* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download GPRS - MobiHealth
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
TV Everywhere wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
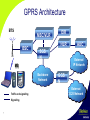
GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) Telefónica Móviles España GPRS Characteristics • GPRS is a new technology that optimises the use of network and radio resources: – Users share radio resources. – Only used when data are sent or received. – Uses a packet-mode technique to transfer data and signalling in an efficient manner. • GPRS data transfer is based on the Internet Protocol (IP). The packet data transmission is carried out on an end-to-end basis, including the air interface. • GPRS operates on the same radio frequencies as the circuit-switched GSM system. Co-existence of GSM and GPRS networks. 2 Introducción GPRS Characteristics • Billing based on data volume, NOT on time. • Data transfer rate depends on the load: number of users (GPRS and non GPRS). • GSM-GPRS network turns into a “Wireless LAN” with IP mobile devieces connected. • Always-ON. • Assignment divided into uplinks and downlinks. 3 What IS and IS NOT GPRS? What is? Data transmission technology in mobility A substitute for WAP A substitute for GSM A complement for GSM An alternative to UMTS Technological support for new services A new service New business model generator 2.5 G: a step forward 3G 4 What is NOT? Multimedia services ADSL for mobile phones GPRS rates Radio Carrier: 8 channels 12345678 GSM Voice: 1 conversation 1 channel 1 channel for GSM data 9.6 kbps GPRS: Use of until 8 channels per user Depending on the code algorithm, we can get several transmission rates: CS-1: 9.05 kbps/slot CS-3: 15.6 kbps/slot CS-2: 13.4 kbps/slot CS-4: 21.4 kbps/slot Actually terminals support until 4+1 slots 5 Efficiency in resources use: until 8 users/channel. GPRS Applications • Burst Applications with high bandwidth: – E-mail, WWW, FTP • Applications with low bandwidth: – Telemetry, Remote control, e-commerce. • Multicast Services: – Metereological, Traffic or Corporate Information. 6 GPRS Architecture BTS MSC/VLR BSC EIR HLR SGS N External IP Network MS Backbone Network Traffic and signalling Signalling 7 AUC GGS N External X.25 Network GPRS Architecture • GPRS is implemented on the GSM structure through the addition of two new network nodes: – SGSN (Serving GPRS Support Node) provides packet routing to and from the geographical SGSN area. – GGSN (Gateway GPRS Support Node) provides interworking with external packet-switched networks. • BSC needs a SW and HW upgrade, the PCU (Packet Control Unit). 8 SGSN Main Tasks • Packet routing towards the adequate GGSN. • Security over radio access: ciphering and authentication. • Mobility management: keeps track of the MS (Mobile Station) location. • Logical link management towards the MS. • Connection to GSM nodes: MSC, HLR, BSC, SMS-C. • Charging data. 9 GGSN Main Tasks • Interface with the external IP packet networks. • Security functions toward the Internet (Radius client). • GPRS session management on IP level; communication setup towards external network. • Associating subscribers with the appropriate SGSN. • Charging data. 10 PCU Main Tasks • Multiplexing of GPRS traffic and circuit switched traffic. • Handling of GPRS radio resources: allocating channels for GPRS connections. • Distribution of packet data to the MS. • Handling connections towards the SGSN. 11 BTS & HLR • BTS (Base Transceiver Station): Responsible for separating the MS originating circuit-switched (CS) calls from packet data communication before the BSC forwards: – CS calls to the MSC/VLR – PS data to the SGSN • HLR (Home Location Register): The subscriber file must contain GPRS subscription data: – Address of the SGSN currently serving the subscriber – Addresses of GGSNs that will be contacted when activity from MS is detected – Access Point Name (APN) describing the access point to the external computer network 12 GPRS security • SGSN performs authentication and cipher setting procedures based on the same algorithms, keys, and criteria as in existing GSM. • SGSN and GGSN use GTP (GPRS Tunnelling Protocol) in order to encapsule the packets. GTP is assembled over TCP/IP. • Tunnelling: The information will be ciphered and additional data will be included to every packet to guarantee confidentiality. 13 GPRS MoviStar Services • e-moción GPRS: Mobile Internet Access Service. It uses WAP protocol over GPRS to access to different contents in e-moción. • MoviStar Internet: Allows to surf to everywhere and everytime with only a laptop or PDA and a MoviStar GPRS mobile telephone. The customer has direct, generic and anonymous access to Internet without the need of an ISP. • MoviStar Intranet: Allows direct access to LAN networks and corporate applications (Intranet, e-mail, databases, corporate directory, agenda) everywhere and everytime with only a laptop or PDA and a MoviStar GPRS mobile telephone. 14