* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS)
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Remote Desktop Services wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
Cellular network wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
SIP extensions for the IP Multimedia Subsystem wikipedia , lookup
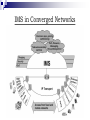
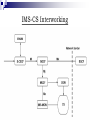
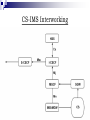
IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) 江培文 Agenda Background IMS Definition IMS Architecture IMS Entities IMS-CS Interworking Background - AMPS Advanced Mobile Phone System (AMPS) First generation (1G) cellular network Analog mobile phone system Standardized by ANSI Operate in the 800 MHz band Voice call Background - GSM Global System for Mobile communications (GSM) Second generation (2G) cellular network Digital mobile phone system Most GSM networks operate in 900 MHz or 1800 MHz bands Each radio channel bandwidth is 200 kHz Standardized by ETSI Voice call, short message service Background - GPRS General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) 2.5G packet oriented mobile network Provide data rates from 56 up to 114 kbps Standardized by ETSI/3GPP Short Message Service (SMS), Wireless Application Protocol (WAP), Multimedia Messaging Service (MMS), Internet Access Background - EDGE Enhanced Data rates for GSM Evolution (EDGE) 2.75G packet oriented mobile network Data rate up to 236.8 kbps Standardized by 3GPP Multimedia services, Internet access Background - WCDMA Wideband Code Division Multiple Access (WCDMA) Third generation (3G) cellular network 1885–2025 MHz for uplink band and 2110–2200 MHz for downlink band Each radio channel bandwidth is 5 MHz Data rate up to 384 kbps Standardized by 3GPP The world's first commercial WCDMA network, FOMA, was launched by NTT DoCoMo in Japan in 2001. Background - HSDPA High Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA) 3.5G packet oriented mobile network Adaptive Modulation and Coding (AMC) Depend on signal quality and cell usage QPSK in initial scheme, 16QAM in good radio condition. Data rate up to 14.4 Mbps for downlink and 384 kbps for uplink Standardized by 3GPP (since release 5) Background - LTE Long Term Evolution (LTE) Fourth generation Orthogonal FDMA (4G) cellular network? (OFDMA) for downlink and Single Carrier FDMA (SC-FDMA) for uplink Support Multiple-Input and Multiple-Output (MIMO) Improve communication performance Increase data throughput Without additional bandwidth or transmit power Channel bandwidth between 1.5 and 20 MHz All IP Network (AIPN) Data rate up to 326.4 Mbps for downlink and 86.4 Mbps for uplink Standardized by 3GPP (since release 8) IMS Definition 3GPP Release 5 introduced the IMS as part of 3GPP specifications in March 2002 The IMS is supposed to be a standardized access-independent IPbased architecture that interworks with existing voice and data networks for both fixed (e.g., PSTN, Internet) and mobile (e.g., GSM, WCDMA) users IMS in Converged Networks IMS Architecture IMS Entities Routing and Session Management Databases Services Interworking Functions Support Functions Routing and Session Management Call Session Control Functions (CSCF) Proxy Call Session Control Function (PCSCF) Interrogating Call Session Control Function (I-CSCF) Serving Call Session Control Function (SCSCF) P-CSCF The first contact point for users within the IMS SIP compression IPSec security association Interaction with Policy Decision Function (PDF) Emergency session detection I-CSCF Obtain the name of the S-CSCF or Application Server (AS) from the Home Subscriber Server (HSS) Assign an S-CSCF based on received capabilities from the HSS Route incoming requests to an assigned S-CSCF or AS S-CSCF Handle registration process Store service profile Make routing decision Maintain session state IMS Entities Routing and Session Management Databases Services Interworking Functions Support Functions Databases Home Subscriber Server (HSS) Subscription Locator Function (SLF) HSS The main data storage for all subscriber and service-related data User identities Private and public user identities Registration information Access parameters Allocated S-CSCF names Service triggering information SLF The resolution mechanism that enables the I-CSCF, the S-CSCF and the AS to find the address of the HSS that holds the subscriber data for a given user identity when multiple and separately addressable HSSs have been deployed by the network operator. IMS Entities Routing and Session Management Databases Services Interworking Functions Support Functions Services Multimedia Resource Function Controller (MRFC) Multimedia Resource Function Processor (MRFP) Application Server (AS) MRFC A signalling plane node Provide the mechanism for bearerrelated services such as announcement Handle SIP communication to/from the S-CSCF Control the MRFP MRFP A media plane node Mix the incoming media streams for multiple parties Process the media stream source for multimedia announcements AS Provide value-added multimedia services Process the incoming SIP sessions from the S-CSCF Originate SIP requests Send accounting information to the charging functions IMS Services Presence Multimedia Chat Push to talk Over Cellular (POC) Conferencing IMS Entities Routing and Session Management Databases Services Interworking Functions Support Functions Interworking Functions For exchanging signalling and media between IMS and CS Core Network Breakout Gateway Control Function (BGCF) Media Gateway Control Function (MGCF) Signalling Gateway (SGW) IMS Media Gateway (IMS-MGW) BGCF It chooses where a breakout to the CS domain occurs If the breakout happens in the same network, then the BGCF selects a MGCF to handle the session. If the breakout takes place in another network, then the BGCF forwards the session to another BGCF in a selected network. MGCF Send a converted request via the Signalling Gateway (SGW) to the CS CN Control the IMS Media Gateway (IMSMGW) Perform protocol conversion between SIP and ISDN User Part (ISUP) SGW Perform signalling conversion at the transport level between the IP-based transport of signalling and the Signalling System No. 7 (SS7) i.e., between SCTP and SS7 IMS-MGW Provide the user plane link between CS domain and IMS domain Perform transcoding for the user plane traffic i.e., between TDM and RTP IMS Entities Routing and Session Management Databases Services Interworking Functions Support Functions Support Functions Policy Decision Function (PDF) Security Gateway (SEG) PDF Session establishment in the IMS involves the end-to-end messages exchange using SIP and SDP The P-CSCF forwards the relevant SDP information to the PDF The PDF authorizes the IP flows of the media components and transfers the authorized IP QoS parameters to the GGSN to establish an IMS session SEG Protect control plane traffic between security domains Enforce the security policy of a security domain Coincide with operator borders IMS-CS Interworking CS-IMS Interworking Thank You