* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Radiological anatomy of the chest
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
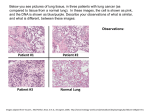
Radiological Anatomy Of The Chest Objectives By the end of the lecture the students should be able to: 1- Identify the bones of the thoracic cage. 2- Identify superficial soft tissues. 3- Identify the trachea and lunge fields. 4- Describe the mediastinum and the cardiac shadows. 5- Brief knowledge about Bronchography. 6- Brief knowledge about Coronary Angiography. Radiography Different views of the chest can be obtained by changing the relative orientation of the body and the direction of the x-ray beams. The most common views are: Posteroanterior(PA), Anteroposterior (AP), Lateral . Radiography A chest x-ray may be used to diagnose and plan treatment for various conditions, including: Fractures of the bones in the chest, including ribs, sternum, clavicle, scapula and vertebrae. Lung disorders such as pneumonia, emphysema, pleural effusion, tuberculosis and lung cancer. Heart disorders such as congestive heart failure (which causes the heart to enlarge). Chest radiographs are also used to screen for job-related lung diseases in industries such as mining where workers are exposed to dust, (asbestosis). Chest x-ray is also requested as preemployment demand. Posteroanterior radiograph For Posteroanterior radiograph the following systems must be examined in order. Superficial soft tissues; the nipples in both sexes and the breast in female are seen superimposed on the lung fields. Posteroanterior radiograph (Bones) Bones of the thoracic cage (anterior ribs, posterior ribs). Thoracic vertebrae. Cost-transverse joints. Clavicles. Medial border of the scapula. Posteroanterior radiograph (Diaphragm) The diaphragm appears as a domeshaped shadow on each side; the right side is slightly higher than the left. Beneath the right dome is the homogeneous, dense shadow of the liver. Beneath the left dome a gas bubble mostly seen in the fundus of the stomach. Posteroanterior radiograph (Diaphragm) Note the costophrenic angle, where the diaphragm meets the thoracic wall. The angle becomes blunt or obscured due to pleural fluid (effusion) or fibrosis. Posteroanterior radiograph (Trachea) The radio-translucent, air-filled shadow of the trachea is seen in the midline of the neck as a dark area. This is superimposed by the lower cervical and upper thoracic vertebrae. Posteroanterior radiograph (Lungs) Lung roots: relatively dense shadows caused by the presence of the bloodfilled pulmonary and bronchial vessels, the large bronchi, and the lymph nodes. Lower margin of left hilum is at the level of upper margin of right hilum. Posteroanterior radiograph (Lungs) The lung fields, by the air so they are more translucent on full inspiration than on expiration. The pulmonary blood vessels are seen as a series of small, rounded, white shadows radiating from the lung root. The large bronchi, are seen as similar round shadows. The smaller bronchi are not seen. Posteroanterior radiograph (Mediastinum) The right border of the mediastinum; consists of: Right brachiocephalic vein, Superior vena cava, Right atrium, and Inferior vena cava. Posteroanterior radiograph (Mediastinum) The left border of mediastinum consists of: Aortic knuckle, knob (aortic arch), Pulmonary trunk, Left auricle, Left ventricle. Posteroanterior radiograph (Mediastinum) The transverse diameter of the heart should not exceed half the width of thoracic cage. On deep inspiration, when the diaphragm descends, the vertical length of the heart increases and the transverse diameter is narrowed. Bronchography and contrast visualization of the esophagus Bronchography; It is special study of the bronchial tree by introduction of contrast medium into a particular bronchus. Bronchography and contrast visualization of the esophagus Contrast visualization of the esophagus by swallow a contrast media, (barium swallow). Identification of the aortic arch and left bronchus. Identification of enlargement of left atrium. Coronary Angiography The coronary arteries are visualized by introduction of radio-opaque material into their lumen. Pathological narrowing or blockage of coronary artery can be identified.




















![6-Radiological_Anatomy_of_Thorax_(2)[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008603136_1-f3acf9a4bea61d2932dd681364a44dc8-150x150.png)
![06 Radiological_Anatomy_of_Thorax_(2)[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000576414_1-742a4dc499e0753b1c920d47b2cac2b5-150x150.png)
![06 Radiological_Anatomy_of_Thorax_(2)[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000414327_1-04da754cadb08122653c700a0fc76def-150x150.png)