* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download World War II
Military history of Greece during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Pursuit of Nazi collaborators wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Operation Bodyguard wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Collaboration with the Axis Powers wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the Battle of France wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Invasion of Normandy wikipedia , lookup
German evacuation from Central and Eastern Europe wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Écouché in the Second World War wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
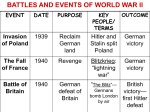
World War II Europe Allies Fight Back • U.S. entrance into WWII – Turned tide of war in Battle of Atlantic • Delivery of supplies = key! • German U-Boats – “wolf pack” dangerous subs countered by U.S. convoy system • Enigma – German code broken by Enigma machine in 1941 – Advanced knowledge of German movements Soviet Union • Hitler invaded in 1941 – Soviets used winter to advantage • Stalingrad (1942) – Soviets refuse to fall > counterattack – Defeated Germans in 1943 – *Marked beginning of German collapse in Soviet Union – Germans lost 2 million vs. Soviets 12 million North Africa • Prime oil territory > conflict between Britain & Italy – Britain defeats Italy & gains access to Suez Canal • General Erwin Rommel – “Desert Fox” – brilliant German general – Lost Battle of El Alamein to Britain Operation Torch • Operation Torch – U.S. efforts in Africa • General Dwight D. Eisenhower – Led U.S. attack – *U.S. gained valuable combat experience – Helped in German defeat Axis Powers Collapse • 1943 U.S. invades Italy • FDR & Churchill – “… die for Mussolini & Hitler or live for Italy” • Tuskegee Airmen – Aid in U.S. victory – Approximately 300,000 killed or wounded D-Day • June 6, 1944 • Operation Overlord – Allied invasion of France (5 beaches) – U.S., British & Canadian troops attack from sea, air & land – German response slow – High casualty rates but Allied victory – *General Eisenhower became Supreme Allied Commander after victory Battle of the Bulge • Battle of the Bulge (Dec. 16, 1944) – *Last major German offensive – Gen. George Patton provided relief for American forces – Allied victory The Holocaust • Kristallnacht – Night of Broken Glass – *1st open attack on Jews • 3 stages – Jews cannot live as Germans – Jews cannot live with Germans – Jews cannot live U.S. Response to the Holocaust • Limited immigration of Jews by U.S. & other Western countries • War Refugee Board 1944 – Too little too late? – Lacked money & authority • Nuremberg Trials – 22 Nazis tried for war crimes Yalta Conference • Yalta Conference (Jan. 1945) – Big 3 meet (Stalin, Churchill & Roosevelt) – agree to “occupy” Germany once war ends by dividing the country into 4 sectors – Also agree to elections in Eastern European countries – Stalin agrees to help in war on Japan 3 months after Germany defeated • Why is this an issue? Victory in Europe (V-E Day) • V-E Day (Victory in Europe) – Hitler finally recognized the end & committed suicide April 1945 – News of Hitler’s death spread & fighting slowly stopped – surrender of Germany took effect on May 8, 1945 – Proclaimed V-E (Victory in Europe) Day