* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Today`s Agenda
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
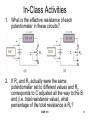
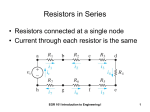
Today’s Agenda Potentiometers Ohm’s Law Continued Power & Energy EGR 101 1 Review from Last Week • How is voltage related to charge and energy? • What is the formula for resistance? • What is Ohm’s Law? • What does it mean? EGR 101 2 Potentiometers • A potentiometer is a variable resistor • The total resistance is fixed between terminals A and B A • A portion of the resistance is between A and C C • The remainder is between B and C B • C can be physically moved between A and B EGR 101 3 2 Basic Ways to Use Potentiometers • As a variable resistor: – The center tap (C) is connected to one end (B) – The total resistance is only from A to C A B/C • As a voltage divider (to be covered in a later lecture) EGR 101 4 In-Class Activity If you have a 1k Ω potentiometer and the center tap, C, is set ¼ of the way between A and B (closer to A), • What is the resistance between A and C and between B and C? • What is the resistance R if the potentiometer is connected as below (assume C has not been moved): R A EGR 101 B/C 5 Relationship between Current and Voltage • Current through a FIXED resistance – Increases when the voltage increases – Decreases when the voltage decreases • The current changes as a result of the change in voltage! + + _ _ What is the value of the resistance? EGR 101 6 Relationship between Current and Resistance • For a FIXED voltage, – The current decreases proportionally to an increase in resistance – The current increases proportionally to a decrease in resistance • The current changes as a result of the change in resistance + + _ _ EGR 101 7 In-Class Activities 1. What is the effective resistance of each potentiometer in these circuits? + + A 5V C R1 10 V _ A C R2 _ B B 2. If R1 and R2 actually were the same potentiometer set to different values and R2 corresponds to C adjusted all the way to the B end (i.e. total resistance value), what percentage of the total resistance is R1? EGR 101 8 Energy • Think of a battery like sand in an hour glass – Sand = charge • Voltage is the force that moves charge – Think of gravity on the moon vs the Earth • Energy = V.Q – You use much more energy to move sand on Earth than on the moon where gravity is 1/6th the Earth’s EGR 101 9 Power & Energy • The Instantaneous Power, P, is the Change of Energy, E, per unit time. – In our sand analogy, power is a measure of how quickly the hourglass is emptying • Units: E P t [E] = Joules (J). [t] = seconds (s). J P Watt W s EGR 101 10 Power & Energy E P t The change in energy can be written as: E P t We often assume initial energy is zero EGR 101 11 Power in terms of Voltage and Current Energy Previously you learned that Voltage Charge E or V Q Using this and E yields V Q P t Q Since I t Q or V P t then EGR 101 P t P V I 12 Power - The amount of energy used per unit time - The battery shown below uses 1 J/s to generate current – it has used 1 W of power. EGR 101 13 Determining Power P VI EGR 101 14 Other Power Equations P V I V IR P I R In this example, 2 P= EGR 101 15 Other Power Equations (continued) P V I V I R V P R 2 In this example, P= EGR 101 16 In-Class Activity for Power and Ohms Law • In pairs, complete the following chart ITEM # CURRENT 1 10 mA 2 VOLTAGE RESISTANCE 4W 32 V 16 mW 3.3 kΩ 3 4 15 mA 5 24 mA POWER 231 mW 45 V 1.2 kΩ EGR 101 17 In-Class Activity Practice Problem 3.11 (p 88) • Calculate the total energy used by a 1500W dishwasher, a 3600W clothes dryer, and a 750W air conditioner that are all being used for 2 hours. • Report your answer in J and Btu. • Report your answer in kWh. • Use the internet to find a recent cost per kWh and report the total cost for this problem. EGR 101 18 In-Class Activity continued • If I turn the AC off after 1 hour, how many kWh do I use? • If, instead, I told you that the dishwasher goes through 4 20-minute cycles in the 2 hours (prewash, wash, rinse, dry), each of which draws 1500W and virtually no power is used between cycles; how many kWh do I use? EGR 101 19