* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PPT_692410021
Wireless USB wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Multiprotocol Label Switching wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
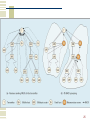
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
Policies promoting wireless broadband in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
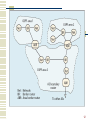
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Routing in delay-tolerant networking wikipedia , lookup
Multicast: Wired to Wireless Hrishikesh Gossain Carlos de Morais Cordeiro Dharma P. Agrawal IEEE Communication Magazine June 2002 資工所 蔡家楷 Outline Introduction Multicast Support Multicast in the Internet Multicast in Wireless Mobile Environment Conclusion & Future Direction 2 Introduction Provide efficient way of services for application Real-time Class、 Multiplayer on line gaming IPv4 reserved Class D address to support multicasting 3 Multicast Support Initial Support Multicast-capable routers (MRouters) Dedicated Tunnels Multicast backbone (MBone) Presently No need dedicated tunnels Native multicast 4 Multicast Support Multicast Group Membership IP supports dynamic joining and leaving of a group by IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol) 5 Multicast Support Packet Forwarding Multicast forwarding algorithm Source-based Core-based 6 Source-based RPB – Reverse Path Broadcasting Spanning tree is created for each (source,group) pair TRPB – Truncated Reverse Path Broadcasting Manage group by IGMP Prune non-leaf router Source Router Membership 7 Source-based RPM – Reverse Path Multicasting Spans only to routers and subnetwork with group member 8 Core-based CBT - Core Based Tree Build a single shred multicast tree with a core router All packets are forwarded through the core Group managed by the core Receiver-oriented 9 Multicast in the Internet Routing Protocol DVMRP – Distance Vector Multicast Routing Protocol Source-based First packet forward to entire interface Prune message Graft message 10 Multicast in the Internet Routing Protocol MOSPF – Multicast Extensions to OSPF Unicast routing information obtained from OSPF Group membership obtained from IGMP Build a multicast forwarding tree on demand for each (source,group) pair Hierarchical routing – hosts are partitioned into autonomous system (ASs) 11 12 Multicast in the Internet Routing Protocol PIM-SM - Protocol-Interdependent Multicast-Sparse Mode Support multicast independent of any underlying unicast routing protocol For sparse distributed receiver on Internet 13 Multicast in the Internet RP – Rendezvous point Forwarding packets destined for the multicast group DR – Designated router Handles multicast group membership message in it’s domain S Group M DR M RP DR S M M 14 Multicast in Wireless Mobile Environment Issue in Mobile Environment Multicast forwarding algorithm Dense or sparse mode protocols QoS provisioning 15 Multicast in Wireless Mobile Environment Proposals for multicast over MIP by IETF Remote Subscription An MH resubscribe to the multicast group each time it moves to a new foreign network Frequent resubscription may lead to lost packets Bidirectional Tunneling Using unicast Mobile IP tunnels from their Has Requires the HA of an MH to be a multicast router 16 Multicast in Wireless Mobile Environment Multicast support using Mobile IP (MoM) Tunnel convergence problem Select one HA as DMSP (Designated Multicast Service Provider) Packet loss when MH handoff Select more than one DMSP 17 18 Multicast in Wireless Mobile Environment Multicast for Mobility Protocols (MMP) Provide fast and efficient handoffs for MH Combines Mobile IP and CBT MIP for controls communication up to the foreign network CBT for movement of hosts inside foreign network 19 Multicast in Wireless Mobile Environment MMP working flow BS send beacon include multicast CoA According CoA, MH send join message to BS BS transmits a CBT join request to the Core The core request the HA of MH to replace the CoA to its own address 20 Multicast in Wireless Mobile Environment MMP drawback Assumes a large-scale deployment of multicast-capable routers in each domain Not protocol-indendpent 21 Reliable wireless Multicast Protocols RMDP Protocol – Reliable Multicast Data Distribution Protocol FEC (Forward error Control) & ARQ (Automatic Repeat Request) A data object to be transmitted is a file Split file into packets, and encoded to transmission Drawback: encoding/decoding done by software, affect performance 22 Reliable wireless Multicast Protocols RM2 Protocol – Reliable Mobile Multicast Used for both wired & wireless Rely on IGMP: to manage group membership IETF’s Mobile IP to support CoA MADCAP – Multicast Address Dynamic Client Allocation Protocol 23 Reliable wireless Multicast Protocols RM2 Protocol NACK for request retransmitting NACK: Negative acknowledgements RS manage retransmission for fixed/mobile user or mixture of them 24 25 Conclusion & Future Direction There is no one-size-fits-all protocol for multicast Both wired & wireless multicast proposal designed to cope with specific scenario QoS, Security and so on 26