* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 18
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
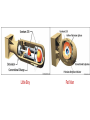
• Japan’s attack on China caused US alarm as to trade status – Open Door Policy • Japan declared policy obsolete • US retaliated by loaning money to China and asking US munitions makers not to sell to Japan • Sep 1940 – US stopped sale of scrap iron to Japan – Japan retaliated by signing alliance with Germany and Italy • FDR extended embargo to machine tools • Neither Japan nor US wanted war – US made demands Japan refused to meet concerning expansion in Asia • Japanese code broken – US knew attack imminent • Surprise attack knocked US Pacific fleet out of action • 2,300 killed 1,100 wounded • Admiral Kimmel and General Short blamed • Defeat due to confusion and poor communication at all levels • Though Democrats retained majorities in both houses, conservatives kept lid on many of FDR’s initiatives • Roosevelt good war leader but poor administrator – inspired the nation towards war effort but administration mired in confusion, inefficiency, bickering • War caused huge increase in production effectively ending the Depression • The South saw a revival with more manufacturing also establishment of many military camps • By December 1941, Depressionera administrations squabbling with industry over resources, etc. FDR refused to get involved • By 1943 economy was being managed by Office of War Mobilization under former Supreme Court Justice Byrnes • Rents, wages, food prices were strictly regulated • Important food and other items were rationed • Labor shortages caused by draft and increased manufacturing gave unions more power • FDR created National War Labor Board to arbitrate disputes between labor and management • Coal strike caused Congress to give president power to take over any war plant threatened by a strike • Despite war, average citizen saw no drop in standard of living • Production of cars ceased and gas severely rationed but all other civilian activities went on • Meat, sugar, shoes rationed but average needs met • Skirts shortened, cuffs disappeared, as did vests to conserve cloth • Silk stockings no longer available • Federal government spent more $ between 1941-1945 than in its entire previous history • National debt rose from <$49 billion to >$260 billion • More than 40% of expenditures met through taxation – high taxes on high incomes • Annual incomes limited to $25,000 • Taxes paid even by the poorest segments of society • First time taxes withheld by employers • Tax policies resulted in smaller wealth gap • Migrations to new industrial areas • Population of California rose >50 % • Marriage and birth rates increased • Population increased 3 million during 1930’s – in next five years it rose 6.5 million • Blacks treated better in military than in WWI • Segregation still maintained in all services • Segregation led to several small riots and mutinies • US Navy continued to keep blacks in demeaning non-combat tasks • Doris “Dorie” Miller • Black economic situation improved More employed Migration to Northern cities Acquired more advanced skills Concentration in ghettos increased political clout • NAACP adopted a more militant stance • Whites reacted to black advancements with strikes – riots erupted killing blacks and whites • Thousands of Mexicans came north to take jobs • Bracero Program – migrant agricultural work • Work plentiful and standards of living rose • Many Mexican-Americans served in military • Zoot Suit Riots Who's that whisperin' in the trees? It's two sailors and they're on leave Pipes and chains and swingin' hands Who's your daddy, yes I am Fat cat came to play now he can't run fast enough You had best stay away when the pushers come to shove Zoot suit riot, (Riot) Throw back a bottle of beer Zoot suit riot (Riot) Pull a comb through your coal black hair Zoot suit riot, (Riot) Throw back a bottle of beer Zoot suit riot (Riot) Pull a comb through your coal black hair Blow Daddy A whipped up jitterbuggin' brown eyed man A stray cat frontin' up an eight-piece band Cut me Sammy and you'll understand In my veins hot music ran You got me in a sway, and I want to swing you done Now you sailors know, where your women come for love Zoot suit riot, (Riot) Throw back a bottle of beer Zoot suit riot (Riot) Pull a comb through your coal black hair Zoot suit riot, (Riot) Throw back a bottle of beer Zoot suit riot (Riot) Pull a comb through your coal black hair You're in a Zoot Suit riot Zoot zy-ow - Zoot za zoo zay Hey al-oo-ay-en - zay zay zay Zoot zy-ay-ay ow - Zoot za zoo zay Ze-zoo-ze-zehoo - day de day You got me in a sway, and I want to swing you done Now you sailors know, where your women come for love Zoot suit riot, (Riot) Throw back a bottle of beer Zoot suit riot (Riot) Pull a comb through your coal black hair Zoot suit riot, (Riot) Throw back a bottle of beer Zoot suit riot (Riot) Pull a comb through your coal black hair You're in a zoot suit riot • Indian assimilation was encouraged - >24,000 served in the war while others moved to cities and worked in factories • Windtalkers- Navajo tribe used as radio operators as Navajo was unwritten language • Pearl Harbor caused fear of Japanese sabotage • Executive Order 9066 Japanese to be interned in camps throughout the West • Korematsu v. The United States • 442nd Regimental Combat Team • Women worked in almost all fields including high-paying industrial jobs • Others enlisted in women military auxiliaries • Men initially resistant – “women not capable” • Demand for labor broke all barriers • Loneliness brought on infidelity and divorce rates skyrocketed Rosie the Riveter • Allies decided to tackle Europe first • USSR and Britain had backs to wall • Allied planes began bombing German cities from 1942 on • First American assault on North Africa Churchill’s motives Vichy French – Admiral Darlan Kasserine Pass • Attack on Sicily • Attack on Italy Surrender of Italy Stalemate at Monte Cassino Invasion at Anzio Mussolini killed by Italian partisans D-Day 6 June 1944 Invasion of Western Europe • Patton’s drive east • Operation Market-Garden Airborne assaults on bridges – cross Rhine River • Battle of the Bulge Last-gasp attempt by Hitler to stop Allied advance in West • • • • • Bridge at Remagen Race to Berlin Concentration camps May – VE Day Deaths of Roosevelt & Hitler Scissors beats paper every time! Every individual flag equals 100,000 soldiers dead Every individual skull equals 100,000 dead civilians Every individual Star of David equals 100,000 dead Jews • Battle of the Coral Sea – carrier battle – peak of Japanese expansion • Battle of Midway – Japan goes on defense • General Douglas MacArthur • Island Hopping Guadalcanal Tarawa, Saipan, Guam Philippines • • • • Kamikazes Battle of Leyte Gulf Iwo Jima and Okinawa Invasion of the Japanese home islands? Hell in the Pacific Parts I and II • The Manhattan Project Multi-national effort under US leadership Director - J. Robert Oppenheimer • Russian declaration of war against Japan 8 August 1945 • VJ-Day – 15 August The Atomic Bomb • Little Boy Uranium core Gun method Dropped on Hiroshima 6August 1945 • Fat Man Plutonium core Implosion method Dropped on Nagasaki 9 August 1945 Little Boy Fat Man • Debate Was the use of nuclear weapons against Japan necessary and/or ethical? Did nuclear weapons force the surrender of Japan? Was an invasion of Japan necessary to win the war? • US pushed image of Russia (USSR) as a friend during war • Russia appeared to back US plans for post-WWII world including UN • Russia: seeking domination or security? • Yalta US agreed to Russian annexation of Poland in return for free elections Discussed partition of Germany Agreed to establishment of UN • Potsdam Allies agreed on war crimes trials Confirmed division of Germany into occupied zones Called on surrender of Japan • The General Assembly • The Security Council (Permanent Members) US, Great Britain, USSR, France, China Veto