* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Protocols used in NM - Test Page for Apache Installation
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
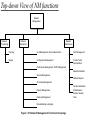
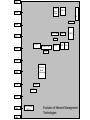
Overview of Network Management Outline Describe responsibilities of a network manager Define network management vocabulary Discuss network management principles Provide an example of network management implementation Identify new network management approaches The evolution of network management Common Network Problems Loss of connectivity (Link, Node, Interface) Duplicate IP address (Procedural) Intermittent (間歇的) problems Network configuration issues Performance problems Network Management (NM) Goal To ensure that network users receive IT services with the quality of service (QoS) that they expect Maintenance Network performance Failures (hardware and software) Network capacity Security Certifications CAN (Novell’s Certified Netware Administrator) MCP (Microsoft’s Certified Professional) CNE (Novell’s Certified Netware Engineer) MCSE (Microsoft Certified System Engineer) Top-down View of NM functions Network Management Network Provisioning Network Operations Network Maintenance Planning Fault Management / Service Restoration Fault Management Design Configuration Management Trouble Ticket Administration Performance Management / Traffic Management Network Installation Security Management Network Repairs Accounting Management Reports Management Facilities Installation & Maintenance Inventory Management Routine Network Tests Data Gathering & Analyses Figure 1.21 Network Management Functional Groupings Network-Based Management SNMP: Simple Network Management Protocol (RFC1157) MIBs: Management Information Base NMS: Network management system RMON1: Remote Monitor (RMON1) RFCs: Request for Comments IETF: Internet Engineering Task Force Network Management Vocabulary Network Management System (NMS) Consisting Management Station Managing of applications device - management software (NMS) Management Agent Managed device – computer, hub, router, or switch NMS Management Agent Management Station Network Management Vocabulary (cont.) Mgmt (Management) process Service management application programs Provide an interface to the network management protocol, e.g, SNMP Agent process An integrator of processes that access information requested by a network management application An interface to the network management protocol Collect the values of a specified set of variables when a request is made by the Management Station The virtual store of such values is called the Management Information Base (MIB), actually maintained by the managed device Mgmt App Mgmt Process Mgmt Protocol Agent Process Agent Protocol Presentation Presentation Session Session Transport Transport Network Network Data Link Data Link Physical Physical Management Station Management Agent Figure 2-2: Protocol Stacks on the Management Station and the Management Agent A Network Management Example The management application calls for the service of the management process The management process calls the program that implements the network management protocol, e.g., SNMP The network management protocol implementation constructs a request packet, which is sent to the management agent The implementation of the network management protocol on the management agent causes the request packet to be passed to the agent process The agent process accesses the value of the requested variable and passes it to the implementation of the network management protocol The network management protocol constructs the response packet, which is sent to the management station The implementation of the network management protocol at the management station receives the response packet and passes it to the management process The management process either passes the value to the application program, or stores it in memory for later retrieval Network Management Vocabulary (cont.) Trap The management agent send unsolicited messages to the management station E.g., a device goes from powered-up to the powereddown state Probe (remote monitors, RMON) Monitor traffic on the network segment, not a particular device The management agent thus is remote from the devices it is monitoring Evolution of Network Management DATE EVENT REFERENCE 1968 ARPA funds development of packet switching networks 1. RFC 1120 Internet Activities Board. V. Cerf. Sep-01-1989. (Obsoleted by RFC 1160) 2. RFC 1160 Internet Activities Board. V. Cerf. May-01-1990. (Obsoletes RFC 1120) 1974 TCP/IP concept proposed Cerf V., and R. Kahn, "A Protocol for Packet Network Interconnection", IEEE Trans. on Communications, Vol. COM-22, No. 5, pp. 637-648, May 1974. [Ref 26] 1976 Ethernet Developed Metcalfe, R., and D. Boggs, "Ethernet: Distributed Packet for Local Computer Networks", Communications of the ACM, Vol. 19, No. 7, pp. 395-404, July 1976. 1978 OSI Reference Model Development Initiated 1983 OSI Reference Model becomes international standard ISO/IEC 7498 (CCITT X.200) [Ref 1] 1987 SGMP development started ASN.1 developed [Ref 24] ISO 8824, Parts 1-4 Evolution of Network Management (cont.) 1988 IAB initiates study of SGMP and CMIP SNMPv1 becomes Interim Draft Standard SNMPv1 becomes Draft Standard IAB initiates development of Internet Standard Network Management Framework (SMI) Draft Standard MIB I developed Interim RFC 1028 (SNMPv1) Draft RFC 1098 (SNMPv1) Draft RFC 1065 (SMI) Draft RFC 1066 (MIB I) [Ref 10] 1989 CMOT approach abandoned SNMP becomes the defacto standard for TCP/IP management 1990 SMI becomes Recommended Standard SNMPv1 becomes Recommended Standard MIB I becomes Recommended Standard RFC 1155 (SMI) RFC 1157 (SNMP) RFC 1156 (MIB I) MIB II RMON1 RFC 1213 (MIB II) RFC 1271 (RMON I) [Ref 12] 1991 [Ref 3] [Ref 11] Evolution of Network Management (cont.) 1993 SNMPv2 Proposed SNMPv2 Security SNMPv2 MIB SNMPv2 SMI RFC 1441(SNMPv2 Management Framework RFC 1446(SNMPv2 Security Protocols RFC 1450 (SNMPv2 MIB) RFC 1442 SNMPv2 Structure of Management Information 1995 RMON I RFC 1757 [Ref 13] 1997 RMON II RFC2021 1998 Desktop Management Interface (DMI) Specification v 2.0s 1. 2. Web-based Management Initiative http://www.dmtf.org/standards/standard_w bem.php 1999 SNMPv2 Management Frameworks SNMPv3 Security RFC 2571 RFC 2574 (User-based Security Model) 2002 SNMP Management Frameworks SNMPv3 Security RFC 3411, STD 62 RFC 3414 (User-based Security Model), STD 62 RFC 3415 (View-based Access Control Model), STD 62 RFC 3418, STD 62 SNMP VACM SNMP MIB http://www.dmtf.org/sped/dmis Network Computing, Feb 2001, p57 2004 Web Based Mgmt 2000 SNMPv3 DMI RMON 2 1996 SNMPv2 MIB SNMPv2 RMON 1 1992 MIB 2 CMOT SGMP & CMIP SNMPv1 SMI MIB1 1988 SGMP 1984 OSI Reference Model Development 1980 Ethernet 1976 TCP/IP 1972 1968 1964 Packet Switching (ARPA) Evolution of Network Management Technologies