* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Readmission Reduction Strategies for
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
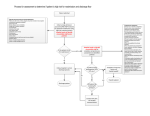
Readmission Reduction Strategies for Kaiser Permanente Colorado Region The Transition Bundle and PACT Shelley Cooper, MBA, PMP Senior Manager Implementation Support Jodi Smith, MSN, ANP-BC, ND PACT Program Lead We have no conflicts of interest to report Presenters • • • • • Colorado’s oldest and largest group health care 540,000 members with 85,500 Medicare members 26 medical offices 6,000 Health Plan staff and Permanente Medical Group physicians Recognized by NCQA as the top-ranked private health plan in Colorado and No. 13 in the entire nation for 2013-2014 Kaiser Permanente Colorado • • • KP Colorado does NOT own its own hospitals We contract with 5 area hospitals New CMS regulations created a ripe environment to work on readmission reduction with our hospital partners Kaiser Permanente Colorado The Problem... OUR READMISSION RATE WAS HIGHER THAN WE THOUGHT The Gap... OUR READMISSION REDUCTION STRATEGIES WERE “ONE-SIZE-FITS-ALL” The Solution(s)... DEVELOP READMISSION REDUCTION STRATEGIES THAT ARE TAILORED ACCORDING TO A MEMBERS RISK OF READMISSION Transitions Network Team (TNT) Governance Transitions Summit Nov 2012 Formation of TNT Governance Jan 2013 Established Interdepartmental Work Groups Feb 2013 - present 2013 Goal: Region-wide, ALL departments within KPCO are “on-the-line” to reduce the 30-day hospital readmission rate. Risk Stratification Readmission Review and Feedback System Care Pathways Goal: Reduce Readmissions Special Transition Phone Number Medication Reconciliation Standardized Same Day Discharge Summary The Transition Bundle Same Day Discharge Summary and Transition Phone Number “Will my doctor know what happened to me in the hospital?” and “Who should I call if I have a question about my hospitalization?” • Hospitalists, PCPs and Specialists collaborated to create a simple, electronic DC Summary completed the day the patient leaves the hospital. • The standardized discharge summary has been implemented at our core contract hospitals, representing 90% of total patient discharges. • A “special” phone number was added to the DC instructions for patients to use between discharge and outpatient follow up • Calls are answered by a live person 24/7 Standardized Same Day Discharge Summary Risk Stratification Know Your Population and Where to Focus Your Efforts / Resources Risk Stratification : LACE Risk of Readmission Scoring Tool(1) The “LACE” model was developed in Ottawa as a tool to predict 30-day readmission / death rates. 48 variables were evaluated, including living situation, age, functional limitations, medications, comorbidities, season, and others. Four variables were found to be the most powerful predictors of 30-day risk of readmission/death. (1) Walvaren et al. (CMAJ (2010) 182(6) : 551-557 The Canadian delivery systems is, in many respects, similar to the KP system It has been validated against 1,000,000 Ottawa patients It has been validated against our own data retrospectively for 2009 LACE continued… Baseline Readmission Rates by LACE Score LACE Score 30-Day Readmission Rate 1 0.0 % 2 0.0 % 3 9.1 % 4 5.9 % 5 6.3 % 6 5.7 % 7 8.7 % 8 8.9 % 9 24.8 % 10 17.1 % 11 15.7 % 12 23.8 % 13 22.0 % 14 32.0 % 15 26.1 % 16 31.8 % 17 33.3 % Low Risk 5.7% Moderate Risk 15.4% High Risk 21.5% Very High Risk 32.5% Care Pathways Interventions According to Risk KPCO Adult Medicine Risk Pool Low -Transition call from TCC team within 48-72 hours Moderate High Same as low risk, except: Same as low and medium risk, except: - Office visit with PCP within 7 days - PACT home visit within 72 hrs - Medication Reconciliation - Appoint booking / confirmation - Phone visit with PCP within 7 days - PCP appointment per PACT APN recommendation - Override to higher level of care or forward to RNCC if necessary Care Pathways According to Risk of Readmission Transitions Care Coordinator (TCC) - - Telephonic transitional care coordination within 72 hours of discharge “Owns” the patient for first 72 hours RN Care Coordinator (RNCC) - - - Embedded in the primary care clinics Provides longitudinal, telephonic disease management and care coordination Collaborates with PACT team for NCQA QI7 Care Coordination Medication Reconciliation “I understand my medications, how to take them and why I need them.” Medication