* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download IPC Atoms and Periodic Table
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
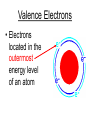
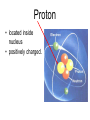
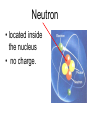
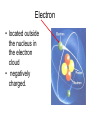
Atoms The smallest particle of an element. Valence Electrons • Electrons located in the outermost energy level of an atom Proton • located inside nucleus • positively charged. Neutron • located inside the nucleus • no charge. Electron • located outside the nucleus in the electron cloud • negatively charged. Energy Levels / Shells • The space an electron occupies in the electron cloud • Determined by the amount of energy the electron contains • Less energy = lower level • More energy= higher level. Groups Elements in the same vertical (up and down) column of the periodic table; also called a family. Periods A horizontal row (side-to-side) of elements in the periodic table. Alkali Metals Elements with only one electron in the outermost energy level of their atoms; located in Group 1 on the Periodic Table; not stable and tend to lose their one electron easily. Alkaline Earth Metals • Elements in group/family 2. • Form positive ions • 2 valence electrons Transition Metal • any element in any of the series of elements with atomic numbers 21–29, 39– 47, 57–79, and 89– 107, that in a given inner orbital has less than a full quota of electrons Halogens Elements that have seven valence electrons in their atoms; need one additional electron to have a filled outer energy level; tend to gain one electron from other elements; not stable. Noble Gas The elements located I the far right column of the Group 18; their outermost energy level is holding the maximum number of electrons possible; stable. Metalloid/Semiconductor • an element that has both metallic and nonmetallic properties, as arsenic, silicon, or boron. Lanthanide Series • Fifteen elements that start with lanthanum (La) at atomic number 57 and finishing up with lutetium (Lu) at number 71. Actinide Series • Fifteen elements that start with actinium (Ac) at atomic number 89 and finishing up with lawrencium (Lr) at number 103. • They are all radioactive and some are not found in nature. Metals An element that easily gives up its valence electron in a chemical reaction and that be classified based on physical properties such as hardness, shininess, ease of malleability, and ductility. Nonmetal An element that lacks most of the properties of metals. Ions An atom that has an electrical charge because it no longer has an equal number of protons and electrons. Isotope • any of two or more forms of a chemical element, having the same number of protons in the nucleus, or the same atomic number, but having different numbers of neutrons in the nucleus, or different atomic weights. Atomic Number • Number of protons in an element • Also the number of electrons in a stable element. Mass Number • Number of atomic particles in the nucleus of an atom • Protons + neutrons = mass number • Also referred to as atomic mass. Average Atomic Mass • the weighted average of the atomic masses of the naturally occurring isotopes of an element • Reported as atomic mass on the periodic table. Element A substance that cannot be broken down into any other substances by chemical or physical means. Malleability • The ability of an element to be hammered into thin sheets. Ductility • Ability of an element to be pulled into wire.