* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit II Review
Compound (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ojibwe grammar wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
Georgian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ukrainian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Sanskrit grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lithuanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Preposition and postposition wikipedia , lookup
Udmurt grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Romanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Arabic grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Norse morphology wikipedia , lookup
Icelandic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Pipil grammar wikipedia , lookup
Archaic Dutch declension wikipedia , lookup
Grammatical case wikipedia , lookup
Old Irish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Romanian nouns wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Latvian declension wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
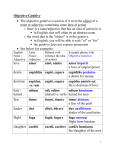
Chapters 5 - 9 Unit II Review Case Uses Nominative Subject (noun doing the action) Genitive Defined by the word ‘of” Possession (the noun which possesses) Equus agricolae – the horse of the farmer Partitive – the ‘whole’ from which a part is taken (copia aquae – a supply of water) Dative Indirect Object (noun to or for whom action done) Accusative Direct Object (receives the action of the verb) Ablative Various Uses - Most Prepositions (you know ablative of means) NOTE – look at page 62 for a discussion of ways to make sense of –ae endings! Ablative of Means Used to express the means, or instrument, by which something is done. (How did you move all that loot? By means of carts!) In English, we almost always use the prepositions by or with to express this, but in Latin it is shown by putting an ablative case ending on the noun (the object of the preposition). A Preposition is a word showing the relationship between 2 nouns. VERBS – new information in this unit The future tense is formed by adding the tense sign –bi- to the stem. The i is dropped in the first person singular and becomes –uin the 3rd person plural. IMPERATIVE – if something is imperative, it MUST be done! The imperative form is a command or direction. Formed by using the present stem of the verb for the singular. The plural is formed by adding a –te ending. The Genitive Case The Genitive Case is used to show possession Genitive Endings (singular) are similar to Nominative Endings (plural) for both declensions. – Use translation tips to possibly eliminate nominative singular as a possibility Uses the keyword ‘OF’ The Dative Case The Indirect Object uses Dative Case Endings Indirect Object – The noun TO or FOR WHOM the action is done The keywords are TO or FOR The Ablative Case The Ablative Case is used for most prepositional phrases We have learned the ‘Ablative of Means’ – No Latin preposition is used – We must add the keywords: by, with, or by means of