Reconciliation MEDICATION DISCREPANCY EXAMPLES: Patient taking double dose of B-blocker. DC instructions state, “Metoprolol 25 mg, take 2 tabs twice daily”. Pt had 50 mg tabs at home and was taking "2 tabs“ as stated in the DC summary, therefore, taking Metoprolol 100 mg twice daily (200 mg total). Pulse was 46 at PACT visit, BP 96/48. DC instructions stated STOP Amlodipine and to START Metoprolol. At PACT visit, wife was giving patient both medications. Medication Management and Discrepancy Reconciliation f d s d sf d f d f d p p p p p ff p f d s d f d sf d ss f d sf d sf d f d Regional Medication Reconciliation Strategies o Primary Care o Successfully reduced the average number of duplicate medications per 100 office visit encounters from 14% in 2010 to 8% as of the end of September 2013 o Hospital Medicine o Med rec done on admission and discharge o PACT o During the PACT visit, discrepancies are resolved and reconciled in real-time with the pt o Pharmacy o o Transition pharmacist reviews meds for 100% of patients discharged from SNF to home Care Coordination o Telephonic med rec on hospital and ED discharges to home PACT Home Visits "What the organizations … share in common is this clear-eyed view that the status quo is not sustainable and that new models to simultaneously improve health, improve health care, and reduce per-capita costs aren’t just needed, they’re needed urgently." ~Alide Chase A NEW MODEL ‘POST-ACUTE CARE TRANSITIONS’ By coupling a robust readmission prediction tool (LACE) with strategically-designed post-discharge home visits (PACT), KPCO is able to target high intensity interventions specifically to patients who are at high risk of readmission. A NEW MODEL…..PACT PACT - A one-time home visit within 72 hours of hospital discharge - To targeted, high-risk members - Conducted by nurse practitioners INTERNAL to KPCO - Who collaborate and communicate across our care delivery system regarding each specific patient care plan and needs PACT The Secret Sauce Taking care of uncertainty and leveraging competencies – medical care and community care – to create a supportive wrap-around system for the most vulnerable and complex patients. - - - Stagger points of care over time, not overwhelming patient with lots of care up front Right message in the right place at the right time Not the same as Home Health Care PACT Keys for Success In-person home visits by internal providers offers: Objective empirical assessment of the patient’s needs in his/her home environment which is then communicated to all downstream providers. On-site, real-time medication reconciliation, Referral to appropriate follow up and supportive care An exceptional level of ownership Nurse Practitioners May titrate/modify medications May assess and treat post-hospitalization complications or treatment failures May refer patients as necessary to additional services not considered at the time of discharge BRIDGE OVER TROUBLED WATERS PACT Teaching People How to Swim Upstream Downstream Readmission Review and Defect Analysis Negative Feedback Loop Defect Analysis Summary o Most of the readmissions reviewed were: o o The likelihood that a defect will be identified increases: o o As the number of medications increase The majority of readmissions are for reasons related to the index stay o o Medicare members Regardless of whether or not the readmission was related to the index stay, approx 40% of cases reviewed had a defect identified “Deterioration of Condition”, “Medication Issues” and “End of Life Issues” accounts for more than half of identified readmission defect issues TNT Governance Group PPS Continuing Care Primary Care Hospital Medicine World Congress ??? Thanks to … Risk stratify your population Target / tailor interventions according to risk Develop dashboards to monitor progress Engage stakeholders Overly communicate Continue to persevere with your plan, no matter how difficult it is to change current practices Keep the patient at the center of all you do In conclusion Thank you: Questions? KPCO Post-Acute Discrepancies Medication Discrepancy Summary Total PACT Patients 449 Total Medication Discrepancies 933 Average Number of Med Discrepancies/patient 2.1 PACT POST-ACUTE CARE TRANSITIONS “What had tended to be seen as just an evitable consequence of people being sick is now increasingly seen as often being the consequence of not having done as good a job as we could have.” Good Enough?