* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Causes of Diseases
Survey
Document related concepts
Rocky Mountain spotted fever wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Brucellosis wikipedia , lookup
Meningococcal disease wikipedia , lookup
Bioterrorism wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Chagas disease wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Leishmaniasis wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Cross-species transmission wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Visceral leishmaniasis wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
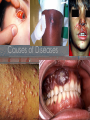
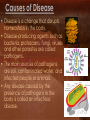
Causes of Diseases Causes of Disease • Disease is a change that disrupts homeostasis in the body. • Disease-producing agents such as bacteria, protozoans, fungi, viruses and other parasites are called pathogens. • The main sources of pathogens are soil, contaminated water, and infected people or animals. • Any disease caused by the presence of pathogens in the body is called an infectious disease. Live Worm In patient’s eye Causes of Disease • One-half of all human diseases are infectious. • Not all diseases are caused by pathogens. 1. inherited disease: sickle cell anemia 2. body aging (wear and tear): osteoarthritis • Pathogens can be transmitted in 4 main ways: 1. direct contact: STD’s and influenza 2. by an object: food poisoning 3. through the air: sneezing 4. intermediate organisms (vectors): malaria (spread by mosquitoes) Causes of Disease • Endemic diseases: diseases that are constantly present in a population like a cold. • Epidemic: occurs when many people in a given area are afflicted with the same disease in a short period of time. (polio in the 1950’s) • Carriers are people who harbor a disease without showing any signs, yet they can pass the disease on to others. Procedure to establish cause of disease Koch’s postulates: 1. pathogen must be found in host 2. pathogen must be isolated and grown in a pure culture 3. pathogen from the pure culture is placed in a healthy host (ex: rat) 4. pathogen must then be isolated from the new host and be shown to be the original pathogen Procedure to establish cause of disease Exceptions to Koch’s postulates: 1. some organisms have never successfully grown in an artificial medium (syphilis and leprosy) 2. viral pathogens cannot be cultured using this method Interesting Fact When you sneeze, all bodily functions stop, even your heart.