* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mesoamerican Civilizations
Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire wikipedia , lookup
Tepotzotlán wikipedia , lookup
Templo Mayor wikipedia , lookup
National Palace (Mexico) wikipedia , lookup
Fall of Tenochtitlan wikipedia , lookup
Aztec warfare wikipedia , lookup
Aztec cuisine wikipedia , lookup
Aztec Empire wikipedia , lookup
Human sacrifice in Aztec culture wikipedia , lookup
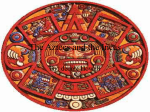
Mesoamerican Civilizations Maya, Aztec, Inca Olmec 1200 B.C.The first civilization of Mesoamerica They were located in the hot and swampy lowlands along the coast of the Gulf of Mexico south of Veracruz. They had large cities that were centers for religious rituals. They carved colossal stone heads They may have been to represent their ancestors or gods. Teotihuacán Was the first major city in Mesoamerica Arose around 250 B.C. and collapsed about 800 A.D. May have had as many as 200,000 inhabitants at its height. Has a main thoroughfare, known as the Avenue of the Dead, had two main temples. The Temple of the Sun and the Temple of the Moon. Meso-America • Meso-America was home to 3 major civilizations in Pre-Columbian times. • Pre-Columbian means before the time of exploration (think before Columbus) • The 3 highly developed civilizations were: 1. Mayans 2. Aztecs 3. Incas Mayans • The Mayans were a powerful civilization from 1500BCE-1548CE • Their economy was based on Farming, Trade, and Artisans • Their religion was polytheistic • That meant they believed in more than one god • The priests did human sacrifices to please these gods. Mayans • Their capital city was Tikal • The Mayans had many important achievements: Hieroglyphics, a writing system “glyphs” An accurate calendar of 365 days to plan agriculture A number system that included the idea of zero Chichen Itza was an observatory Yucatán Peninsula -Maya were found in the Yucatan Peninsula and Part of Guatemala Maya: Between 300 and 900 A.D. -Flourished during this time. We do not know why it fell into decline. The Maya abandoned their cities, we do not know why. Political and Social Structure Cities-Were built around a central pyramid Pyramid-Was topped with a shrine to the gods. City-States-Each governed by a hereditary ruling class Tikal, Guatemala Mayan Kings -Ruled the Mayan Kingdom They claimed they were divine Were assisted by nobles and a class of scribes Made special blood sacrifices to maintain the kingdom. People -Included townspeople, skilled artisans, and, officials, and merchants. Many people were peasant farmers who worked on terraced hillsides farming. Men did the fighting and hunting, women made cornmeal and were responsible for homemaking and raising children. Religion The Maya were Polytheistic. They believed that all of life was in the hands of a divine power. They were responsible for pleasing the gods. Their gods were ranked in order of importance, the Jaguar was the god of night and was seen as evil. The Maya practiced human sacrifice to appease their gods. Human sacrifice was also used to mark special occasions. When a king ascended to the throne war captives were tortured and beheaded to mark the occasion. Accomplishments Language The Maya developed an independent Hieroglyphic language. The Spanish destroyed most of the Mayan writings. They were not seen as having any value. Their language was not translated until the 20th century. Calendar The Maya developed a calendar that had two different parts. It had a solar calendar with 365 days, divided into 18 months with 20 days each with 5 extra days at the end. A Lunar calendar and a Calendar based on the movement of the Planet Venus. This was a sacred calendar with 260 days and 13 weeks of 20 days each. The Mayan calendar says our present world was created in 3114 B.C. and the current calendar restarted on December 23 2012 A.D. • • • • • Mayan civilization Located in the Mexican and Central American rain forest Represented by Chichen Itza Groups of city-states ruled by kings Economy based on agriculture and trade Polytheistic religion: Pyramids Aztecs • The Aztecs were a powerful civilization from 1400-1520CE • Their economy was based on agriculture and warriors expanding the empire by capturing goods and prisoners • Their religion was polytheistic Aztecs • Their capital city was Tenochtitlan. It was built on islands and floating rafts (current day Mexico City) • The Aztecs had many important achievements: Strict legal system, they used the death penalty Education for Aztec children Gold and silver jewelry Aztecs • The Aztecs were unpopular with their neighbors • Why? They kidnapped them for human sacrifices • The EFFECT of this was: neighboring people led explorers and conquistadors to Aztecs • Conquered by the Spanish conquistador Cortez The Aztec began c. 12th century A.D. Began a long migration that brought them into the Valley of Mexico. They established their capital city at Tenochtitlán. Tenochtitlán- means