* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Psycho-Addictive Disorders
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
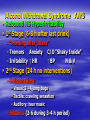
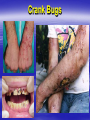
Psycho-Addictive Disorders Elisa A. Mancuso RNC, MS, FNS Professor Substance Abuse – – – – Maladaptive pattern of excessive use Recurrent use = ↑↑ impairment Failure to meet role obligations ↑↑ Use with Legal, social or interpersonal problems Intoxification – – – – – – Reversible substance induced syndrome Slurred speech Ataxia = ↓ Coordination ↓ Cognition Poor memory & judgment ↑↑Impulsive behavior Substance Dependence – – – – – Cognitive, behavioral & psychological symptoms Pt. believes substance needed for optimal health Persistent desire and ↑ time spent to obtain & use Use ↑ quantities more frequently = Addiction Unsuccessful attempts to stop using Tolerance – Need ↑↑ amounts to achieve desired effects Cross Tolerance – Pt. tolerant to drug A – When use drug B (similar to A) has ↓ effect – Need ↑↑ dose of B Withdrawal Syndrome – – – – – Cessation of heavy prolonged use Autonomic Hyperactivity Hallucinations Dementia Seizures 3rd ETOH Major health problem 50% ER visits & 12 million adults ETOH dependent Teens fastest growing group of alcoholics ↑ 50% risk with alcoholic family member Parents role model ETOH as coping skill ↑ Predisposition = ↑ Sensitivity ETOH produces morphine like substances TIQs – Activate opioid brain receptors = addiction ↓ ETOH Dehydrogenase = ↓ ETOH metabolism – ETOH goes directly from blood to brain ↓ Self Esteem ↓ Frustration ↑↑ Impulsive & ↑ Immediate Gratification Peer & media influence = + Reinforcement – ↓ Inhibitions = ↑ confidence & risky behaviors Cultural Influences Asians – Lowest ETOH rate 2.5% – Genetic ETOH intolerance (+) Punishment Flushing HA Palpitations Native Americans – Highest ETOH rate 12.5 % – 5th leading cause of death – Community oriented culture Drinking is group activity Irish, German, Scandinavian – ↑ ETOH use & dependency – RT Socialization & aggression release Family Dynamics Co-Dependency – Caretaker derives self worth from others – Over-functioning takes on all responsibilities – Enabling behaviors Adult Children of Alcoholics 1/8 – Learn dysfunctional family roles – Secrecy, mistrust, shame and denial of abuse. – Primary goal is to please parent – Hero/Caretaker Child Take on family responsibilities Trying to keep it all together” – Scapegoat Child Act out @ home – Child is focus of conflict – Lost Child Avoid conflict & pain (Escape from family) Run away – Mascot/Clown Comic relief to mask sadness Truly unhappy ETOH CNS Depressant – ↓ Anxiety Relaxation ↓ Inhibitions – ↓ Judgment Slurred speech ↓ Sleep BAC Blood Alcohol Concentration – – – – – 0.05 = Euphoria, impairment 0.08 = Intoxication (Legal limit) 0.15-0.2 = ↓ coordination, double vision 0.3 = stupor 0.4 = coma & death Absorbed in 5 mins Liver detoxifies ETOH (¼ oz) per hour = – 12 oz. Beer – 4 oz. Wine – 1 Shot Cognitive Effects Poor judgment ↓Learning ↓ Control Impulsive/Abusive Behavior Seizures Blackouts “Fugue-like” state – Amnesia of events during drinking period – No loss of consciousness during episode Wernicke’s Encephalopathy – Thiamine deficiency→ Grey matter damage – Abnormal thinking patterns ↓ Memory Ataxia Korsakoff’s Psychosis (2nd to Wernicke’s) – – – – Niacin & Thiamine deficiency Irreversible cell death & progressive mental deterioration Confabulation Loss of recent memory Diplopia Somnolence → Stupor → Death Systemic Effects Cardiovascular – Autonomic Hyperactivity = ↑ HR ↑ BP CHF – Myopathy RT Vasoconstriction = Chest pain – Bone Marrow Toxicity ↓ RBCs ↓ WBCs ↓ Plts Gastrointestinal – Esophagitis RT Vomiting – Esophageal Varices RT Portal HTN – Gastritis & Ulcers RT ↑HCL – Malnutrition → Ascitis – Pancreatitis → DM & CA – Hepatitis & Cirrhosis → Liver Failure Systemic Effects Respiratory – COPD PN – Lung CA RT ↑↑ Smoking Skin/Skeletal – ↓↓ Reflexes RT Peripheral Neuropathy – Muscle weakness = ↑↑ Falls – Skin ulcers – Spider Angiomas Genitourinary – ↑↑ Urination RT diuretic action of ETOH – ↑ FAS Alcohol Withdrawal Syndrome AWS Rebound NS Hyperirritability 1st Stage (6-8 h after last drink) – “Morning after jitters” – Tremors Anxiety C/O “Shaky Inside” – Irritability ↑ HR ↑ BP N&V 2nd Stage (24 h no interventions) – Hallucinations Visual: 3 - 4’ long bugs Tactile: crawling sensation Auditory: hear music – Seizures (2-6 during 3-4 h period) Alcohol Withdrawal Syndrome AWS 3rd Stage (48h) Delirium Tremens- DTs – Acute Medical Condition (20% mortality) – Dehydration →Fluid & Electrolyte imbalance – ↑↑ Autonomic Hyperactivity ↑HR ↑BP ↑Temp – Fatal Arrhythmias – Global confusion & unaware of environment – Vivid Hallucinations & Delusions – ↑↑ Agitation & Seizures AWS Therapy Detoxification 3-7 days AWS Protocols – – – – – – Librium, Valium or Ativan 10-20x dose initially! Thiamine (IM) Cyanocobalamine (Vit B12) Niacin (Vit B6) Folic Acid IV Glucose ß Blockers: Propanonol (Inderal) Clonidine (Catapres) – Dilantin or Mg SO4 – NO Mellaril or Haldol for hallucinations (↑↑ Seizures) – Tryptophan & Trophamine – Odansetron (Zofran) AWS Nursing Primary Priority = Assessment! V/S & LOC Monitor Pt’s response to therapy Pt. Safety = √ S/S of depression & suicide Calm, quiet environment Provide uninterrupted periods of rest Firm limits & consistent support Reorient to reality Confront denial, rationalization, projection Monitor visitors Medications Antabuse (Disulfiram) Aversion Therapy –Blocks oxidation of ETOH –↑ Pt sensitivity –↑ HA ↑ HR N & V Flushing –Chest Pain → Death Naltrexone HCL (ReVia) Opioid antagonist = ↓ ETOH craving Can not be used with narcotics for 7-10 days Therapy 12 Step Programs: AA NA CA – Life-long commitment – Attain & Maintain sobriety Peer group & sponsor – Accept ETOH dependency as illness – Develop adaptive coping skills – ↑↑ Self-Esteem Hallucinogens LSD: Acid, Purple Haze Big D Mescaline: Peyote, Half-Moon PCP: Angel dust (lipophilic) Ketamine: Special K Marijuana: Pot, Weed, Grass, Joint, MJ Dronabinol (Marinol) & Nabilone (Cesamet) – used for Chemo induced N & V Action – Alter mood & perception of time & space – Alter cognitive function = insight into life? – Synesthesia = altered visual/auditory – – – – “ Hear Colors” “See Music” Paranoia , Hallucinations & Illusions Bad Trips = fear of losing one’s mind ↑ suicide ↑↑ Aggression & ↑↑ Physical Strength (PCP) Flashbacks (up to 5 -15 years) Stimulants Amphetamines: Ecstasy, MDMA, Amylnitrate – Ice “Crank” smokeable form of methamphetamine – Euphoria lasts 12 -30 h ↑ violence ↑ strength Cocaine: Coke – Crack “Rock” smokeable