* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1.2_nutrient_cycles 880KB May 22 2015 12:21:18 PM
Survey
Document related concepts
Water splitting wikipedia , lookup
Electrolysis of water wikipedia , lookup
Water pollution wikipedia , lookup
Blue carbon wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Eutrophication wikipedia , lookup
Isotope analysis wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Biosequestration wikipedia , lookup
Freshwater environmental quality parameters wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
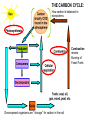
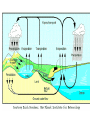
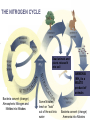
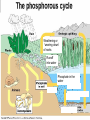
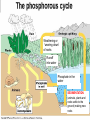
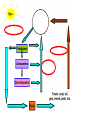
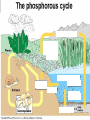
NUTRIENT CYCLES Nutrients are chemicals that organisms need to survive. Example – All organisms need Nitrogen to make protein NUTRIENTS must be RECYCLED when animals and plants die so that new animals and plants can get nutrients too. PHOTOSYNTHESIS AND RESPIRATION ARE PARTNERS! Photosynthesis: Producers CONVERT solar energy to sugar. Carbon Dioxide + Water + Sun’s Energy --> Oxygen + Sugar PHOTOSYNTHESIS AND RESPIRATION ARE PARTNERS! Photosynthesis: Producers CONVERT solar energy to sugar. Carbon Dioxide + Water + Sun’s Energy --> Oxygen + Sugar Oxygen + Sugar--> water+ carbon dioxide + chemical energy RESPIRATION: Animals (and plants) use Sugar as a source of energy for growth, movement, repair, and reproduction PHOTOSYNTHESIS AND RESPIRATION ARE PARTNERS! Carbon Dioxide + Water + Sun’s Energy --> Oxygen + Sugar Oxygen + Sugar--> water+ carbon dioxide + chemical energy RESPIRATION: Animals (and plants) use Oxygen and Sugar to make energy! CO2 is a product of this reaction and RECYCLES the CO2 in the air. THE CARBON CYCLE: How carbon is balanced in ecosystems Combustion means Burning of Fossil Fuels Decomposed organisms are “storage” for carbon in the soil Carbon conundrum • Sources of atmospheric CO2 are increasing • SINKS (ways to remove CO2) from the atmosphere are DECREASING • We therefore have an excess CO2 in our atmosphere • This creates a blanket around the earth that traps solar energy (GREENHOUSE EFFECT) Greenhouse Effect Widespread Pollution The OCEAN is an important part of the carbon cycle too. THE NITROGEN CYCLE Dead animals and plants release N into soil AMMONIA (NH3) is a WASTE product of animals Bacteria convert (change) Atmospheric Nitrogen and Nitrites into Nitrates Some Nitrates leech or “leak” out of the soil into water Bacteria convert (change) Ammonia into Nitrates Weathering or ‘wearing down’ of rocks Runoff into water Phosphate in the water Weathering or ‘wearing down’ of rocks Runoff into water Phosphate in the water SEDIMENTATION (animals, plants and rocks settle to the ground) making new rocks THE NITROGEN CYCLE