* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Third Punic War Through Attempts at Reform
Executive magistrates of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Military of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman economy wikipedia , lookup
Berber kings of Roman-era Tunisia wikipedia , lookup
Factorum ac dictorum memorabilium libri IX wikipedia , lookup
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Promagistrate wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Elections in the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman command structure during First Mithridatic War wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Demography of the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Rome (TV series) wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Early Roman army wikipedia , lookup
Constitution of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Senatus consultum ultimum wikipedia , lookup
Cursus honorum wikipedia , lookup
History of the Roman Constitution wikipedia , lookup
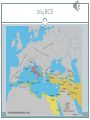
Today’s Flipped Lesson 1. WRAPPING UP PUNIC WAR #2 2. PUNIC WAR #3 WAS A QUICK HITTER 3. THE EFFECTS OF CONQUEST 4. TIBERIUS GRACCHUS The Second Punic War As we saw yesterday, Hannibal was a tough enemy, but eventually, was defeated by the Romans. But his memory will live on. Rome wins – 201 BCE Answers to the Video Questions Study Guide Study Guide The Third Punic War 149 BCE Carthage regaining power Romans attacked Carthaginians were finished Rome attacked Corinth, Greece, for good measure. 264 BCE 50 BCE 120 AD The Effects of Conquest Decline of the Roman Republic (135 BCE) Due to Hannibal Small Farms to Large Estates (latifundias) What was grown on these estates? What did this cause? Luxuries bought in other cities=Merchants grew poor Who worked the latifundias? Farmers lost land/independence Farmers moved to Rome – awful living conditions What did this cause? Government officials busy getting rich Rich-----------------------------------------------------Poor Roman Reform Next 100 years spent trying to improve Rome. REFORMERS Tribune Tiberius Gracchus (133 BCE) Limit land ownership Gave public lands to the poor Ran for a second term (against the law) Killed with his followers by the Senate. Gaius Gracchus Tiberius’s younger brother, Tribune in 123 B.C. Had government take over sale of wheat and sell it to the poor below market price. Eventually, 1/3 Romans were receiving wheat for free Senate felt threatened and in 121 B.C. had him killed Military Leadership - Gaius Marius GENERALS General who became consul in 107 B.C. First lower class Roman to be elected this high Opened the Army to everyone – provided jobs to the poor (made being a Roman soldier a full time job) Offered pay, land, pensions, and items. Loyalty was to the general that hired them, not Rome. Marius Military Leadership - Lucius Sulla General who opposed Marius; Sulla took his army and seized the city. Civil War broke out, in the end Sulla made himself dictator of Rome. Believed power of Senate was key to end Rome’s troubles. Senators had more duties, power of Tribunes weakened. Generals could not have more than one year at a time. Sulla “Proscripted” all followers of Marius. A young Caesar was spared, was nervous, left Rome to join the army. 78 BCE Sulla dies. Caesar can return to Rome. Sulla Study Guide Answers Study Guide Answers Made in America Series Good Morning America Map of where American Goods are made