* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Application Layer - Teknik Elektro UGM
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
TCP congestion control wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Remote Desktop Services wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Peer-to-peer wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
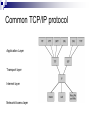
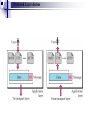
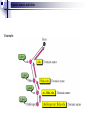
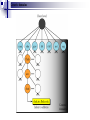
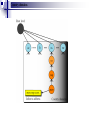
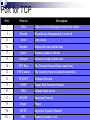
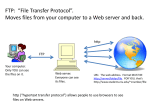
Application Layer Widyawan Review… Layered network model The concept of layers is used to describe communication from one computer to another. A conversation between two people provides a good opportunity to use a layered approach to analyze information flow. It is important that all the devices on the network speak the same language or protocol. TCP/IP model The designers of TCP/IP felt that the application layer should include the OSI session and presentation layer details. They created an application layer that handles issues of representation, encoding, and dialog control. The transport layer deals with the quality of service issues of reliability, flow control, and error correction. One of its protocols, the transmission control protocol (TCP), provides excellent and flexible ways to create reliable, well-flowing, low-error network communications. TCP is a connection-oriented protocolrequire that a logical connection be established between two devices before transferring data. The purpose of the Internet layer is to divide TCP segments into packets and send them from any network to their destination. The specific protocol that governs this layer is called the Internet Protocol (IP). Best path determination and packet switching occur at this layer. The network access layer, also known as the host-tonetwork layer, is concerned with all of the components, both physical and logical, that are required to make a physical link. It includes the networking technology details, including all the details in the OSI physical and data link layers. Common TCP/IP protocol Application Layer Transport layer Internet layer Network Access layer Movie PDU in packet tracer Introduction Application layer (AL) prepares human communication for transmission over the data network it is where the data enters the data network This layer provides interfaces to the network (interfacing human and data network) AL software initiates the data transfer process, provides services, and defines the protocols that are carried out by the applications Applications are the physical interface with the outside world that allow anyone to initiate the data transfer process. Applications provide the means for generating and receiving data that can be transported on the network. AL supports applications such as: Web browser E-mail telnet FTP Application layer responsible for services to user Protocols in AL: Define processes on either end of the communication Define the types of messages Define the syntax of the messages Define the meaning of any informational fields Define how messages are sent and the expected response Define interaction with the next lower layer Network layer duties Common network model Client/server network model Peer-to-peer network model (P2P) Client-server model Files are download from server to client A client is a hardware/software combination that people use directly Resources are stored on the server Larger organizations may need many servers, each fulfilling a single task such as file transfer (e.g.FTP), email, and web Smaller organizations may use a single server to provide multiple tasks. A daemon: a background service that listens for traffic of a specific typea web server will listen for web requests and ignore FTP requests. Advantage of client/server network: centralized management make administration and security enforcement much easier compared to P2P network E.g.: e-mail, http, ftp Example of a single server with a single task Client-server relationship Telnet client 1 Telnet Daemon Telnet client 2 Server processes may support multiple clients. e.g.: Telnet Server Application P2P network model P2P network allow computers to act as both clients and servers during the same communication. Each of them is called ‘peer’ because they can perform both tasks. Each user is in charge of his own access policies Disadvantage: Difficult to manage because management is decentralized Decentralized management also makes security difficult to enforce P2P applications allow users to directly share specified file types across P2P or client/server networks, e.g. Napster Domain Name System Domain Name System (DNS) is a system used on the Internet for translating names of domains and their publicly advertised network nodes into IP addresses. It follow client/server paradigm Domain Name Space DNS uses a hierarchical name space where the names are defined in an inverted-tree structure with the root at the top. * a name space is used to maps each IP address to a unique name (constructed from characters). The tree can have only 128 levels: level 0 (root) to level 127, see next figure. Domain name space Each node in the tree has a different label: which is a string with a max.63 chars. The root label is a null string (empty string). Each node in the tree has a domain name (DN). A full DN is a sequence of labels separated by dots (.), that read from the node up to the root (null label). Domain names and labels Example: Domains •A domain is a group of computers that are associated by their geographical location or their business type. •It is a sub-tree of the domain name space that also can be divided into subdomains a. Distribution of Name Spaces Hierarchy of Name Servers Zone Root Server Primary and Secondary Servers Hierarchy of name servers It is inefficient and unreliable to store a huge amount of information only in one computer and any failures makes the data inaccessible. DNS servers