* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CHAPTER 12, Section 2
Fifteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Reconstruction era wikipedia , lookup
Carpetbagger wikipedia , lookup
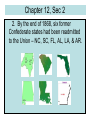
Chapter 12 - RECONSTRUCTION 1865-1877 SECTION 1 RECONSTRUCTION PLANS Chapter 12, Sec 1 RECONSTRUCTION – rebuilding after the Civil War LINCOLN’S PLAN - moderate policy (10% PLAN) Proclamation of Amnesty & Reconstruction He offered a pardon to all Southerners who took an oath of loyalty to the U.S. & accepted the Union’s proclamations concerning slavery. When 10% of a state’s voters in the 1860 presidential election had taken this oath, they could organize a new state government. Chapter 12, Sec 1 Radical Republicans! Wanted to change the South. Leaders – Thaddeus Stevens & Charles Sumner THREE MAIN GOALS 1. Prevent leaders of the Confederacy from returning to power after the war. Wanted the Republican Party to become powerful institution in the South. Wanted the federal government to help African Americans achieve political equality by guaranteeing their right to vote in the South. 2. 3. Chapter 12, Sec 1 1. 2. 3. WADE-DAVIS BILL -Moderate Republicans Majority of all adult white men in a former Confederate state to take an oath of allegiance to the Union. State could then hold a constitutional convention to create a new state government. Each state’s convention would then have to abolish slavery, reject all debts the state had acquired as part of the Confederacy, & deprive all former Confederate government officials and military officers of the right to vote or hold office. Chapter 12, Sec 1 FREEDMEN’S BUREAU 1. Fed and clothed war refugees in the South using surplus army supplies. 2. Helped formerly enslaved people find work on plantations & negotiated labor contracts with planters. 3. Established special courts to deal with grievances between workers and planters. Note: The bureau also worked closely with Northern charities to educate formerly enslaved African Americans and it provided housing for schools, paid teachers, & helped to establish colleges for training African American teachers. CHAPTER 12, Section 2 CONGRESSIONAL RECONSTRUCTION Chapter 12, Sec 1 I. ANDREW JOHNSON – Southerner (TN) A. Became president when Lincoln was killed. B. Johnson’s plan: 1. Pardon to former Confederates who took the oath of loyalty and return their property to them. 2. Former Confederate officers & officials & those who owned more than $20,000 of property were excluded; they could apply directly to the president for a pardon. 3. States had to call a convention, revoke secession, ratify the 13th Amendment, & reject all Civil War debts. Chapter 12, Sec 1 C. C. Many Manyformer formerConfederates Confederatesgot gotelected elected totoCongress, Congress,including includingthe theVP VPfor forthe the Confederacy Confederacy(Stephens). (Stephens). This This angered angeredthe theNorthern Northernpoliticians. politicians. D. D. BLACK BLACKCODES CODES ---- limited limitedAfrican African Americans’ Americans’rights rightsininthe theSouth. South. Chapter 12, Sec 2 II. Radical Republicans Take Control. A. Civil Rights Act of 1866 – granted Citizenship to all persons born or Naturalized in the U.S. (except Native Americans)!!!! B. The Fourteenth Amendment – 1. Grants citizenship to all persons born or naturalized in the U.S. 2. Forbids states from depriving any person of life, liberty, or property without due process of law. 3. Provides equal protection of the law. Chapter 12, Sec 2 C. Election of 1866 – Republicans (Johnson) win an overwhelming victory – 3-1 majority. D. MILITARY RECONSTRUCTION. 1. MILITARY RECONSTRUCTION ACT (Congressional Republicans passed this act that wiped out Johnson’s programs!!) This act divided the former Confederacy into five military districts with a Union general in charge of each district. Chapter 12, Sec 2 Five Military Districts Chapter 12, Sec 2 • Military Reconstruction Act 1. Each former Confederate state had to hold another constitutional convention to design a constitution acceptable to Congress. 2. New state constitutions had to grant the right to vote to all adult male citizens, regardless of race. 3. After ratification of the new constitution, states had to ratify the 14th Amendment. Chapter 12, Sec 2 2. By the end of 1868, six former Confederate states had been readmitted to the Union – NC, SC, FL, AL, LA, & AR. Chapter 12, Sec 2 E. IMPEACHMENT. Johnson had charges brought against him because he challenged the TENURE OF OFFICE ACT when he fired Secretary of War Stanton. He was charged with “high crimes and misdemeanors.” AND he had fired four military commanders in the South which the Republicans felt undermined the Reconstruction Program. He was not convicted. Chapter 12, Sec 2 F. THE ELECTION OF 1868 Republican Candidate – Grant WON!! G. THE FIFTEENTH AMENDMENT the right to vote “shall NOT be denied…on account of race, color, or previous condition of servitude.” Chapter 12, Sec 2 EXPANDING THE NATION Under President Johnson, Secretary of State Seward bought Alaska from Russia for $7.2 million. At first it was called “Seward’s Icebox,” but later it became valuable because of its oil and gold. CHAPTER 12, Sec 3 REPUBLICAN RULE IN THE SOUTH CARPETBAGGERS AND SCALAWAGS Carpetbaggers – Northerners who moved South; many came with suitcases made of carpet fabric. Southerners felt that they were intruders taking advantage of the South. • SCALAWAGS – an old Scotch-Irish term for weak, underfed, worthless animals. They were white Southerners who worked with the Republicans & supported Reconstruction. Chapter 12, Sec 3 AFRICAN AMERICANS enter politics! • Some became legislators; others became administrators in the government. • Some were elected to local government positions such as mayor or police chief. • No African American was ever elected governor. 