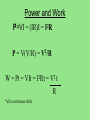* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download OHM’S LAW
Survey
Document related concepts
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Lumped element model wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
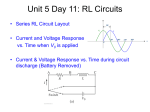
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
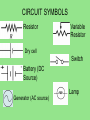
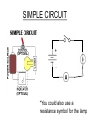
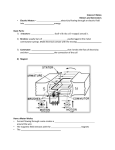
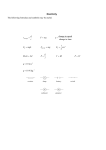
V Ohm’s Law • The ratio of the potential difference to the current in a metal conductor is a constant. This is equal to the resistance. R = V/I R- resistance(Ω) I- current (Amps) V- Potential difference (V) EXAMPLE a) What is the resistance of a lamp that is plugged into a 120V outlet and has a current of 0.75Amp? R = V/I = 120V / 0.75Amp R= 160Ω b) What is the power of the bulb? P=VI = 120V(0.75Amp) P = 90 Watts Power and Work P=VI = (IR)I = I2R P = V(V/R) = V2/R W = Pt = VIt = I2Rt = V2 t R *all on reference table CIRCUIT SYMBOLS Resistor Variable Resistor Dry cell Switch Battery (DC Source) Generator (AC source) Lamp MORE SYMBOLS Motor Electrical ground Voltmeter- Measures drop in potential across a resistance. (Placed in parallel) Ammeter- measures current in the circuit (placed in series) Galvonometer- used to measure very small amounts of current. SIMPLE CIRCUIT *You could also use a resistance symbol for the lamp When diagraming Always label values for voltage, current and resistance. Always show direction of current when a battery is in the circuit. Make sure you use the correct symbols Example A circuit contains a 60V battery, an ammeter, a switch and a lamp of 30Ω. Draw a circuit diagram and determine the reading on the ammeter. R=30Ω R= V/I 30Ω = 60V / I V=60V I = 2 Amp I = 2Amp