* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Bez nadpisu - Univerzita Karlova v Praze
Survey
Document related concepts
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Drug-eluting stent wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Ventricular fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
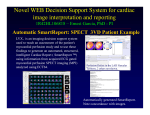
NUCLEAR CARDIAC IMAGING K.Michalová Klinika nukleární medicíny a endokrinologie UK 2. LF a FN Motol Nuclear medicine methods in Cardiology are available for the evaluation of 1. Myocardial Perfusion 2. Ventricular Function 3. Cardiac Metabolism and Myocardial Viability 4. Myocardial Innervation 5. Infarct Imaging Kupka K .a kol: Nukleární medicína, 2007 MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION SCINTIGRAPHY This test is designed to evaluate regional myocardial perfusion under rest and stress condition in order to define regional myocardial perfusion reserve. MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION SCINTIGRAPHY It involves the injecton of a radiolabelled substance which is extracted by the myocardium and accumulates in proportion to myocardial blood flow. Such radipharmaceuticals are injected under stress as well as resting conditions, and images are obtained to define the regional distribution of radioactivity within the myocardium. MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION SCINTIGRAPHY The main indication is the detection and localization of myocardial ischaemia or scar. MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION SCINTIGRAPHY Myocardial ischaemia is defined as a perfusion defect present during stress but not resting conditions. Scar tissue is associated with a relative perfusion defect at rest as well as under stress. MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION SCINTIGRAPHY RADIOPHARMACEUTICALS 201Thallium 99mTc-Labeled Myocardial Perfusion Agents 99mTc-SESTAMIBI (MIBI, 2-methoxy-isobutyl-isonitril, Cardiolite, CardioSPECT…) 99mTc-Tetrofosmin (Myoview) 99mTc-Teboroxim MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION SCINTIGRAPHY 201Thallium - is an analog of potassium - it is actively transported into cardiac muscle via the sodium-potassium ATPase pump MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION SCINTIGRAPHY 201Thallium - is a cyclotron-produced radiopharmaceutical - emits x-rays of energy 69- to 83 keV - physical half-life is 74 h MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION SCINTIGRAPHY 99mTc-SESTAMIBI x 201THALLIUM ADVANTAGES : - increased myocardial count density - lower radiation doses - no wash out of myocardium MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION SCINTIGRAPHY Tc-99m-Labeled Myocardial Perfusion Agents 99mTc-SESTAMIBI = is a lipophilic cationic Tc-99m complex - it enteres pasivelly into the cells - and binds at the intracells membranes, especially of mitochondrials - it does not wash out of the myocardium in 3-4 hours MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION SCINTIGRAPHY 99mTc-SESTAMIBI 99mTc - gamma rays of energy 140 keV - half life T1/2 = 6 hours Two-Day Patient Protocol Dose Position Exercise Rest 700 MBq 700 MBq Supine or prone Supine or prone Delay Time (Intervals) Injection - Imaging 15 min 60-90 min Exercise Stress * is performed by cardiologist * graded stress is usually performed with bicycle ergometr * it is necessary to reach the gender and age predicted 85% maximal heart rate * suboptimal stress level reduce sensitivity of this procedure for detection of CAD * the radiopharmaceutical is injected 1-2 minut before end of exercise Pharmacologic Stress Patients who are unable to exercise for non cardiac reasons - e.g.arthritis, amputation, neurologic diseases or cardiac reasons - with LBBB may be stress farmacologically Pharmacologic Stress * vasodilators : adenosine dipyridamole * inotropic : dobutamine Pharmacologic Stress using dipyridamole * mechanism of action different from exercise * directly tests flow reserve * dipyridamol causes vasodilatation * normal vessel vasodilate, increasing flow five times * stenotic vessels are already maximally vasodilatated, cannot increase flow * results in heterogenity on scan * does not depend on induction of ischemia * Heart rate increases 13 beats per minute (20%) * Blood pressure decreases 6 mm Hg (2 ti 8%) * Contraindication: Asthma bronchiale Pharmacologic Stress produced by dobutamine * similar to exercise * indirectly tests flow reserve * increases myocardial oxygen consumption 1) chronotropic effects 2) ionotropic effects Acquisition SPECT study Dual head gamma camera moves around the patient viewing the