* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CN 8.1B The Binomial Theorem - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
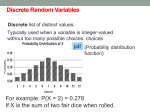
AP Statistics Notes Name: ____________ Date: _____________ Lesson 8.1B: The Binomial Probability Theorem Learning Targets: A: Identify a random variable as binomial by verifying four conditions: two outcomes (success and failure); fixed number of trials; independent trials; and the same probability of success for each trial. B: Use technology or the formula to determine binomial probabilities and to construct probability distribution tables and histograms. C: Calculate cumulative distribution functions for binomial random variables and construct cumulative distribution tables and histograms. Vocabulary: Binomial coefficient 1. Binomial probability formula (binomial pdf and cdf) Binomial Probability Theorem Recall the example from the previous lesson: Ex: Brighton Eager wants to determine the probability that he passes the MC portion of an AP Stats test that has 10 MC questions, each with answer choices A-E, given that he randomly guesses on each question. What is the probability that Brighton answers at least 6 of the 10 MC questions correctly, thus earning at least a 60% (passing grade) on that portion of the test. In statistical notation, find P( X 6) . Let’s look at a simpler problem first – the probability that Brighton answered exactly 6 of the 10 questions correctly P( X 6) . Step 1: Find the probability of getting 6 successes in 10 observations in a specific case, say, SSSSSSFFFF. Step 2: Determine how many arrangements there are for 6 successes in 10 observations. [Hint: Think combinations -- n Ck !] Step 3: Find P(X = 6) P(X = k) binompdf(n, p, k) The Binomial Probability Theorem If X has the binomial distribution with n observations and probability p of success on each observation, the possible values of X are 0, 1, 2, … n. If k is any one of these values, n P(X = k) = p k (1-p) nk k n The expression is called the binomial coefficient. k n n! = k!(n k )! k As a class, let’s find P(X 6), the probability that Brighton passes the MC part. P(X k) binomcdf(n, p, k) 2. Binomial Probability Distribution Let’s have the calculator generate the probability distribution for the binomial random variable, X, in our Brighton Eager example. 1. Store the values 0, 1, 2, … 10 in L 1 . Seq(x, x, 0, 10, 1) 2. Store the probabilities in L 2 . binompdf(10, .20, L 1 ) L 2 3. Construct a probability histogram using the values in L 1 and their probabilities in L 2 . StatPlot 4. Store cumulative probabilities in L 3 . binomcdf(10, .20, L 1 ) L 3 5. Construct a cumulative probability histogram using the values in L 1 and their cumulative probabilities in L 3 . StatPlot List/Ops AP Statistics Notes Name: ____________ Date: _____________ Lesson 8.1B: Permutations, Combinations, Pascal’s Triangle Suppose that Amy, Brad, Carla, and Danny are the four members of a small club here at Highlands High School. They decide to elect a president, secretary, and treasurer for the club, with no one person holding more than one position. In how many ways can they do this? List all of the possible outcomes. Now suppose that these four people need to select 3 members to act as representatives on a school council. In how many ways can they do this? List all possible outcomes. Suppose that Amy, Brad, Carla, and Danny decide that they don’t really need a secretary – just a president and a treasurer. In how many ways can they do this? List all of the possible outcomes. Suppose that they need to select 2 members to talk to Mr. Robinson about some fundraising events. In how many ways can they do this? List all possible outcomes. 𝑃𝑘 = 𝐶𝑘 =