* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 17 - Effingham County Schools
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
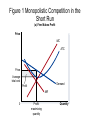
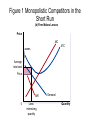
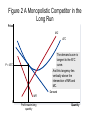
Chapter 17 Monopolistic Competition Characteristics of Monopolistic Competition 1. Many sellers 2. Product differentiation 3. Free entry Examples: books, CD’s, restaurants, movies, etc. In the Short Run… • Because the product is differentiated, it faces a downward D curve and MR curve • Profit-Maximization is same as monopoly: go to MR=MC for Q of output, then to D curve to find P • Firms will make profits or losses just like a monopoly in short run Figure 1 Monopolistic Competition in the Short Run (a) Firm Makes Profit Price MC ATC Price Average total cost Demand Profit MR 0 Profitmaximizing quantity Quantity Figure 1 Monopolistic Competitors in the Short Run (b) Firm Makes Losses Price MC ATC Losses Average total cost Price MR 0 Lossminimizing quantity Demand Quantity In the Long Run… • Profits = entry; shifts D curve to left • Losses = exit; shifts D curve to right • This process continues until firms are making exactly 0 economic profit • D curve and ATC curve become TANGENT • P > MC • P > MR • P = ATC Figure 2 A Monopolistic Competitor in the Long Run Price MC ATC The demand curve is tangent to the ATC curve. P = ATC And this tangency lies vertically above the intersection of MR and MC. Demand MR 0 Profit-maximizing quantity Quantity Monopolistic vs. Perfect Competition 1. Excess Capacity – firms produce on the downward-sloping portion of ATC, not at efficient scale. Therefore, they could produce more and decrease costs. 2. Markup – P > MC because firm always has some market power, so an extra unit sold = higher profit Monopolistic Competition and the Welfare of Society • Inefficiency comes from P > MC, so a mon. comp. market has same DWL as monopoly pricing • There is no way to regulate firms • # of firms in market is not “ideal” because of too much or too little entry Externalities with entry/exit • Product-variety externality – consumers get some consumer surplus from the intro of a new product, entry of a new firm is a positive externality to consumers • Business-stealing externality – other firms lose customers and profits from entry, it is a negative externality on existing firms Advertising • Varies with products • Firms selling highly differentiated goods spend about 10%-20% of revenue on advertising (soft drinks, razor blades, cereal, dog food…) • Firms selling industrial goods spend very little on advertising (satellites, etc.) • Firms selling homogeneous products spend nothing (wheat, peanuts, oil) Critique of Advertising • manipulative of people’s tastes • Psychological vs. informational • Impedes competition – convinces people products are more different than they really are Defense of Advertising • Information allows customers to make better decisions • Fosters competition by allowing customers to take advantages of price differences • Decreases market power • Can signal to the consumer that the quality of product is high Make sure to… • Read case study about eyeglasses • Read section on brand names and the pros and cons of them