object in 180 degrees in 64 steps for 25 seconds 45 deg. RAO 135 deg. LPO GATED SPECT study • ECG is acquired at the time of the SPECT acquisition • for simultaneous assessment of perfusion and function of the left ventricle in one examination evaluation of regional wall motion ejection fraction systolic thickening of the walls GATED SPECT study We obtain myocardial perfusion images within one representative cardiac cycle : from end-diastole through end-systole to end-diastole of next cardiac cycle Kamínek M. et al. : Atlas of Nuclear Cardiology, 2003 Initial Display of selected studyReconstruction With ellipse we select region of the heart in anterior view in left lateral view. The selected data sets are processed. We must alignment axes of heart for creation of the vertical long and short axis tomograms Summed imageadded multiple projection images slices in the short axis slices in the long axis vertical slices in the long axis horisontal 99m TcMIBI MYOCARDIAL ISCHEMIA Can be identified by comparing the results of exercise-injected studies and rest images . As narrowing of coronary vessel approaches 70% lesion is hemodynamically significant during exercise. 99m-TcMIBI Polar maps Short axis slices are sequentially diplayed from base to apex. Conical myocardium is transformed into a disk. MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION IMAGING INTERPRETATION CRITERIA 1. NORMAL FINDINGS 2. REVERSIBILE DEFECT - lesion is seen at stress and improves on the rest - is usually due to ischemia 3. NONREVERSIBILE DEFECT - lesion at rest is usually associated with myocardial scar or with severe ischemia. NORMAL FINDING 57 yo MALE REVERSIBILE DEFECT NONREVERSIBILE DEFECT MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION IMAGING Clinical Indications Diagnosis of coronary artery disease - presence - location (coronary territory) -extent (number of vascular territories involved) Determine prognosis Society of Nuclear Medicine Procedure Guideline for Myocardial Perfusion Imaging MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION IMAGING Clinical Indications Determination of the significance of anatomic lesions detected by angiography MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION IMAGING Clinical Indications Monitoring treatment effect after coronary revascularization MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION IMAGING Determine prognosis risk stratification *Patients with normal perfusion imaging after adequate stress have a very low cardiac event rate independently of the presence or absence of angiographic CAD (yearly rate of myocardial infarction or death of less than 1%). *A benign prognosis is asociated with a small fixed defect and a normal global left ventricle function. 57 yo MALE MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION IMAGING Determine prognosis risk stratification * The risk of cardiac event can be suspected in all patients with the reversible perfusion defect. * A higher risk can be expected in patients with a large perfusion defect, when more territories are affected, if the anterior wall is affected or if signs of postress dysfunction appear (transient ischemic dilation, deterioration of postress EF, increased uptake 201Tl in the lungs). MYOCARDIAL VIABILITY detection of myocardial viability has clinical importance for - patients with chronic ischaemic left ventricular dysfunction and low left ventricle ejection fraction it is necessary to know, if defect of myocardial perfusion is - ischemia vs. scar - predict improvement in function following revascularization REQUIREMENTS FOR CELLULAR VIABILITY -adequate myocardial blood flow -sarcolemmal metabolic integrity -preserved metabolic activity MYOCARDIAL VIABILITY The gold standard method evaluation of myocardial glucose utilisation with fluorine-18 fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) and positron emission tomography (PET) MYOCARDIAL VIABILITY Principle Under fasting conditions the normal myocardium primarily utilises free fatty acids. In ischaemic myocardium glucose becomes an important energy substrate, FDG uptake will be enhanced. VIABLE MYOCARDIUM is characteristic in NONREVERSIBILE PERFUSION DEFECT ( 99m-Tc MIBI) vs. PRESERVED MYOCARDIAL METABOLISM (18-FDG) = mismatch 99mTc MIBI 18FDG non viable viable match mismatch - we can expect improvement in function following revascularization 99m-TcMIBI SCAR is characteristic in NONREVERSIBILE PERFUSION DEFECT ( 99m-Tc MIBI) vs. NO PRESERVED MYOCARDIAL METABOLISM (18-FDG ) = match 99mTc MIBI 18FDG nonviable viable match mismatch - we can´t expect improvement in function following revascularization