* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download the evolution of a new mass medium
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
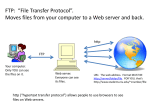
ORIGINS of the Information Highway: the evolution of a new mass medium Charles Babbage Cambridge, UK – mathematician and inventor Made detailed plans in 1800s – for calculating math tables. logical structure of the modern computer “Father of Computing” Babbage’s Analytical Engine Powerful punch-card controlled general purpose calculator Babbage’s idea never got past the prototype stage; full functioning engine never built “As We May Think” Article in The Atlantic Monthly, July 1945 Authored by Vannebar Bush, electrical engineer at MIT and U.S. advisor during World War II Introduced concept of a “memex,” a device that would allow a user to connect different pieces of associated information ENIAC Built in 1946 at the University of Pennsylvania First large-scale electronic computer Had 17,468 electronic vacuum tubes 5,000 additions per second; today’s microprocessor can do 100 million additions per second Sputnik 1957 The Cold War and computing 1958: Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) created under the auspices of the Department of Defense. ARPA would become the home of ARPAnet, a network of computers funded by the military and designed to allow communication in the event of a nuclear attack. ARPAnet established 1969: First four nodes, or points of access, to the forerunner of the Internet are established (UCLA, UC Santa Barbara, Stanford, University of Utah). Doug Engelbart Stanford Node Vint Cerf UCLA Node Ted Nelson 1965: Introduces the principle of hypertext, associating information through “links” into a coherent organization. back Vinton G. Cerf “Father of the Internet” Helped develop TCP/IP protocol in 1970s Transmission research 1967: Plan for packet switching presented at technology conference The minicomputer 1975: Release of Altair 8800 Yours for the low price of $397 Users had to not only assemble the Altair themselves, but write software for it also. Along comes Microsoft 1975: Two young software developers – Bill Gates and Paul Allen write and market a software program for the Altair. Their version of the BASIC language program for the Altair was a success, and Microsoft Corporation was born. Birth of the Apple 1977: Steve Jobs and Steve Wozniak launch the Apple II, which featured built-in programming, color graphics, and increased memory capacity compared to the Altair. The Apple II was an almost immediate success, and is credited with being a ground-breaking model for home computers. Home computing 1981: IBM launched a personal computer model featuring microprocessor chips from Intel, and MS-DOS operating system from Microsoft. 1984: Apple introduces the Macintosh during the third quarter of the Super Bowl, with a 45-second commercial. Tim Berners-Lee 1989: Founds the World Wide Web initiative for his own use as a researcher at CERN (European Organization for Nuclear Research) – drawing from Bush 1991: Specified the Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) Also developed URLs (uniform resource locators) and HTTP (hypertext transfer protocol) Birth of the browser 1993: Marc Andreessen, an undergraduate student at the University of Illinois, helped create the path-breaking browser Mosaic. 1994: Andreessen co-founded a company, now named Netscape Communications Corporation, with James H. Clark, founder of Silicon Graphics Inc. Sitepal Stage 1:Novelty or Developmental Stage Rationale Computer network impervious to attack DOD - ironically, no central authority Technology Digital Communication Packet Switching Microprocessors E-mail and bulletin boards Digital communication Packet switching Microprocessor Stage 2: Entrepreneurial Develop. 1982: National Science Foundation network Rapid spread beyond government and academic worlds Other technological developments Fiber optic cable Commercialization of Internet as a mass medium Stage 3: WWW – 1991 and graphic browsers (Mosaic 1993) (Netscape 1994) 1993: multimedia capability on Net Graphics, audio, video, streaming Rapid growth rate Companies seek to turn Net users into consumers through ads and Web sites E-commerce MAPPING THE INTERNET: four major mapping systems COMMERICAL ISPs WORLD WIDE WEB BROWSERS WEB SEARCH ENGINES and DIRECTORIES Google OWNERSHIP ISSUES ON THE INTERNET Increasing convergence of owners and players in mass media industries Players and companies jockeying for position Media mega-corporations Computer hardware/software companies Internet access and service providers Phone and cable TV companies Internet search engines, portals, and Web browsers TV networks Promises for democracy Wide accessibility for all citizens Decentralized social network Development from “bottom-up” rather than “top-down” Major involvement of amateurs Massive sharing and storage of useful information Disadvantages Increased circulation of “cyberspace litter” (hoaxes, spam, chain e-mails) Rooney remarks Lack of editorial control for accuracy --> proliferation of misinformation Concerns about security, child protection, hatemongering Knowledge gap between users and those without access (stats)