* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Metabolic Diversity
Survey
Document related concepts
Bioluminescence wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Cyanobacteria wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
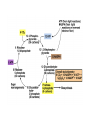
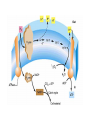
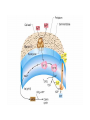
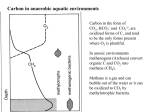
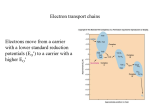
Metabolic Diversity • Every living being needs: – Energy source (inorganic,organic, light) – Carbon source (inorganic or organic) Phototrophy • Microbial phototrophs: – Anoxygenic • Purple (non)-sulfur bacteria (proteobacteria) • Green sulfurs • Green non-sulfurs – Oxygenic • Cyanobacteria • Prochlorophytes Photosynthetic Pigments • Chlorophylls – Porphyrins (like cytochromes) with Mg+ – Bacteriochlorophylls a, b, c, d, e, g • Phycobilins (phycoerythrin, phycocyanin) • Carotenoids – Hydrophobic – Hydrocarbon chains with conjugated bonds • Light reaction: – Light energy is conserved as chemical energy • Dark reaction: – Chemical energy is used to reduce CO2 to organic compounds • Reaction center • Light harvesting (antenna) Photosynthetic complex in PSB Oxygenic Photosynthesis • Involves two distinct photochemical reactions (photosystems I(P700) and II(P680)) • Use light to generate both ATP and NADPH • Electron transfer in photosystem I produces H+ gradient (also cyclic photophosphorylation) CO2 Fixation • Calvin cycle requires NAD(P)H and ATP • Ribulose biphosphate carboxylase (RubisCO) • Stoichiometry: – 6 CO2 + 12 NADPH + 18 ATP C6H12O6(PO3H2) + 12 NADP+ + 18 ADP +17 Pi • Carboxysomes – Polyhedral cell inclusions with crystalline arrays of RubisCO Reverse Citric Acid Cycle • Green sulfur bacteria and green non-sulfur bacteria • Archaea Sulfolobus and Thermoproteus • Ferredoxin linked enzymes Hydroxypropionate Cycle • Chloroflexus (green non-sulfur) • 2 CO2 are reduced to glyoxylate • key intermediate is hydroxypropionate Chemolithotrophy • Obtain energy from the oxidation of inorganic compounds • ATP synthesis is coupled to oxidation of electron donor • Possible electron donors: H2, sulfide, S0, ammonium, NO2-, Fe2+ • H2-oxidation catalyzed by hydrogenase, soluble or membrane-bound; most H2oxidizer are also capable of chemoheterotrophic growth • Oxidation of reduced Sulfur compounds (H2S, S0, S2O3-) via SO32• Iron oxidation (Fe2+ to Fe3+), anaerobic ferrous iron oxidation by anoxygenic phototrophs (banded iron formation) Nitrification • Nitrogen compounds as e--donors: NH3 and NO2• Nitrifiers in soil and water • Ammonia monooxygenase • Anammox Anaerobic Respiration • Terminal e--acceptors others than O2: Fe3+, NO3-, fumarate, SO42-, CO2, S0 • Yields less energy than the oxidation of the same compound with O2 would • Dissimilative metabolism