* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Modeling and Evaluation of Fibre Channel Storage Area Networks
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
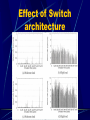
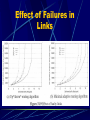
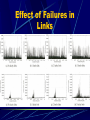
Modeling and Evaluation of Fibre Channel Storage Area Networks Xavier Molero, Federico Silla, Vicente Santonia and Jose Duato Introduction What is a SAN (Storage Area Network) A separate high-speed network for storage Isolated from messaging network Optimized for moving data between servers and storage devices How it is different from traditional server-storage network Traditional ServerStorage Architecture Limitations: Unavailability of data in case of a failure on server Bandwidth saturation during backups Typical SAN Architecture Fibre Channel Generic transport mechanism Provides an interface for high-speed data transfer(gigabit per second) and long distance(up to 10 km) Standard provides definitions about physical layer characteristics, transport control protocol, and upper level interface to TCP/IP, SCSI, and other protocols Some features are not specified(routing algorithm, internal switch architecture) Fibre Channel (cont.) Switching Mechanism virtual cut-through: incoming messages are forwarded as soon as they are routed and out port is free Flow Control Mechanism credit scheme System Model Switch Architecture Network Topology Routing Algorithm Communication Pattern Disk response time model I/O load generation Switch Architecture Switch Architecture Network Topology Single room Regular: Fattrees, meshes, multistage networks, and fully connected topologies Irregular: randomly generated, a single link connects two switches Floor topologies Routing Algorithm Distributed routing Leaving routing decisions to each switch Up*/down* routing (partially adaptive) Based on breadth-first spanning tree(BFS) Minimal adaptive routing (fully adaptive) Communication Pattern Request parameters: Disk ID Access type (read or write) Starting location (sector number) Requested size Communication Pattern Disk Response Time Model A single server queue with a FIFO discipline service Composed of three parts: Seek time Rotational latency Transfer time Disk Response Time Model I/O Load Generation Use auto-similar arrival pattern Real traffic is bursty and the bursts exist over many time scales Model each server as a set of ON/OFF sources Model the length of ON/OFF periods with Pareto distribution Simulator can be feed with real-world I/O traces Evaluating SANs Performance Effect of switch architectures on performance Effect of faulty links on performance Effect of Switch architecture Effect of Switch architecture Effect of Failures in Links Effect of Failures in Links Summary SAN is a alternative to traditional server-to-disk approach Fibre channel is a prominent technology for implementing SAN. The simulator considers a wide set of characteristics and is a key tool for the design and evaluation of SANs. Questions What is a storage area network? What are the limitations of traditional server-storage architecture? Name some features of fiber channels.