* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download functions
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
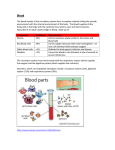
TAKS OBJECTIVE 2: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the organization of living systems. TEKS OBJECTIVE 10: The student knows that, at all levels of nature, living systems are found within other living systems, each with its own boundary and limits. (A) interpret the functions of systems in organisms including circulatory, digestive, nervous, endocrine, reproductive, integumentary, skeletal, respiratory, muscular, excretory and immune (B) compare the interrelationship of organ systems to each other and to the body as a whole Integumentary Systems Function: Cover and protect the body, controls body temperature, prevents fluids from leaving the body Organs Included: Skin, hair, nails, sweat glands, sebaceous (oil) glands Skeletal System Function: Supports the body, helps with movement and protects internal organs. Is responsible for creating blood cells in red marrow. Includes: all bones *Joints= The place where 2 bones meet, allowing the skeleton to move. *Ligaments= Bands of connective tissue that connect the 2 bones that form joints Muscular System Function: Moves food through the digestive tract, allows for movement and causes the heart to contract. Includes: 3 types of muscles*Skeletal muscle - voluntary (can be controlled) and makes up the muscles that moves the skeleton. Work like levers with the skeletal system to move body part. *Cardiac muscle - involuntary (cannot be controlled) and makes up the heart muscle. *Smooth muscle - involuntary and is found in the walls of the body (ex: stomach, intestines, blood vessels) TAKS PRACTICE Red marrow is the principal tissue that produces red blood cells in humans. In which body system is red marrow found? F Integumentary system G Respiratory system H Nervous system J Skeletal system Remember, the skeletal system is responsible for red blood cell production. Which structure in the upper arm is responsible for raising the lower arm? A B C D 1 2 3 4 Flexing the bicep will raise the lower arm. The diagram represents a human arm. Which structure is most responsible for moving the arm to a straighter position? A Tendons of origin B Biceps C Radius D Triceps Flexing the triceps will lower/straighten the lower arm Which of the following is directly caused by muscle action? F Regeneration of nerves G Healing of wounds H Release of hormones J Extension of limbs Muscles work as levers for body movement Nervous System Function: Carries information between all parts of the body and the brain by electrical and chemical messages transmitted by neurons. Includes: Brain, spinal cord, and nerves. Endocrine System Function: Makes hormones, controls growth, metabolism and reproduction. The 2nd most important system. Includes: Hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid, adrenal glands and gonads. In the diagram above, one cell creates and releases chemicals that travel to a second cell and quickly induce that cell into action. This diagram represents part of the — A endocrine system B skeletal system C muscular system D nervous system Neurons transmit chemical Messages. Which of these statements describes one possible interaction between the endocrine and respiratory systems? F The heart is composed of muscle tissue. G Hormones can trigger asthma attacks. H The rib cage expands to move air into the lungs. J Blood cells can attack pathogens. The Endocrine system is responsible for hormonal release Pelicans prevent serious wing damage by entering the water in the manner shown above. Which two organ systems in the pelican work together the most to accomplish this maneuver? A B C D Circulatory and nervous systems Nervous and muscular systems Muscular and digestive systems Digestive and circulatory systems The Nervous system controls all skeletal muscle action Circulatory System Function: Carries nutrients & oxygenated blood from the lungs to all the body cells and removes waste with help from the protein, hemoglobin. Includes: Heart, arteries, veins Note: Arteries are red and carry oxygenated blood away from the heart. Veins are blue, and carry deoxygenated blood to the heart for reoxygenation. Lymphatic/Immune System Function: Defends the body from disease. Includes: Lymph nodes, tonsils, spleen, lymphatic vessels and bone marrow. Respiratory System Function: Performs gas exchange: Takes oxygen from the air/lungs and delivers it to all body cells. Removes poisonous carbon dioxide from the body. Includes: Nose, mouth, pharynx, larynx and lungs. Which body system is directly responsible for delivering nutrients to cells throughout the body? A Circulatory system B Integumentary system C Endocrine system D Respiratory system Responsible for carrying nutrients and oxygenated blood to body Hemoglobin carries oxygen to body cells. Which body system contains hemoglobin? A B C D Circulatory system Respiratory system Endocrine system Nervous system Hemoglobin is the protein that carries oxygen on red blood cells The medulla, part of the brain stem, reacts quickly to increased levels of CO2 in the blood and stimulates a response from the — A excretory system B immune system C respiratory system D integumentary system Respiratory system is responsible for ridding the body of poisonous CO2. Nutrients from digested food move from the digestive system directly into the — A circulatory system B integumentary system C excretory system D endocrine system Responsible for delivering nutrients to the rest of the body Digestive System Function: Breaks down food to a form the body can use. Includes: Mouth, esophagus, stomach, intestine, liver and pancreas. Note: There are 2 types of digestion: 1. Mechanical digestion (chewing) and 2.Chemical digestion (stomach acid breaking down food). Which system is responsible for producing enzymes that aid in breaking down substances to be absorbed for the body’s growth and repair? F Digestive system G Reproductive system H Respiratory system J Skeletal system Breaks down food to a form the body can use Some organs of the gastrointestinal tract — A fit in more than one organ system B perform only one function at a time C supply the body with platelets D produce soluble vitamins Pancreas is part of the endocrine and digestive systems The small intestine is to nutrient absorption as the blood is to nutrient — A B C D assimilation distribution regulation elimination Blood carries nutrients and oxygen that are delivered to the body How is the circulatory system related to the digestive system? F The brain stem controls the heart rate. G Blood carries nutrients to body cells. H Stomach muscles contract and expand. J The pharynx is a passageway for air and food. Blood carries the nutrients absorbed from the digestive system Urinary/Excretory System Function: Removes nitrogenous waste from the body in the form of urine. Includes: kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra. Reproductive System Function: Produces offspring Includes: *Female - ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus and vagina. *Male - penis, scrotum, testes, vas deferens, prostate and urethra. VIDEOS\REPRODUCTIVE\Ovaries and Testes Endocrine Glands and Sexual Maturity.asf A portion of the human excretory system is represented in the diagram. The order in which urine flows through the system is — F urethra bladder ureter kidney G ureter kidney bladder urethra H kidney ureter bladder urethra J bladder urethra kidney ureter Some waste in blood is collected by kidneys and then moved to exit the body The diagram illustrates the parts of this flower. Which of these parts are not directly involved in sexual reproduction? A Stigma and style B Sepal and pedicel C Anther and filament D Receptacle and ovary These structures are for protection How is the excretory system most likely to respond when an animal is thirsty? F By relaxing the smooth muscles G By retaining body fluids H By absorbing heat from lymph glands J By releasing hormones The body wants to keep as many fluids as possible until body fluids are equalized