1st Black U.S. Senator Chapter 12, Sec 3 REPUBLICAN REFORMS in the SOUTH. 1. Repealed the Black Codes. 2. Made more state offices elective. 3. Established state hospitals. 4. Established institutions for orphans, the hearing & visually impaired, & mentally ill. 5. Rebuilt roads, bridges, railways & provided funds for new industry in the South. 6. Established a new system of public schools. HOWEVER – many Republicans were not honest. GRAFT (gaining money illegally) was common. Chapter 12, Sec 3 AFRICAN AMERICAN COMMUNITIES • EDUCATION – By 1876, 40% of African American children attended school in the South. • Fisk University (TN), • Atlanta University (GA), • and Morehouse College (GA) were new African American colleges. Chapter 12, Sec 3 CHURCHES and SOCIAL ORGANIZATIONS • Churches served as the center of most African American communities. • Churches housed schools and social activities. • Churches often acted as unofficial courts by promoting social values, settling disputes and disciplining people. Chapter 12, Sec 3 The Ku Klux Klan • Secret society started in 1866 by former Confederate soldiers in Pulaski, TN. • GOAL – to drive out the Union troops & carpetbaggers; regain control of the South for the Democratic Party. Chapter 12, Sec 3 • Republicans & African Americans formed their own groups and fought back. • The Enforcement Acts – 1. Made it a federal crime to interfere with a citizen’s right to vote. 2. Put federal elections under the supervision of federal marshals. 3. KKK Act - outlawed the activities of the klan. Chapter 12, SECTION 4 RECONSTRUCTION COLLAPSES C 12, Sec 4 I. The Grant Administration Little political experience! A. Republicans controlled Congress 1. Kept tariffs HIGH 2. Tightened banking regulations 3. Promised to repay debts with gold and not paper money 4. increased federal spending on RR, port facilities, & the national postal system. 5. Kept “sin taxes” (alcohol/tobacco) B. Liberal Republicans – pulled away from the Republicans because they did not want Grant to be president again – nominated Horace Greeley. C 12, Sec 4 C. Scandals in Grant’s Second Term A. William Belknap – Sec of War, accepted bribes – resigned. B. Whiskey Ring - 1875 – gov. officials & distillers in St. Louis cheated the gov. out of millions by filling false tax reports. D. The Panic of 1873 – caused by bad railroad investments that forced a banking firm to declare bankruptcy. This caused small banks to close the Stock Market to plummet and businesses to shut down causing unemployment. C 12, Sec 4 II. RECONSTRUCTION ENDS A. Democrats “REDEEM” the South! Democrats were able to win back the support of white owners of small farms who had backed Republicans by appealing to the white racism and making it a white/black struggle. B. The Turning Point – The Compromise of 1877 1. Election of 1876 – Republicans – Nominated Rutherford B. Hayes (wanted to end Radical Reconstruction). Democrats – Nominated Samuel Tilden C 12, Sec 4 2. Tilden – 184 electoral votes (1 short of a majority.) Hayes - 165 electoral votes 20 votes are in dispute. 3. Congress appointed a commission of 15 made up of the House, Senate, & Supreme Court. (8 Republicans, 7 Democrats) 4. Hayes won, but many thought a deal had been made, but never proved. Chapter 12, Sec 4 5. April 1877 – Hayes pulled troops out of the South. RECONSTRUCTION was over and the Democrats REDEEMED the South. III. A “NEW SOUTH” Arises. Henry Grady, editor of the Atlanta Constitution created this phrase – the South had to develop a strong industrial economy. C 12, Sec 4 – Hayes with his Secretary of the Interior in the White House. C 12, Sec 4 A. NEW INDUSTRIES. 1. Northern capital helped rebuild railroads. 2. Iron and Steel – Birmingham, AL 3. Tobacco processing – North Carolina 4. Cotton Mills appeared in towns. 5. HOWEVER, the South remained mainly agrarian. Chapter 12, Sec 4 6. For many African Americans the end of Reconstruction meant a return to the “OLD SOUTH” where they had little political power and were forced to labor under difficult and unfair conditions. Chapter 12, Sec 4 B. African Americans worked as: 1. Tenant Farmers – paid rent for the land they farmed. Chapter 12, Sec 4 2. Sharecroppers – did not pay their rent in cash; instead, they paid a share of their crops to cover rent as well as the cost of the seed, fertilizer, tools, & animals they needed. Chapter 12, Sec 4 3. Furnishing Merchants. Provided sharecroppers with the supplies they needed on credit but at interest rates often as high as 40 percent. Crop liens – Merchants could take some crops to cover their debts. Debt peonage – trapped sharecroppers. Chapter 12, Sec 4 The Civil War ended slavery. BUT Many African Americans were trapped in economic circumstances where they lost much of their newly gained freedom.