* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download World War II (1939
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Fascism in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
American Theater (World War II) wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
European theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
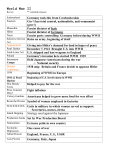
World War II 1939-1945 Vocabulary Fascism-a political philosophy that supports a strong central government, controlled by the military and led by a powerful dictator. Communist- a system of social organization in which all economic and social activity is controlled by a totalitarian state dominated by a single and selfperpetuating political party. (does away with social classes) Nazi- claimed German nation represented most racially pure people. Jewish nation was greatest threat to German race. World War I Leads to World War II? The Treaty of Versailles helped lead to the start of WWII. Humiliated the Germans Kept the nation from rebuilding itself and move forward economically In 1933 Adolf Hitler becomes Germany’s Nazi leader. In 1935 Germany ceased to recognize the Treaty of Versailles. Start of WWII Start of WWII-September 1, 1939, Nazi Germany invades Poland. Hitler (Germany) was trying to take back land they lost to Poland after WWI. France and Great Britain declare war on Germany on September 3, 1939. Italy joined the war in 1940 to support Germany. Japan Joins the War Japan was severely affected by the Great Depression. They relied heavily on imported resources and needed more land for their growing population. They saw expansion as the best solution. Japan began to occupy parts of China and they officially went to war in 1937. Japan signed an alliance in 1940 with Germany and Italy. Pearl Harbor The U.S. disapproved Japan’s actions and placed a heavy trade embargo on Japan. This restricted its ability to import oil, scrap metal, and other vital resources to its war effort. This angered the Japanese officials…. Pearl Harbor …Who then launched a surprise attack on Pearl Harbor in retaliation for the embargos. December 7, 1941 More than 3,400 people died or suffered wounds in the attack. The attack brought the U.S. into World War II. Pearl Harbor (Dec. 7, 1941) Pearl Harbor (Dec. 7, 1941) Allied Powers U.S., Great Britain, France, Russia, and China Axis Powers Germany, Italy, and Japan Adolf Hitler Nazi dictator of Germany who committed suicide at the end of the war. Blamed the Jewish people for Germany’s financial difficulties. Tried to eliminate (genocide) the Jews as part of his Final Solution plan. Benito Mussolini Fascist dictator of Italy. Was captured and executed in April 1945. Hideki Tojo Prime Minister of Japan who ordered to go to war and attack Pearl Harbor. Was executed for his responsibility to Japan’s war crimes. Joseph Stalin Communist dictator of Russia (U.S.S.R./Soviet Union) Started on the side of Germany, but switched sides when the Germans began to occupy parts of Russia. Totalitarianism Nazi Germany, Fascist Italy, and Communist Russia are all totalitarian governments. Adolf Hitler and Benito Mussolini both led fascist states. Franklin Delano Roosevelt (FDR) President of the U.S. during WWII. Wanted to stay neutral in the beginning. D-Day Turning point of war. Marked the beginning of the Allied invasion of western Europe. The Allies invaded German occupied France on June 6, 1944, along the beaches of Normandy, France. D-Day D-Day Nuclear Warfare The U.S. uses new technology to drop two nuclear bombs in Japan. Hiroshima The first nuclear bomb “Little Boy” was dropped on August 6, 1945, on the city of Hiroshima in Japan. Killed over 100,000 people over a few months. Atomic Bomb Nagasaki U.S. dropped the second nuclear bomb “Fat Man” on the city of Nagasaki in Japan on August 9, 1945. Killed between 60,000-80,000. Japan surrendered 6 day later to the Allies. Complete Devastation… Before and After Atomic Bomb Video http://video.google.com/videoplay?docid= -6974472576991137411# WWII Over Ended on September 2, 1945, with Japan signing surrender on the U.S.S. Missouri in Tokyo Bay. Over 22-25 million soldiers killed. Between 60-70 million people killed during WWII. Division of Eastern and Western Europe There was a division of Eastern and Western Europe after WWII, known as the “Iron Curtain”. The Berlin Wall is an example of that division. United Nations Created after WWII to maintain peace and prevent future wars. The United Nations is a means to solve international problems.