* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cats - Workforce3One
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
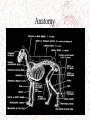
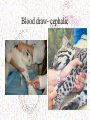
• Clinical Textbook for Veterinary Technicians • 6th Edition • By: Dennis M. Mccurnin • Joanna M. Bassert • • • • Animal Restraint for Veterinary Professionals By: C.C. Sheldon Teresa Sonsthagen James A. Topel Cats Felis catus Terminology • Queen = – adult intact female used for breeding • Tom-intact male • Kitten Queening Vital Parameters • Temperature = 100.5-103.5°F • Pulse = 120-200 beats/minute. • Respiration = 20-30 respirations/minute • Gestation- 65 days. Anatomy • Whiskers-The whiskers of a cat are enlarged stiffened hairs more than twice the thickness of ordinary hairs, and are embedded three times deeper. • They are supplied with a great many nerveendings which transmit information to the cat's brain about any contact they make or changes in air pressure that may occur. Anatomy • Claws-when a cat is relaxed that the claw is retracted or sheathed. When the cat voluntarily tightens certain muscles the claws are unsheathed and ready for action. Thus the feline claws are not retractile, but rather protractile. Anatomy Anatomy • Sexing Mating and conception • When a female cat reaches puberty, her heat cycles (estrus cycles) will begin. January-August • Until she mates or is spayed, these cycles will repeat themselves as often as every two or three weeks. • Estrus is the period of receptivity to mating, and is linked with the production of estrodial, a type of estrogen produced by ovarian follicles. It is rare to see any signs of blood, although an occasional mucous discharge may be evident. • In female cats ovulation does not take place without mating or manual stimulation (induced ovulation). Diet • Cats are strict carnivores and, because of this, they have a tremendous ability to produce glucose from protein, but have difficulty processing carbohydrates Behaviors • • • • Retain much of their instinctive behavior Establish territories quickly Cannot establish dominance over a cat Pay attention to body language – – – – – Ears pulled backed Leaning away from you Vocalizing Batting at you Flicking of the tail Aggression • Play Aggression: • If a kitten fails to learn to temper aggressive "playfulness" (i.e. to retract its claws or inhibit its bite during play) from the queen • Signs: – flattening of the ears against the head – twitching of the tail – unsheathing of the claws • Fear Aggression: • Fear...and the flight-or-flight response to it...is an ingrained and potent (over) response. • All cats are capable of expressing such aggression, • Signs: – Ordinarily a fearful cat will flee or hide from a perceived danger – If a cat...any cat...is placed in circumstances of shrinking space (backed into a corner; no escape route), it will assume a defensive attack posture. • The tell-tale postures associated with fear aggression are these: – Flattening of the ears against the head – Crouching, with the head drawn close to the body – Rolling on the back ( NOT a submissive posture!!!) • Predatory Behavior: – Occurs in cats regardless of whether or not hunger is present – Involves killing of natural prey without eating (just beheading, usually) – Is "normal" in some cats, usually develops by 5-7 weeks of age. • Predatory Aggression: – Involves inappropriate predatory behavior towards natural and "unnatural" prey (e.g. human infants!) – Hallmarks of this type of behavior are: • Stealth/Silence, heightened attentiveness, slinking posture, tail-twitching • Pouncing...if the victim exhibits sudden movements Behaviors Restraint Techniques • Removal from carrier • Removal from cage Restraint Techniques • • • • • Sitting/sternal Scruffing (fetal hold) Lateral recumbency Dorsal recumbency Pretzel hold • The Pretzel Restraint Techniques • Distraction – – – – Caveman pats Puffs of air Rubber band @ base of ears Pencil on nose Restraint Tools • • • • • • Towel/blanket- kitty burrito Cat restraint bag Muzzle Gauntlet gloves Cat nabber Net/snare pole Elizabethan collar Squeeze Cage Anesthesia Box Medication Administration • • • • • • Oral (tablet, liquid, tubing) Parenteral (IM, IV, SQ, ID, IC) Nasal Otic Opthalmic Rectal Pilling • Can use pill gun as well to save fingers! Vaccinations • Always give in the most distal portion of limb due to a vaccine induced sarcoma. SQ other than Vaccines Blood draws • • • • Medial saphaneous Lateral saphaneous Jugular Cephalic • Cephalic Jugular blood draw Jugular Blood draw- cephalic Zoonotic Mycoses • Ringworm – Tricohyton spp. – Microsporum spp. Zoonotic Parasites • Scabies = Sarcoptes scabiei (contact) • Schistsomiasis = Schistsoma spp. (contact) • Larval migrans: Contact/Ingestion – Toxocara – Ancylostoma – Strongyloides Zoonotic Protozoa • Cryptosporidiosis = Cryptosporidium spp. – (Ingestion) • Toxoplasmosis = Toxoplasma gondii – (ingestion) • Sarcocystosis = Sarcocystis spp. (ingestion) • Giardiasis = Giardia lamblia (ingestion) Zoonotic Bacteria • Plague = Yersinia pestis (flea bite) • Campylobacteriosis = Campylobacter fetus (Ingestion/contact) • Cat-scratch disease = Bartonella henselae – (Cat bite/scratch) • Leptospirosis = Leptospira spp. (contact w/urine) • Salmonellosis = Salmonella spp. (ingestion) • Tuberculosis = Mycobacteria spp. (ingestion and inhalation) • Tularemia = Francisella tularensis (tick bites, contact with tissue) • Lyme disease = Borrelia burgdorferi (Tick bite) Significant Bacteria • CBA = Cat bite abscess – This phenomenon is primarily caused by pasteurella. This particular bacteria is an anaerobic bacteria that loves puncture wounds. – Cats and humans are both prone to infections from bites. Vaccinations • • • • • • • • Rabies Panleukopenia (FVP, feline distemper) Chlamydial pneumonitis (a URI) Feline leukemia virus (FeLV) Rhinotracheitis (FVR, a URI) Calicivirus (FCV, a URI) Feline infectious peritonitis (FIP, a corona virus) Feline immunodeficiency virus (FIV) Nail trimming Additional Info Kudos • http://www.pawsonline.info/index.htm • http://www.catnutrition.org/catkins.php This workforce solution was funded by a grant awarded under the Workforce Innovation in Regional Development (WIRED) as implemented by the U.S. Department of Labor’s Employment and Training Administration working in partnership with the Colorado Department of Labor and Employment, the Metro Denver Economic Development Corporation, and the City and County of Denver's Office of Economic Development. The solution was created by the grantee and does not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Labor. The Department of Labor makes no guarantees, warranties, or assurances of any kind, express or implied, with respect to such information, including any information on linked sites and including, but not limited to, accuracy of the information or its completeness, timeliness, usefulness, adequacy, continued availability, or ownership. This solution is copyrighted by the institution that created it. Internal use by an organization and/or personal use by an individual for non-commercial purposes is permissible. All other uses require the prior authorization of the copyright owner.