* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Diode detector
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
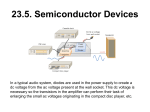
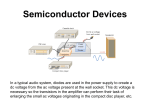
7th of Jan, 2014 Diode detector (PIN photo diode detector) Hyun Suk Kim [email protected] Contents 1. Basic Physics of Diode as a Radiation Detector 2. Diode detector (P-type, N-type) 3. Photodiode detector (PIN-Photodiode) 1. Basic Physics of Diode as a Radiation Detector What is Diode • Made of silicon or germanium • Low (ideally zero) resistance to current flow in one direction, and high (ideally infinite) resistance in the other Use of Diode detector in SNUH ① Diode ② Photo-diode SFD diode detector(P-type) CT detector array Mapcheck2(N-type) EPID (Hydrogenated amorphous silicon (a-Si:H) PIN photodiode) History of Diode detector in Radiation Oncology • Silicon diode detectors have been used in high-energy photon and electron beam dosimetry for many years (from Jones 1963) • Diodes have gained in popularity since the 1980s • Now, one of the most useful dosimeters ∴ medical physics understanding is required for users to accurately and effectively use What is semiconductor • Semiconductor – Material which has electrical conductivity between conductor and insulator – Ability to change conductivity by the addition of impurities ("doping") – Require only a few eV to generate a charge carrier Radiation detection & measurement, 4/E, Knoll ① N-type semiconductor • N-type semiconductor – doped with impurities of 5 valance electrons element P(phosphorous) called a “donor” – “donor” contribute a free electron to the silicon – Electrons(-) are the majority carriers – Holes(+) are the minority carriers Silicon has 4 valence electrons, each making a covalent bond with a neighbor ② P-type semiconductor • P-type semiconductor – doped with impurities of 3 valance electrons element B(boron) called an “acceptor” – “acceptor” contribute a free electron to the silicon – Holes(+) are the majority carriers – electrons(-) are the minority carriers P-N junction • • Made of p-type and n-type semiconductor in direct contact Also called the “depletion region” In p-n junction Majority carriers from each side diffuse to the opposite side(electron in n-side → p-side) concentration equilibrium opposite charge ions establish an electric field (“built-in potential” = 𝜺) Prevents further diffusion of the majority carriers Diode detector is made by P-N junction principle 2. Diode detector (P-type & N-type) P-type & N-type diode detector • N-type diode is formed by doping “acceptor” (3 valance electrons element) into N-type semiconductor • P-type diode is formed by doping “donor” (5 valance electrons element) into P-type semiconductor Diode detector is made by P-N junction principle Mapcheck2 N-type diode SFD P-type diode Need no bias voltage in diode detector • The typical width of the “depletion region” is less than several μm • “built-in potential” is less than 1 volt, the electric field across the pn junction is very high (greater than 103 V/cm) ∴ The high electric field across the pn junction makes charge collection possible for the diode without external bias TG-62, 2005 (DIODE IN VIVO DOSIMETRY FOR PATIENTS RECEIVING EXTERNAL BEAM RADIATION THERAPY) How can we measure dose using diode? Incident ionizing radiation electron-hole pairs + The minority carriers (electrons on the p-side and holes on the n-side) diffuse toward the opposite side Measured by the electrometer TG-62, 2005 (DIODE IN VIVO DOSIMETRY FOR PATIENTS RECEIVING EXTERNAL BEAM RADIATION THERAPY) 3. Photodiode detector (PIN-Photodiode) What is PIN-Photodiode • Made of a PIN structure PIN diode is a diode with intrinsic semiconductor region between p-type semiconductor and n-type semiconductor Intrinsic semiconductor – In concentration, hole = electron – Intrinsic semiconductor = pure semiconductor Diode Operation(Bias) • Forward bias : – As electrons and holes are pushed toward the junction – “Depletion region” is reduced – Act like “conductor” • Reverse bias : – As electrons and holes are pulled away from the junction – “Depletion region” widen – Act like “opened circuit” (no leakage current) → detect only photo-generated carrier ∴ Reverse bias can be used as Photodiode detector Physical Principles of PIN photo diode Reverse bias ↓ radiation greater than the band-gap energy of the material (1.12 eV for Si) ↓ Excite a valance band electron into the conduction band ↓ causing a current to flow in an external circuit Fundamentals of Photonics, 2nd Edition, Saleh Use of Photodiode detector in Radiation oncology EPID(Electronic Potal Imaging Devices) CT detector array Hydrogenated amorphous silicon (a-Si:H) P-I-N photodiode Varian Image Acquisition System 3 Reference guide, 2011 Courtesy of Prof. Kim J-H Advantage of PIN-photodiode • Sensitive detectors susceptible to visible and infrared radiation(R. Nowotny et al, Nuc. instr. and meth. 147, 1977) • Used with x- and gamma-ray spectroscopy with a high energy resolution(Takahiko Aoyama et al, Med. Phys 29(7), 2012) • PIN improve response time and higher efficiency than PN structure Visible ray linearity in low dose range. Takahiko Aoyama et al, Med. Phys 29(7), 2012 What can we do? • Apply the photodiodes in MV energy region – Feasibility study was performed (Benigno et al, Med. Phys. 41(1), 2014) • Using commercially available PIN-photodiodes for measuring organ dose in kV energy region – Immediately readout Discussion & Question Thank you for your attention