form of coke – Onset 6-7 secs, High 2-5 min, Severe crash → ↑↑ use Caffeine Action – – – – – ↑↑ DA ↑↑ NE ↑↑ 5-HT ↑ Alertness ↑Endurance ↑Elation Euphoria ↑↑ Self-Esteem ↑↑Assertiveness ↑ Sexuality Verborrhea Tolerance in hours – days Vasoconstriction = ↑ HR ↑ BP ↑ Temp Arrhythmias Withdrawal – – – – Tobacco Respiratory depression Dilated pupils Fatigue Vivid Dreams ↑↑ Appetite Psychomotor retardation Crashing = Suicidal Ideation Psychosis ↑↑ Tremors Methamphetamine Methamphetamine Facial Effects Meth Aging Crank Bugs Opioids Morphine MSO4 Codeine Heroin Action – Euphoria ↓↓ Pain Perception ↑↑ Passivity – ↓ Anxiety & ↓ ↓ Aggression = Apathy – ↓ Hunger ↓ Thirst ↓ Libido – Pin point Pupils ↓↓ Respirations – Rapid weak pulse Withdrawal (5-14 days) – Watery eyes Rhinitis – Yawning Sneezing Tremors – Abdominal spasms Sedatives, Hypnotics & Anxiolytics Brevital, Seconal Restoril, Halcion Valium, Xanax, Ativan, Rohypnol ‘Roffis” Gamma Hydroxybutrate (GHB): – G Liquid X Georgia Homeboy Action – Relaxation & well being = Sense of Calm – ↓↓ HR ↓↓ BP ↓↓ RR – ↓↓ Muscle spasms & ↑↑ Sleep – ↓↓ Coordination = Ataxia Mental Impairment – Quick temper ↓↓ Patience & tolerance – ↑↑ Dose = ↓↓ Anxiety → Sedation → Coma → Death Impaired Nursing Practice 1/8 Nurses are addicted = impacts their practice. 1/5 are chemically dependent 45,000 Alcoholic RNs Narcotic addiction is 30x > public 50-70% due to inadequate pain management for work related injury. Hx of ETOH or substance abuse in family. ↑↑ Social stigma against female addicts Warning Signs of Abuse Poor judgment & work performance – Errors in charting & ↓↓ Pt. care – ↑Accidents/incidents during shift Inaccurate med counts – ↑↑ vial breakage & waste Volunteers to work extra shifts & give meds. – ↑ Reports from Pt of unrelieved pain ↑↑ Absenteeism (after many days off) Leaves floor frequently – Spends ↑↑ time in bathroom ETOH breath Flushed face Reddened eyes Unsteady Gait Hyperactivity Irritability/Apathetic Nursing Interventions Document RN behavior, Pt or medication incidents objectively. Approach colleague with compassion Express concern for her health and Pt’s safety. Remain in touch with colleague Notify supervisor to report impaired colleague – Ethical & legal obligation – Facilitates RN to obtain EAP services, RX – Protects the public! Peer Assistance Program PAP Established in 1982 by ANA RN voluntarily submits license during program (5 years) Facilitates impaired nurses to recognize their illness. Maintain confidentiality & obtain needed RX. Regain accountability within profession. Contract – Method of RX, work guidelines, spot drug testing and quarterly evaluations. Work site monitor √ progress during treatment. If unsuccessful refer to the State Board of Nursing, – Office of Professional Discipline (OPD). – Any Pt. harm or criminal charges Narcotics taken (Federal Law) & theft of property FL 2009 Law – Hx of abuse – Unable to reapply for license for 15 years! Statewide Peer Assistance for Nurses (SPAN) Voluntary participation with PAP. SPAN Advocate – Mentor maintains weekly contact for 1:1 counseling and support. Weekly support group meetings – With other impaired nurses. Open ended participation – Encouraged to stay active c PAP program Evolve into sponsors for their colleagues. Terminated for non-participation – PAP notified.