* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit Circle - Denise Kapler
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
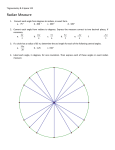
Unit Circle And Trigonometric Functions (x, y) = (cos Ɵ, sin Ɵ) Trigonometry relies on triangle proportionality. Given right triangles with congruent acute angles, the trig function is built from the proportionality constant. Proportionality constants are written within the image: sin θ, cos θ, tan θ, where θ is the common measure of the acute angle. Angle Measure a. Degrees b. Radians Radian is a unit of angular measure defined such that an angle of one radian subtended from the center of a unit circle produces an arc with arc length 1. Subtended Angle: The angle made by a line, arc or object. Example: The Subtended Angle of the tree (from the person's point of view) is 22° Measuring in Radians. Trig Ratios Trig Ratios Trig Ratios Trig Ratios y = sin(x) using a unit circle Compare Graphs of sin and cos Naming convention Angles: Capital Letters Side lengths: Small Letter of Opposite Angle Using Trig What is the height of the tree on the left? Using Trig At 57" from the base of a building you need to look up at 55° to see the top of a building. What is the height of the building? Using Trig Find Reference Angles Quadrant II Quadrant IV Quadrant III Find Reference Angle or Reference Triangle Sin 135°= Sin 45° = 2 2 Sin 300°= Sin -60° = − 3 2 Reference Angle = 30° Reference Angle = 55° Angles greater than 360° Positive and Negative Angles Inverse Trig Functions When you want to find the angle measure Ɵ: arcsin(x) = sin-1(x) Read as: “the angle whose sine is x” arccos(x) = cos-1(x) arctan(x) = tan-1(x) The range of the Inverse Functions is limited as follows. Inverse Trig Function The base of a ladder is placed 3 feet away from a 10foot-high wall, so that the top of the ladder meets the top of the wall. What is the measure of the angle formed by the ladder and the ground? Here we a have a right triangle where we know the lengths of the two legs, that is, the sides opposite and adjacent to the angle. So, we use the inverse tangent function. If you enter this into a calculator set to "degree" mode, you get If you have the calculator set to radian mode, you get