* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Computer Networks BITS ZC481
Policies promoting wireless broadband in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Net neutrality law wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
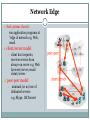
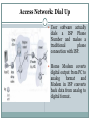
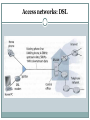
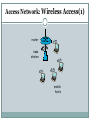
Computer Networks BITS ZC481 LECTURE 1 Grading Policy EC1 : 3 Quizes of 5% Weightage Each (Closed Book). EC2: Mid Sem Test 35% on Sunday 08/09/2013 at 2 PM – 4 PM (Closed Book). EC3: Compre Exam 50 % on Sunday 10/11/2013 at 2 PM – 5 PM (Open Book). Required Textbook Text Book: Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach Featuring the Internet, 3rd edition. Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley, 2005. R1: Andrew S. Tanenbaum, Computer Networks, Fourth Edition, Pearson Education, 2006. R2: William Stallings, Computer Networking with Internet Protocols and Technology, Pearson Education, 2004 L. Peterson and B. Davie, Computer Networks: A Systems Approach, Fourth Edition, Elsevier, 2007 (Book From 24x7 Online Book) Course Objectives Learn how communication networks are put together mechanisms, algorithms, technology components Understand fundamental challenges Learn about existing solutions typically: no single dominant solution What problems still need solving? Today’s Agenda Introduction to Internet/computer networks Uses of Computer Networks Network Hardware: The Network Edge, The Network Core, Access Networks Internet :Nuts & Bolts View Internet is hundreds of millions of connected computing devices (nodes). End Systems are the hosts. Internet applications run on end system but don’t run in packet switches in network core. All the nodes are connected via Communication links (fiber, copper, radio, satellite). Transmission rate to transmit the data between the devices is measured in Bandwidth Internet :Nuts & Bolts View(1) Intermediate Nodes between two hosts forwards the packets (Packet Switching) from one node to other towards destination host can be routers or switches. PC Mobile network Global ISP server wireless laptop cellular handheld access points wired links router Home network Regional ISP Institutional network Internet :Nuts & Bolts View(2) Internet: “network of networks” loosely hierarchical public Internet versus private intranet Internet standards RFC: Request for comments IETF: Internet Engineering Task Force Internet :Nuts & Bolts View(3) End system attached to the Internet provides an API (Application programming interface). API Specifies how a software piece running on one end system asks the internet infrastructure to deliver data to specific destination software piece running on other end system. It is set of rules the sending software piece must follow. Internet: a service view Most people know about the Internet (a computer network) through applications like World Wide Web Email Online Social Network Streaming Audio Video File Sharing Instant Messaging Internet: a service view(1) Communication infrastructure enables distributed applications: Web, VoIP, email, games, e-commerce, file sharing. Different Communication services provided to apps: reliable data delivery from source to destination. “best effort” (unreliable) data delivery. Protocol All communication activity in Internet governed by protocols. Define format, order of messages sent and received among network entities, and actions taken on messages transmission, receipt, or timeout. eg: TCP, IP, HTTP, Skype, Ethernet Protocol defines the interfaces between the layers in the same system and with the layers of peer system. Protocol(1) Each protocol object has two different interfaces: service interface: operations on this protocol peer-to-peer interface: messages exchanged with peer Protocol(2) Except at the hardware level, where peers directly communicate with each other over a link, peer-topeer communication is indirect—each protocol communicates with its peer by passing messages to some lower level protocol, which in turn delivers the message to its peer. Network Structure Network edge: applications and hosts. Access networks, physical media: wired, wireless communication links Network core: interconnected routers network of networks (Internet) Network Edge End systems (hosts): run application programs at “edge of network e.g. Web, email client/server model client host requests, receives service from always-on server e.g. Web browser/server; email client/server peer-peer model: minimal (or no) use of dedicated servers e.g. Skype, BitTorrent Network Edge: connection-oriented service Goal: data transfer between end systems handshaking: setup (prepare for) data transfer ahead of time TCP service [RFC 793] reliable, in-order bytestream data transfer Hello, hello back human protocol set up “state” in two communicating hosts flow control: sender won’t overwhelm receiver TCP - Transmission Control Protocol Internet’s connectionoriented service loss: acknowledgements and retransmissions congestion control: senders “slow down sending rate” when network congested Network Edge: connectionless service Goal: data transfer between end systems UDP - User Datagram Protocol [RFC 768]: connectionless unreliable data transfer no flow control no congestion control App’s using TCP: HTTP (Web), FTP (file transfer), Telnet (remote login), SMTP (email) App’s using UDP: streaming media, teleconferencing, DNS, Internet telephony Access networks How to connect end systems to edge router? residential access nets institutional access networks (school, company) mobile access networks Access Network: Dial Up User software actually dials a ISP Phone Number and makes a traditional phone connection with ISP. Home Modem coverts digital output from PC to analog format and Modem in ISP converts back data from analog to digital format. Access Network: Dial Up(1) Drawback: up to 56Kbps direct access to router (often less) Can’t surf and phone at same time: can’t be “always on” Access networks: DSL Access networks: DSL(1) Telephone lines carries both data and telephone signals encoded at different frequencies. Splitter separates the data from telephone signals and transfers it to DSL Modem. Upstream and downstream transmission rates are different (asymmetric). Access Network: Cable Cable head end broadcast the television channels through distribution networks of coaxial cable and amplifiers to residence. Hybrid Fiber-coaxial (HFC) access network makes use of both coaxial and fiber cables. Shared broadcast Medium asymmetric: upstream up to 30Mbps downstream, 2 Mbps Access Network: Cable(1) Access Network: Ethernet Access Network: Ethernet(1) company/university local area network (LAN) connects end system to edge router. Ethernet: 10 Mbps, 100Mbps, 1Gbps, 10Gbps Ethernet modern configuration: end systems connect into Ethernet switch Access Network: Wireless Access In wireless LAN, Wireless users transmit/receive packets to/from access point. Eg: 802.11b/g (WiFi): 11 or 54 Mbps. In wide area wireless access network, packets are transmitted to the base station over same wireless infrastructure used for cellular telephony. Wimax(10’s Mbps over wide area). Access Network: Wireless Access(1) router base station mobile hosts Physical Media Bit: propagates between transmitter/reciver pairs physical link: what lies between transmitter & receiver guided media: signals propagate in solid media: copper, fiber, coax unguided media: signals propagate freely, e.g., radio Twisted Pair (TP) two insulated copper wires Category 3: traditional phone wires, 10 Mbps Ethernet Category 5: 100Mbps Ethernet Physical Media: coax, fiber Coaxial cable: two concentric copper conductors bidirectional baseband: single channel on cable legacy Ethernet broadband: multiple channels on cable HFC Fiber optic cable: glass fiber carrying light pulses, each pulse a bit high-speed operation: high-speed point-topoint transmission (e.g., 10’s-100’s Gps) low error rate: repeaters spaced far apart ; immune to electromagnetic noise Physical media: radio signal carried in electromagnetic spectrum no physical “wire” bidirectional propagation environment effects: reflection obstruction by objects interference Radio link types: terrestrial microwave e.g. up to 45 Mbps channels LAN (e.g., Wifi) 11Mbps, 54 Mbps wide-area (e.g., cellular) e.g. 3G: hundreds of kbps satellite Kbps to 45Mbps channel (or multiple smaller channels) 270 msec end-end delay geosynchronous versus low altitude Next Lecture Network Core ISP Delay & loss in packet-switched networks Protocol layers, service models OSI and TCP/IP reference models Thanks!!! Queries?