the Place of the Prickly Pear Cactus. An Aztec legend said that when the people found their new home they would see an eagle perched on a cactus holding a snake. They saw this in lake Texcoco. Their city was built up on rafts made from reeds and covered with dirt. They were called chinampas. PresentDay Mexico-City is built on top of this city. The original was destroyed by the Spanish. Political and Social Structure By 1500 there were about 4 million people in the Aztec Empire. Aztec Emperor Ruled over the Aztec Empire. Was the supreme leader of the people. He claimed that he was divine. People Made up of commoners, indentured workers, and slaves. Most people were farmers, but they also traded with people in the surrounding areas. Men were to be the warriors, while a woman’s role was to be in the home. Women were allowed to own and inherit property and enter contracts. Women wove textiles and raised children. They could also be priestesses. Religion Had a polytheistic religion based on warfare. Huitzilopochtli Their chief god. He was the god of the sun. The Aztec offered him human sacrifice to give him strength to battle the forces of darkness each night so that he could rise each morning. Quetzalcoatl The feathered Serpent He believed he had left the valley of Mexico and promised to return in triumph. Human Sacrifice Each Aztec city contained a pyramid where they practiced human sacrifice as a way to postpone the end of the world. Destruction of the Aztec The subjugation of the people of the Aztec Empire bred hatred and discontent among the people. When the Spanish arrived they did not have a difficult time finding allies to fight the Aztec. Hernán Cortés 1519 Spanish Conquistador who came to the valley of Mexico in 1519 with 550 soldiers and 16 horses. He was at first greeted by the Aztec Emperor Montezuma (Moctezuma). The Spanish later kidnapped the Emperor and made him a puppet. The people rebelled and the Emperor was killed. The Spanish barely escaped. The Spanish returned several months later. Many of the natives had fallen ill with Smallpox. Cortés and his allies destroyed the Aztec capital and subjugated the Aztec people. Tenochtitlan: The “Venice” of the Americas Aztec Chinampa or Floating Garden: 15ft. to 30ft. wide Tenochtitlan - Chinampas Aztec Sun Stone -- Calendar Aztecs Sacrifice Neighboring Tribes to the Sun God • • • • • Aztec Civilization Located in arid valley in central Mexico Represented by Tenochtitlan Ruled by an emperor Economy based on agriculture and tribute from conquered peoples Polytheistic religion: pyramids, rituals Incas • The Incas were a powerful civilization from 1200-1535CE • Their economy was based on agriculture, and silver/gold jewelry trade • Their religion was polytheistic Incas • Their capital city was Cuzco • Machu Picchu was high in the Andes Mts (terrace farming) • The Incas had many important achievements: Stone covered roads to connect empire (bridges) Architecture included stone palaces, temples, fortress Advanced medicine, example: brain surgery Late 1300's Inca The Inca started as a small group that were located in Cuzco. They did not begin to become powerful until after the fall of the Moche of Peru. Pachacuti Unified the Inca and established the Inca Empire. Organization of the Empire Incan state was built on war and bribery. The conquered peoples were all taught the same language. Each region was appointed a governor who answered to the Emperor. Road System: 24, 800 miles of Road The Inca built roads to unify their people. Roads made travel and communication throughout the empire more efficient. There were rest houses and storage depots along with bridges to span ravines and waterways. Culture Were required to marry from within their own social group. Women were expected to live at home, the only alternative was to be a priestess. Most people were farmers, they also herded llamas and alpacas. Quipu-A system of knotted strings used by the Inca to keep records. Great Builders They had great buildings made of stone held without mortar. Their roads also show their ability as great builders. Machu Picchu City built at 8,000 ft above sea level. Urubamba River River below Machu Picchu Inca Gold & Silver Incan Terrace Farming Defeat The Spanish arrived in 1531 1531: Francisco Pizarro Spanish Conquistador led a band of 180 men with superior weapons. The Inca, like the Aztec, were devastated by disease. Smallpox Devastated the Population Civil War After the death of the Inca Emperor a civil war broke out, Pizarro took advantage and defeated the people. Pizarro and his men established Lima as the new capital of the Spanish Colony in 1535. • • • • • • Incan Civilization Located in the Andes Mountains of South America Represented by Machu Picchu Ruled by an emperor Economy based on high-altitude agriculture Polytheistic religion Road System Achievements of Mayan, Aztec, and Incan civilizations • Calendars • Mathematics • Writing system and other record-keeping systems