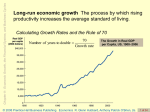
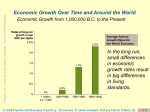
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch3
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
chapter three Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand and Supply Prepared by: Fernando & Yvonn Quijano © 2007 Prentice Hall Business Publishing; Essentials of Economics R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien Carly Fiorina … Because of the importance of printers to Hewlett-Packard, the company devotes significant resources to monitoring and forecasting consumer demand. LEARNING OBJECTIVES CHAPTER 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand and Supply How Hewlett-Packard Manages the Demand for Printers After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1 2 3 4 Discuss the variables that influence demand. Discuss the variables that influence supply. Use a graph to illustrate market equilibrium. Use demand and supply graphs to predict changes in prices and quantities. © 2007 Prentice Hall Business Publishing; Essentials of Economics, R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien 2 of 28 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVE CHAPTER 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand and Supply The Demand Side of the Market The Demand of an Individual Buyer 3-1 Plotting a Price-Quantity Combination on a Graph At a price of $125 per printer, Kate, the purchasing manager for the Prudential Insurance Company, will be willing to buy 5 printers in the next month. Quantity demanded The quantity of a good or service that a consumer is willing to purchase at a given price. © 2007 Prentice Hall Business Publishing; Essentials of Economics, R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien 3 of 28 CHAPTER 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand and Supply The Demand Side of the Market Demand Schedules and Demand Curves 3-2 Kate’s Demand Schedule and Demand Curve Demand schedule A table showing the relationship between the price of a product and the quantity of the product demanded. Demand curve A curve that shows the relationship between the price of a product and the quantity of the product demanded. © 2007 Prentice Hall Business Publishing; Essentials of Economics, R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien 4 of 28 CHAPTER 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand and Supply The Demand Side of the Market Individual Demand and Market Demand 3-3 Deriving the Market Demand Curve from Individual Demand Curves Market demand The demand for a product by all the consumers in a given geographical area. © 2007 Prentice Hall Business Publishing; Essentials of Economics, R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien 5 of 28 CHAPTER 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand and Supply The Demand Side of the Market The Law of Demand The Law of Demand Holding everything else constant, when the price of a product falls, the quantity demanded of the product will increases, and when the price of a product rises, the quantity demanded of the product will decrease. What Explains the Law of Demand? Substitution effect The change in the quantity demanded of a good that results from a change in price making the good more or less expensive relative to other goods that are substitutes. Income effect The change in the quantity demanded of a good that results from the effect of a change in the good’s price on consumer purchasing power. © 2007 Prentice Hall Business Publishing; Essentials of Economics, R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien 6 of 28 CHAPTER 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand and Supply The Demand Side of the Market Total Effect Substitution Effect Income Effect © 2007 Prentice Hall Business Publishing; Essentials of Economics, R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien 7 of 28 The Demand Side of the Market CHAPTER 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand and Supply Price of Good X increases Type Good Substitution Income Effect Effect Total Effect Normal - - - Inferior - + - Giffen - + + Giffen good is the only exception to the law of demand. © 2007 Prentice Hall Business Publishing; Essentials of Economics, R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien 8 of 28 CHAPTER 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand and Supply The Demand Side of the Market Holding Everything Else Constant: The Ceteris Paribus Condition Ceteris paribus (“all else equal”) The requirement that when analyzing the relationship between two variables—such as price and quantity demanded—other variables must be held constant. © 2007 Prentice Hall Business Publishing; Essentials of Economics, R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien 9 of 28 CHAPTER 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand and Supply The Demand Side of the Market Variables That Shift Market Demand Price of related goods Substitutes Goods and services that can be used for the same purpose. Complements Goods that are used together. 3-4 Shifting the Demand Curve Income Normal good A good for which the demand increases as income rises and decreases as income falls. Inferior good A good for which the demand increases as income falls, and decreases as income rises. Tastes Population and demographics Demographics The characteristics of a population with respect to age, race, and gender. Expected future prices © 2007 Prentice Hall Business Publishing; Essentials of Economics, R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien 10 of 28 CHAPTER 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand and Supply The Demand Side of the Market Variables That Shift Market Demand 3-1 Variables That Shift Market Demand Curves © 2007 Prentice Hall Business Publishing; Essentials of Economics, R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien 11 of 28 CHAPTER 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand and Supply The Demand Side of the Market Variables That Shift Market Demand 3 - 1 (continued) Variables That Shift Market Demand Curves © 2007 Prentice Hall Business Publishing; Essentials of Economics, R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien 12 of 28 CHAPTER 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand and Supply The Demand Side of the Market A Change in Demand versus a Change in