* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AH LIVER & GALLBLADDER
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
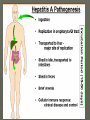
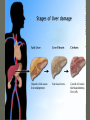
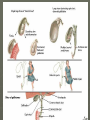
LIVER & GALLBLADDER DISEASES AND DISORDERS JAUNDICE ► PHYSIOLOGICAL CHANGES – Yellowness of skin and sclera Destruction of RBC - HAEMOLYTIC Defective uptake or transport of bilirubin HEPATOCELLULAR Obstruction in bile duct passage OBSTRUCTIVE MAJOR CAUSES ► INFECTIVE – HEPATITIS A, B, C, E ► CIRRHOSIS ► TUMORS ► VASCULAR OBSTRUCTION ► POISONING ► ABCESS – PARASITES ► HEREDITARY DISEASES SYMPTOMSanorexia fatigue non-specific abdominal pain ► ACUTE Fever Nausea, vomiting Diarrhoea Jaundice Bleeding Hepatomegaly Rt hypochondria tenderness ► CHRONIC Portal HT – O varices, piles, ascites, splenomegaly Hepatomegaly – immune deficiencies Palmar erythema Dupuytren’s contracture Spider naevi Major Remedies ► Nux vom – a/f over indulgence ► Bry – great nausea and heaviness with splitting headache ► Podo – vomitting of bile, constipation and light stools ► Merc sol – simple, pain in liver, <lying on rt ► Chel – yellow stools, pain under rt scapula ► China – congested liver and white stools ► Crot h – from blood disorganisation HEPATITIS ► INFECTIOUS VIRUS – A TO G , CYTOMEGALOVIRUS, YELLOW FEVER, EPSTEIN-BARR PARASITES ► NON- INFECTIOUS DRUGS TOXINS AUTO-IMMUNE REACTIONS ALCOHOLIC Infectious Hepatitis ► A, E, F, - ingestion of contaminated food or water ► Usually acute ► E - severe ► B, C, D, G – Transmitted by blood or bodily fluids, sexual contact or exposure to contaminated blood. ► D only occurs in association with B ► B,C,D – lead to chronic Hepatitis Hepatitis symptoms ► Flu like symptoms - nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, less commonly, rash and joint pain. ► Jaundice ► The acute symptomatic phase of viral hepatitis lasts from a few days to many weeks; the period of jaundice that may follow can persist from one to three weeks. ► Complications of acute viral hepatitis include fulminant hepatitis & chronic hepatitis Hepatitis B ► Severe and long lasting ► 40 days to 6 months after exposure ► RISK –IV drug users, sexual partners of infected people, unprotected healthcare workers, organ transplants, blood transfusions ► 100 times more likely to develop liver cancer Major Remedies ► Chelidonium – all liver diseases with pale stools, pain under right scapula, >hot drinks ► China – all liver disorders with fevers, weakness, <touch >hard pressure ► Bryonia - <touch >lying painful side ► Merc sol - <lying painful side, offensive perspiration CIRRHOSIS ► Irreversible change resulting in degeneration of functional liver cells and their replacement with fibrous connecting tissue – scarring of liver tissue ► Excessive and chronic alcohol abuse – common cause ► Early stages – can be stabilised by abstaining from alcohol + good diet Pathology ► Early stages – enlarging – outer capsule smooth and stretched Becomes more yellow, fibrous tissue and more bile ducts form ► Enlarged/ tissue Granular stage with more fibrous Blood vessels thicken and obstruct channels ► Advanced stage Shrinking with loss of lobes and rough Cirrhosis ► Other causes – Hep B or C infection, Cystic fibrosis, Auto-immune disorders, ► Heamochromotosis – inc Fe absorption and deposition in liver ► Wilson’s – inc Copper, making liver green ► COMPLICATIONS – portal venous pressure – haemorrhages, hepatic coma, jaundice, oedema, ascites. Major Remedies ► Phos ► Ars iod ► China ► Aur mur ► Hydrocot (from Clarke’s Prescriber) LIVER CANCER ► PRIMARY OR SECONDARY SPREAD ► RISK – chronic liver infection, cirrhosis, aflatoxins, males, family history, old age ► Symptoms – Pain Rt side abdomen extending to back/ shoulder, Swelling, Wt Loss, Anorexia, nausea & vomiting, Weakness, Yellowness (jaundice), fever, Bloating GALL STONES ► Composed of crystalline substances – Cholesterol, Bile pigments, calcium ► Common – cholesterol saturated bile with low bile salts and phospholipids. ► CHOLELITHIASIS RISKS TO GET STONED ► INFLAMMATION AND STAGNATION Liver damage Chronic GB disease Obesity Hereditary blood disorders (sickle-cell A) Ca of biliary tract Symptoms ► No clinical symptoms ► Acute inflammation – CHOLECYSTITIS ► Obstruction by stone in duct – severe pain – Biliary Colic and Cholangitis ► Recovery Pass thru spontaneously Surgical removal – stones or GB Medication to dissolve Major remedies ► Colocynth – colic >bending double ► Dios – colic >bending backwards ► Calc carb – acute & chronic ► Cardus mar (Q) – left lobe pain ► Berberis (Q) – every 15 min ► Chel (Q) – 5 drops tds after food for several weeks, Can be used with china ► China 6 – for prevention