* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download IEE1451.5QoS - IEEE-SA
Wireless USB wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
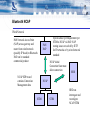
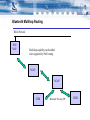
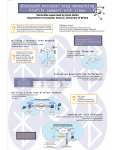
IEEE P1451.5 Wireless Sensor Interface Working Group Wireless QoS Model Peter Flittner Cambridge Silicon Radio Science Park,Milton Road Cambridge, CB4 0WH, United Kingdom Tel: +44 1223 692000 www.csr.com www.btdesigner.com Bluetooth TII Wired Network NCAP maps QoS requirement to Bluetooth Connection Management Protocol NCAP adds new STIMs and reconfigures STIM Connection State STIM SDP record contains Connection Management data STIM NCAP System sends QoS Requirement per STIM to NCAP Bluetooth TII using SPP profile as transport for IEEE1451 protocols and Bluetooth Connection Management protocol HHD STIM HHD can interrogate and reconfigure STIM STIM Bluetooth NCAP Wired Network PAN Network Access Point (NAP) acts as gateway and router from wired network (possibly IP based) to Bluetooth. NAP can be standard commercial product NCAP SDP record contains Connection Management data PAN NAP System sends QoS Requirement per STIM to NCAP via NAP. NAP routing issues are solved by IETF for IP networks or by wired network standard NCAP initial Connection State must allow connection HHD NCAP STIM STIM HHD can interrogate and reconfigure NCAP/STIM Bluetooth NCAP and TII Wired Network PAN Network Access Point (NAP) acts as gateway and router from wired network (possibly IP based) to Bluetooth. NAP can be standard commercial product PAN NAP System sends QoS Requirement per STIM to NCAP via NAP. NAP routing issues are solved by IETF for IP networks or by wired network standard HHD NCAP SDP record contains Connection Management data STIM NCAP Bluetooth TII using SPP STIM HHD can interrogate and reconfigure NCAP and STIM Bluetooth Multihop Routing Wired Network PAN NAP Multi-hop capability can be added when supported by PAN routing NCAP NCAP STIM Bluetooth TII using SPP STIM Comments • Bluetooth TII is mapped to SPP profile because: – TII is point to multipoint, with single NCAP connected to multiple STIMs – For controllers and other NCAPS implemented on host device, SPP requires minimal host memory and application code (virtual com ports) – Inband signalling can be implemented as AT commands – Sideband signalling can be implemented as an extra RFCOMM channel – RFCOMM allows multiplexing of multiple channels on a single link – STIM can implement Bluetooth SPP TII on a single chip Bluetooth device – NCAP can implement Bluetooth SPP TII for multiple STIMS on a single chip Bluetooth device – Most commercial HHDs, PCs and mobile phones support SPP Comments • Bluetooth NCAP network connection is mapped to PAN profile because: – PAN is the logical choice for a Bluetooth network connection – PAN U role is suitable for single chip Bluetooth radio plus transducer – PAN NAP role acts as gateway to a wired network – Future PAN routing methods will add multi-hop capability – NCAP with PAN U can be implemented on a single chip Bluetooth device – Publish subscribe and client server models of IEEE1451 are supported by PAN – PAN allows re-use of commercial ethernet and IP technology – Many commercial HHDs and PCs will support PAN