* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SEPARATION OF MATTER - Los Angeles City College
Organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Photopolymer wikipedia , lookup
Chemical potential wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Ceramic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Inorganic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical element wikipedia , lookup
Electronegativity wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Computational chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Periodic table wikipedia , lookup
Metallic bonding wikipedia , lookup
Extended periodic table wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
Safety data sheet wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
Atomic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
Condensed matter physics wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
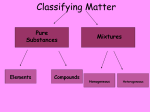
SEPARATION OF MATTER • Matter is separated into three states: SOLID, THE ATOMIC - LIQUID, & GAS. MOLECULAR THEORY OF • Matter can also be broken down into distinct MATTER materials, each category representing a specific type of material. A flow chart will show the linking of these types of materials. The Atomic-Molecular Theory of Matter • Physical properties: characteristics of a material which may be determined without altering the composition of the material; bp (boiling point), mp, color, density etc., no change in the chemical identity occurs. • Chemical properties: characteristics of a material which involves altering the composition of the material, the ability to form new substances by decomposition or reactions with other substances. A rearrangement of the atoms. • Phase: a sample of matter that is uniform throughout, both in its chemical composition and its physical state. • Chemical Bonds: the attractive forces, “ the glue”, strong enough to maintain a group of atoms together for an indefinite amount of time. Physical Changes: The substance or mixture does not alter in atomic composition. Some Physical Changes are boiling, evaporation, condensation, freezing, melting, sublimation, and deposition. Associated with Physical Changes are Physical Properties like boiling or freezing point, density, hardness, and state of matter. H2O (l) H2O (g) Chemical Changes: The substance changes in its atomic composition, the atoms are rearranged and new substances are formed. 2 H2O (l) 2 H2 (g) + O2 (g) The Atomic-Molecular Theory of Matter THE MOLECULAR THEORY OF MATTER Separated by physical methods MATTER HOMOGENEOUS MIXTURE (Solution) HETEROGENEOUS MIXTURE Separated by physical methods PURE SUBSTANCE COMPOUNDS ELEMENTS Separated by chemical methods Separated by physical methods The Atomic-Molecular Theory of Matter *definitions* • Matter : occupies space and has weight. • Energy : the ability to do work • Materials: a particular type of matter, generic term. • Mixture: has variable composition, can be separated by physical methods. • Heterogeneous mixture: has properties which vary from region to region, can be separated into a homogeneous mixture or a substance. • Homogeneous mixture: uniform properties throughout, also called a solution. Can be separated into substances. The Atomic-Molecular Theory of Matter • (Pure) substance: a material which can not be separated by physical methods into 2 or more materials which have different characteristics. • Compounds: a material containing two or more elements or molecules. • Molecules: the smallest grouping which a substance can be divided into without forming a new substance, a group of 2 or more atoms held together by strong forces called "bonds". • Atoms: the smallest particle of matter which has distinctive chemical characteristics, generic term, composed of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. • Elements: a specific substance which can not be decomposed into simpler substances by chemical means, an atom with a specific number of protons, neutrons, and electrons. The Atomic-Molecular Theory of Matter A “microscopic” view The Atomic-Molecular Theory of Matter THE ATOMIC THEORY OF MATTER ATOMS ELEMENTS NUCLEUS ELECTRONS (negative particle) - PROTONS NEUTRONS (positive particles) (neutral particles) + The Atomic-Molecular Theory of Matter • Nucleus: the small positively charged kernel, composed of protons and neutrons. • Protons: a positively charged particle, has a mass = 1.67 x 10-27 kg or 1 amu (atomic mass unit) usually symbolized as H+ or p+. • Neutrons: neutral particles with the same mass as the proton, contributes weight but no charge. • Electrons: a negatively charged particle, has a mass = 9.1 x 10-31 kg (1/1837 amu) usually symbolized as e-. may come in one of three forms: Periodic Table of the Elements Alkali H Alkalin e-earth Inert Chalogen Representative Elements Li Be metalliod Na Mg Transition Metals nonmetal K Ca Sc Ti V Rb Sr Y Zr Nb Mo Tc Cs Ba La - Lu Hf Ta Fr Ra Ac - Lr Rf Db Sg Bh Hs W Ni C N O F Ne Al Si P S Cl Ar Cu Zn Ga Ge As Se Br Kr Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd Re Os Ir Pt He B metal Cr Mn Fe Co Halogen Au Hg Mt Uun Uuu Uub In Sn Sb Te I Xe Tl Pb At Rn Bi Po THE PERIODIC TABLE Metals Nonmetals • Located on the left side of the periodic table • Tends to lose electrons to form cations • Has low ionization energies & electronegativity values • Forms compounds with nonmetals but not other metals • Good conduction of heat and electricity • Lustrous & malleable solids excepts Hg which is a liquid • Ductile • Located on the right side of the periodic table • Tends to gain electrons to form anions • Has high ionization energies & electronegativity values • Forms compounds with both metals and nonmetals • Poor conduction of heat and electricity • Non-lustrous & brittle or gaseous • Non-ductile IONS “a charged atom” The number of protons do NOT equal the number of electrons. Cations: positively charged ions formed when electrons are lost. Na+ Anions: negatively charged ions formed when electrons are gained. Cl- COMPOUNDS MOLECULES Composed of two or more nonmetals IONIC SALTS Composed of a metal & a nonmetal MOLECULE Ionic Salt Reading Chemical Formulas BaCO3 (NH4)3PO4 CuSO4•5H2O CH3COOH CuCO3•Cu(OH)2 •Chemical structure: the position and geometry of the atoms in a molecule. ANALYSIS OF MATTER MATTER Is it uniform? YES NO HOMOGENEOUS MIXTURE HETEROGENEOUS MIXTURE blood, soil Can it be separated by physical methods? YES NO HOMOGENEOUS MIXTURE saltwater, rubbing alcohol PURE SUBSTANCE Can it be decomposed into simpler substances using chemical methods? YES COMPOUND water NO ELEMENT carbon PRACTICE PROBLEMS #4 1. Classify the following as an element, compound, or mixture (heterogeneous or homogeneous). E HO • _____ air _____ oxygen E C • _____ tin can _____ sugar HE HO Windex • _____ _____ crude oil HE HO gummi bear • _____ suntan lotion _____ 2. A white solid is dissolved in water. The resulting colorless, clear liquid is boiled in a beaker until dryness. White crystals remain in the beaker. Homogeneous mixture The liquid can be classified as a(n) ______________. 3. Classify the following as physical or chemical changes. CC CC • _____ photosynthesis _____ baking PC writing with pencil PC • _____ _____ snowing GROUP STUDY PROBLEM #4 1. Classify the following as an element, compound, or mixture (heterogeneous or homogeneous). • _____ wine _____ root beer • _____ penny _____ table salt • _____ Bleach _____ wood • _____ diamond _____ vinegar 2. A clear blue liquid in an open beaker was left in the hood. After 1 week, the beaker contained only blue crystals. The original liquid can be classified as a(n) ______________. 3. Classify the following as physical or chemical changes. • _____ perspiration _____ sugar dissolving • _____ fermentation _____ aging