interleave Voice Packet FTP Session Time to : • High Priority Queue Empty • The Router starts sending packet fragments from another queue FTP FTP Link IP WAN FTP Multilink PPP Interleave Voice Packet FTP Session Time t1 : • New RTP Packets Come • They are INTERLEAVED between FTP fragments “ INTERLEAVED ” VoIP FTP Link IP WAN VoIP FTP Algorithm VoIP FTP VoIP FTP Jumbogram FTP Session VoIP FTP VoIP FTP • Fragment large packets • Let small packets: Use normal encapsulation Interleave with fragmented traffic RTP Compression G.729r8 8Kbps 20ms 20 bytes IP Payload 20 bytes IP Payload 12 bytes RTP 20 bytes IP Payload 12 bytes RTP 8 bytes UDP 20 bytes IP Payload 12 bytes RTP 8 bytes UDP 20bytes Payload 20 bytes IP Header 40bytes Header RTP Compression G.729r8 8Kbps 20ms 40bytes Header 20 bytes IP Payload 12 bytes RTP 8 bytes UDP 20 bytes IP Header Real Time Protocol Header Compression 20 bytes IP Payload 23-25 bytes 20msec 3-5 bytes 9,2Kbps Network Architecture Access POP Backbone POP Edge Functions POP Solutions require cooperative edge and backbone functions. POP Backbone Functions Customer access aggregation High speed transport Policy Application Security Packet classification Admission Control Queuing Congestion management Services & traffic metering Queue management Policy enforcement Traffic management Packet Classification Policy Specification Network Edge Packet Classifier Backbone Layer 3 CAR Filter Customer Premise RSVP Multimedia •Up to 6 Traffic Classes via TOS bits •Classification by Port, IP Address, or Application Port •Network or Customer Assignment Mission-Critical Per Application CAR Drop 3rd 2nd 2nd 1st CAR Policy Examples Drop 1st 1st 2nd CAR + Premium Firm CAR Drop RSVP Multimedia Drop 3rd 2nd 2nd 1st 2nd Mission-Critical 1st CAR & Best Effort Per Application CAR The Problem of Congestion Throughput Managed Congestion Uncontrolled Congestion Offered Load Congestion Management Goals •Max Goodput and Min. Delay •Scale to High Speed Nets •Fairness •Accommodates IP Burstiness •Preserves Traffic Classes •Avoids Global Synchronization Number of Packets Discarded WRED Service Profile Example Two service levels are shown; up to 6 can be defined. Standard Service Profile “Slope” is adjustable Queue Length Std Min. Premium Min. Premium Service Profile Std Max Premium Max Putting it All Together Solutions require cooperative edge and backbone functions Access High Standard Low Core L3 CAR Ingress rate thresholds. L3 CAR WRED/WFQ Determine packet class Administer packet class Egressrate thresholds Multimedia Conference Manager Gatekeeper Proxy • Zone definition • Supported ASR interfaces • Bandwidth management • QoS • Authentication • Limit H.323 traffic on the WAN • Making calls with in a zone • Security • Making calls to H.323 devices out side the Gatekeeper Zone • Remote zone Gatekeeper lookup • Accounting • Address resolution * H.323 Multimedia Conference Manager is implemented on Cisco IOS H.323 Infrastructure Gatekeeper Client H.323 Client H.323 Corp LAN Router Gateway Proxy Gatekeeper H.320 (Over ISDN) Internet Real-time Network Telephone Network H.324 (Over POTs) Speech Only (Telephone) H.323 H.323 Signaling Admission Request RAS H.323 Admission Confirm Gatekeeper Setup Q.931 Connect H.323 Capabilities Exchange Open Logical Channel H.245 Open Logical Channel Acknowledge RTP Stream RTP Stream RTCP Stream Media