* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Where is the Electron Located?
Bell's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Orchestrated objective reduction wikipedia , lookup
Quantum machine learning wikipedia , lookup
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
Interpretations of quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Quantum key distribution wikipedia , lookup
Bohr–Einstein debates wikipedia , lookup
Quantum teleportation wikipedia , lookup
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
Quantum group wikipedia , lookup
Ferromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Canonical quantization wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Spin (physics) wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
Hidden variable theory wikipedia , lookup
Particle in a box wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Quantum state wikipedia , lookup
Tight binding wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
EPR paradox wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
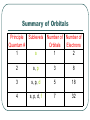
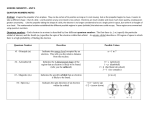
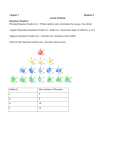
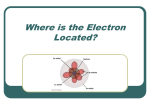
Where is the Electron Located? The Quantum Model of the Atom Heisenberg uncertainty principle: It is impossible to determine both the position and velocity of an electron or any other particle What is the Address of the Electron? Principle Quantum Number (n): Indicates the energy level occupied by an electron. Angular Momentum (l): Indicates the shape of the orbital (s,p,d,f,g) Atomic Numbers and Quantum Numbers Magnetic Quantum Number (m): Indicates the orientation of an orbital around the nucleus. Spin Quantum Number (↓↑): Indicates which way the electron is spinning What are the Rules Governing Electron Configuration? Aufbau Principle: An electron occupies the lowest energy orbital available Pauli Exclusion Principle: Only two electrons per orbital and they must spin in opposite directions Hund’s Rule: Each orbital of equal energy must have one electron before a second electron is added Let’s Fill Up The Orbitals! Summary of Orbitals Principle Sublevels Quantum # 1 s Number of Number of Orbitals Electrons 1 2 2 s, p 3 8 3 s, p, d 5 18 4 s, p, d, f 7 32 Predicting the 1s Orbital Exceptions to Aufbau