Quantity Demanded 3-5 A Change in Demand versus a Change in the Quantity Demanded © 2007 Prentice Hall Business Publishing; Essentials of Economics, R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien 13 of 28 2 LEARNING OBJECTIVE CHAPTER 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand and Supply The Supply Side of the Market Quantity supplied The quantity of a good or service that a firm is willing to supply at a given price. Supply Schedules and Supply Curves Supply schedule A table that shows the relationship between the price of a product and the quantity of the product supplied. Supply curve A curve that shows the relationship between the price of a product and the quantity of the product demanded. © 2007 Prentice Hall Business Publishing; Essentials of Economics, R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien 14 of 28 CHAPTER 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand and Supply The Supply Side of the Market 3-6 Hewlett-Packard’s Supply Schedule and Supply Curve © 2007 Prentice Hall Business Publishing; Essentials of Economics, R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien 15 of 28 CHAPTER 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand and Supply The Supply Side of the Market Individual Supply and Market Supply 3-7 Deriving the Market Supply Curve from the Individual Supply Curves © 2007 Prentice Hall Business Publishing; Essentials of Economics, R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien 16 of 28 CHAPTER 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand and Supply The Supply Side of the Market The Law of Supply Law of supply Holding everything else constant, increases in price cause increases in the quantity supplied, and decreases in price cause decreases in the quantity supplied. © 2007 Prentice Hall Business Publishing; Essentials of Economics, R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien 17 of 28 CHAPTER 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand and Supply The Supply Side of the Market Variables That Shift Supply Price of inputs Technological change 3-8 Shifting the Supply Curve A positive or negative change in the ability of a firm to produce a given level of output with a given amount of inputs. Prices of substitutes in production Expected future prices Number of firms in the market © 2007 Prentice Hall Business Publishing; Essentials of Economics, R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien 18 of 28 CHAPTER 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand and Supply The Supply Side of the Market Variables That Shift Supply 3-2 Variables That Shift Market Supply Curves © 2007 Prentice Hall Business Publishing; Essentials of Economics, R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien 19 of 28 CHAPTER 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand and Supply The Supply Side of the Market Variables That Shift Supply 3 - 2 (continued) Variables That Shift Market Supply Curves © 2007 Prentice Hall Business Publishing; Essentials of Economics, R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien 20 of 28 The Supply Side of the Market CHAPTER 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand and Supply A Change in Supply versus a Change in Quantity Supplied 3-9 The Difference between a Change in Supply versus a Change in the Quantity Supplied © 2007 Prentice Hall Business Publishing; Essentials of Economics, R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien 21 of 28 3 LEARNING OBJECTIVE CHAPTER 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand and Supply Market Equilibrium: Putting Demand and Supply Together 3 - 10 Market Equilibrium Market equilibrium A situation where quantity demanded equals quantity supplied. Competitive market equilibrium A market equilibrium with many buyers and many sellers. © 2007 Prentice Hall Business Publishing; Essentials of Economics, R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien 22 of 28 CHAPTER 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand and Supply Market Equilibrium: Putting Demand and Supply Together How Markets Eliminate Surpluses and Shortages 3 - 11 Surplus A situation in which the quantity supplied is greater than the quantity demanded. The Effect of Surpluses and Shortages on the Market Price Shortage A situation in which the quantity demanded is greater than the quantity supplied. © 2007 Prentice Hall Business Publishing; Essentials of Economics, R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien 23 of 28 4 LEARNING OBJECTIVE CHAPTER 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand and Supply The Effect of Demand and Supply Shifts on Equilibrium The Effect of Shifts in Supply on Equilibrium 3 - 12 The Effect of a Decrease in Supply on Equilibrium © 2007 Prentice Hall Business Publishing; Essentials of Economics, R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien 24 of 28 CHAPTER 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand and Supply 3-4 The Falling Price of Large Flat-Screen Televisions Corning’s breakthrough spurred the manufacture of LCD televisions in Taiwan, South Korea, and Japan, and an eventual decline in price. © 2007 Prentice Hall Business Publishing; Essentials of Economics, R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien 25 of 28 CHAPTER 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand and Supply The Effect of Demand and Supply Shifts on Equilibrium The Effect of Shifts in Demand on Equilibrium 3 - 13 The Effect of an Increase in Demand on Equilibrium © 2007 Prentice Hall Business Publishing; Essentials of Economics, R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien 26 of 28 CHAPTER 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand and Supply The Effect of Demand and Supply Shifts on Equilibrium The Effect of Shifts in Demand and Supply over Time 3 - 14 Shifts in Demand and Supply over Time © 2007 Prentice Hall Business Publishing; Essentials of Economics, R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien 27 of 28 CHAPTER 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand and Supply The Effect of Demand and Supply Shifts on Equilibrium The Effect of Shifts in Demand and Supply over Time 3 - 15 The Demand for Chicken Has Increased More Than the Supply © 2007 Prentice Hall Business Publishing; Essentials of Economics, R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien 28 of 28