* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download integration
United Kingdom employment equality law wikipedia , lookup
Racial stereotyping in advertising wikipedia , lookup
Employment discrimination law in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Jim Crow laws wikipedia , lookup
Racism in association football wikipedia , lookup
International Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Racial Discrimination wikipedia , lookup
Mentalism (discrimination) wikipedia , lookup
Racism in the LGBT community wikipedia , lookup
Scientific racism wikipedia , lookup
Durban Review Conference wikipedia , lookup
Racism in Argentina wikipedia , lookup
Racism in Asia wikipedia , lookup
Racism in the Arab world wikipedia , lookup
Racism in Africa wikipedia , lookup
Racism in Italy wikipedia , lookup
Sexual racism wikipedia , lookup
Racism in North America wikipedia , lookup
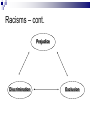
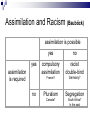
MM202 Lecture 3 Racism(s) & discrimination Multiculturalism In Western Europe And North America Institute Of Western European Studies, FSV UK Spring Lecturer: Antonin Mikeš [email protected] Reviewdifferent forms of assimilation Integration Policy- ‘should be’ Obstacles to integrationPolicy level/ governance level Obstacles arise at high level- dependent on approach taken. Methods and Models for inclusion/racism reduction Rising Racism Polarity of terms Positives Social Justice Equity Equal opportunity Inclusion Human rights Human dignity Equality Freedom Negatives • No justice • Bias, discrimination • No opportunity • Exclusion • Differential treatment • Degradation Humiliation • Partiality • Slavery, Subjugation Racism defined…. • “Racism is an ideology that gives expression to myths about other racial and ethnic groups, that devalues and renders inferior those groups, that reflects and is perpetuated by deeply rooted historical, social, cultural and power inequalities in society.” Human Rights and Equal Opportunity Commission, 1998, Australia Racism & other -isms sexism, disableism, ageism, homophobia Neil Thompson Racism can be defined as an attitude (ideology) or action (behaviour) that disadvantages individuals or groups on the basis of their “racial” inferiority, mainly by means of limiting their access to scarce resources. Racial difference or racial inferiority is often perceived or constructed in terms of different culture, ethnicity, religion, language, etc. Racism as ideology 1. the so called “scientific racism of the 19th century”, manifested for example in the publication by Herrnstein, Murray, 1995 2. “popular” racism or “common sense” racism that is based on ethnocentrism, a tendency to believe that one's own cultural paradigm is universal, neutral and superior to any other culture In other words… Racism 1. Denies all difference in the name of universality of the human nature, but unconsciously it takes back this universality to the dominant model; 2. uses the obvious differences to turn them into instruments of domination, exploitation, condemnation, exclusion, or extermination. Explanations of racism: 1. • • 1. Psychological ”Some people are like that” Lack of knowledge, ignorance „To know is to love“ Intergroup relations ”Birds of a feather” Individuals are racists because the structures, practices, and values of our society are racist. ”Its the system” Racisms – cont. from violent attacks or scapegoating to paternalistic crypto-racist assistance to m. tendency to deny racism (unacceptable) two main meanings: 1) ideology (beliefs) about racial superiority 2) “the whole complex of factors which produce racial discrimination” and sometimes also “those which produce racial disadvantage” Cashmore Racisms- cont. „Racism, in short, involves (a)stereotypes about difference and inferiority (b)use of power to exclude, discriminate, subjugate“ The Parekh Report, 2000 Attitudes Behavior Structures Prejudice Discrimination Inequality Racisms – cont. Prejudice Discrimination Exclusion Avoidance or inclusion? There are differing ways to ‘include’ the other Differing methods How states include the other is dependent on their approach- Models • Assimilationist model • Curriculum (Multiculturalism) model • Equity/Rights Model What countries have done Differing countries have followed differing methods to ‘include’ different groups. Assimilation Cultural pluralism– middle ground? Segregation Inclusion – middle ground? Pluralism Assimilation and Racism (Bauböck) assimilation is possible yes assimilation is required no yes no compulsory assimilation racist double-bind France? Germany? Pluralism Segregation Canada? South Africa? In the past 3 Differing Models • Assimilationist model • Assimilation • Inclusion • Curriculum (Multiculturalism) model • Pluralism • Equity/Rights Model • Anti discriminatory Assimilationist model DIFFERENCE DEFICIT ASSIMILATION COMPENSATORY PROGRAMMES Does the individual fit into the System or ‘Institution’? Curriculum (Multiculturalism) model Cultural Effects CULTURES LIFESTYLES ATTITUDES PLURALIST TOLERANCE AND HARMONY Does the organisation of this ‘institution’ recognise Diversity ? Equity/Rights Model Social and Political Effects EQUITY PARTICIPATION ANTIDISCRIMINATORY LIFE CHANCES Are people enabled in this ‘institution’? Do the structures allow for achievement, growth and opportunities? Solutions to Racism… What are some solutions to racism? Discrimination? Is there a simple answer? People hold prejudices, do you? Can you come up with some solutions? For next week please read the DIRECTIVE and accompanying cases