* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Masses of Atoms
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
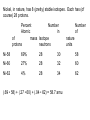
Masses of Atoms Pages 550 - 553 Element ~ matter that is unique from all others, because of different numbers of protons. Element ~ matter that is unique from all others, because of different numbers of protons. Symbol ~ unique letter to represent element Element ~ matter that is unique from all others, because of different numbers of protons. Symbol ~ unique letter to represent element Atomic Number ~ number of protons in the atom of an element Element ~ smallest particle that is unique from all others Symbol ~ unique letter to represent element Atomic Number ~ number of protons in the atom of an element Carbon - 12 (6 protons, 6 neutrons) Carbon - 14 (6 protons, 8 neutrons) Element ~ matter that is unique from all others, because of different numbers of protons. Symbol ~ unique letter to represent element Atomic Number ~ number of protons in the atom of an element Atomic Mass ~ number of neutrons AND number of protons Isotope ~ atoms of the same element, with different numbers of neutrons Element ~ smallest particle that is unique from all others Symbol ~ unique letter to represent element Atomic Number ~ number of protons in the atom of an element Atomic Mass ~ number of neutrons AND number of protons Isotope ~ atoms of the same element, with different numbers of neutrons Carbon - 12 (6 protons, 6 neutrons) Carbon - 14 (6 protons, 8 neutrons) SAME ELEMENT, DIFFERENT NEUTRON NUMBERS Element ~ matter that is unique from all others, because of different numbers of protons. Symbol ~ unique letter to represent element Atomic Number ~ number of protons in the atom of an element Atomic Mass ~ number of neutrons AND number of protons Isotope ~ atoms of the same element, with different numbers of neutrons Atomic Mass Unit ~ 1/12th of the mass of one carbon-12 atom Element ~ matter that is unique from all others, because of different numbers of protons. Symbol ~ unique letter to represent element Atomic Number ~ number of protons in the atom of an element Atomic Mass ~ number of neutrons AND number of protons Isotope ~ atoms of the same element, with different numbers of neutrons Atomic Mass Unit ~ 1/12th of the mass of one carbon-12 atom The periodic table shows the atomic mass of Nickel as 58.693. How can there be a decimal point, if the mass is whole numbers of protons and neutrons? Element ~ smallest particle that is unique from all others Symbol ~ unique letter to represent element Atomic Number ~ number of protons in the atom of an element Atomic Mass ~ number of neutrons AND number of protons Isotope ~ atoms of the same element, with different numbers of neutrons Atomic Mass Unit ~ 1/12th of the mass of one carbon-12 atom The periodic table shows the atomic mass of Nickel as 58.693. How can there be a decimal point, if the mass is whole numbers of protons and neutrons? Example, with boron. Facts: Boron has an accepted amu of 10.811 80% of Boron in nature have 5 protons, 6 neutrons ~ 11 amu 20% of Boron in nature have 5 protons, 5 neutrons ~ 10 amu (.8 • 11 amu) + (.2 • 10 amu) = 8.8 amu + 2 amu = 10.8 amu There are a few extra isotopes out there that we did not include. Nickel, in nature, has 8 (pretty) stable isotopes. Each has (of course) 28 protons. Percent Number Atomic in of mass Isotope protons neutrons Number of nature units Ni-58 69% 28 30 58 Ni-60 27% 28 32 60 Ni-62 4% 28 34 62 What, given this information, is the approximate atomic mass of Nickel? Nickel, in nature, has 8 (pretty) stable isotopes. Each has (of course) 28 protons. Percent Number Atomic in of mass Isotope protons neutrons Number of nature units Ni-58 69% 28 30 58 Ni-60 27% 28 32 60 Ni-62 4% 28 34 62 (.69 • 58) + (.27 • 60) + (.04 • 62) = 58.7 amu