are computers that are used to distribute the huge amount information ‘primary’ and ‘secondary’ servers. Note: A primary server loads all information from the disk file; the secondary server loads all information from the primary server. b. DNS In The Internet Generic Domain Country Domain Generic domains defines registered hosts according to their generic behavior. Country domains section uses 2-character country abbreviation. Generic domains Table 1 Generic domain labels Label Description com Commercial organizations edu Educational institutions gov Government institutions int International organizations mil Military groups net Network support centers org Nonprofit organizations Table 2 New generic domain labels Label Description aero Airlines and aerospace companies biz Businesses or firms (similar to com) coop Cooperative business organizations info Information service providers museum Museums and other nonprofit organizations name pro Personal names (individuals) Professional individual organizations Country domains Packet tracer for DNS FTP Application FTP is a reliable, connection-oriented service that uses TCP to transfer files between systems that support FTP. The main purpose of FTP is to transfer files from one computer to another by copying and moving files from servers to clients, and from clients to servers. HTTP A Web browser is a client-server application, which means that it requires both a client and a server component in order to function. A Web browser presents data in multimedia formats on Web pages that use text, graphics, sound, and video. The Web pages are created with a format language called Hypertext Markup Language (HTML). HTML directs a Web browser on a particular Web page to produce the appearance of the page in a specific manner. In addition, HTML specifies locations for the placement of text, files, and objects that are to be transferred from the Web server to the Web browser. The Web page contains, often hidden within its HTML description, an address location known as a Uniform Resource Locator (URL). /teknik/ www. ugm.ac.id http:// Transport Layer Fungsi transport layer: Segmentation of upper-layer application data Establishment of end-to-end operations Transportation of segments from one end host to another Flow control ensures that a source host does not overflow the buffers in a destination host. Reliability provided by sequence numbers and acknowledgments TL protocols TCP used in FTP, HTTP, SMTP, Telnet UDPTFTP, SNMP, DHCP, DNS Field in TCP segment Source port – Number of the port that sends data Destination port – Number of the port that receives data Sequence number – Number used to ensure the data arrives in the correct order Acknowledgment number – Next expected TCP octet HLEN – Number of 32-bit words in the header Reserved – Set to zero Code bits – Control functions, such as setup and termination of a session Window – Number of octets that the sender will accept Checksum – Calculated checksum of the header and data fields Urgent pointer – Indicates the end of the urgent data Option – One option currently defined, maximum TCP segment size Data – Upper-layer protocol data Port for TCP Port Protocol Description 7 Echo Echoes a received datagram back to the sender 9 Discard 11 Users 13 Daytime 17 Quote 19 Chargen 20 FTP, Data 21 FTP, Control 23 TELNET 25 SMTP 53 DNS 67 BOOTP 79 Finger Finger 80 HTTP Hypertext Transfer Protocol 111 RPC Discards any datagram that is received Active users Returns the date and the time Returns a quote of the day Returns a string of characters File Transfer Protocol (data connection) File Transfer Protocol (control connection) Terminal Network Simple Mail Transfer Protocol Domain Name Server Bootstrap Protocol Remote Procedure Call Field in UDP segment UDP is a connectionless, unreliable protocol that has no flow and error control. It uses port numbers to multiplex data from the application layer. Port number for UDP Port Protocol Description 7 Echo Echoes a received datagram back to the sender 9 Discard 11 Users 13 Daytime 17 Quote 19 Chargen 53 Nameserver 67 Bootps Server port to download bootstrap information 68 Bootpc Client port to download bootstrap information 69 TFTP Trivial File Transfer Protocol 111 RPC Remote Procedure Call 123 NTP Network Time Protocol 161 SNMP Simple Network Management Protocol 162 SNMP Simple Network Management Protocol (trap) Discards any datagram that is received Active users Returns the date and the time Returns a quote of the day Returns a string of characters Domain Name Service Three-step connection establishment A B Synchronization occurs through an exchange of segments that carry a synchronize (SYN) control bit and the initial sequence numbers. 1. The sending host (A) initiates a connection by sending a SYN packet to the receiving host (B) indicating its INS = X: A - > B SYN, seq of A = X 2. B receives the packet, records that the seq of A = X, replies with an ACK of X + 1, and indicates that its INS = Y. The ACK of X + 1 means that host B has received all octets up to and including X and is expecting X + 1 next: B - > A ACK, seq of A = X, SYN seq of B = Y, ACK = X + 1 3. A receives the packet from B, it knows that the seq of B = Y, and responds with an ACK of Y + 1, which finalizes the connection process: A - > B ACK, seq of B = Y, ACK = Y + 1 Kelompok SNMP Dennis Adriansyah G (34172) Putu Bagus Susastra W (34202) Ferlin Dwi R (33559) Fery Setiawan (33827) Agus Joko Sudiarto ( 34213) FTP + Vicky Fazlurrahman (33977) Muhammad Fikri Ali R (34607) Fayruz Rahma (34001) Nurul Qonitah ( 34062) SMTP Fikar El Hazmi (33904) Supradi Sitepu (34148) Pandu Perwira (34304) DHCP Soimin (6066) Aji Priatmoko (5890) Aulia Fajrin (6149) Dicky Aditya Dharma (5887) Telnet Manumpak Aguswan Silalahi (5910) Adit Satria (6134) Feri Wibowo (6142) Puthut Punggawasesa (5891) SSH Dwi Adi Prabawa (31748) Laksono Kurnianggoro (31820) Ryan Ramandito (32201) SNMP, FTP, SMTP, DHCP, Telnet, SSH, DNS FTP Materi, SMTP Materi: 9, TW 8, Presentasi 8 SNMP Materi: 9, TW 9, Presentasi 9 9, TW 9, Presentasi 8 SSH Materi:9. TW 8. Presentasi 9