* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Hospital Based Research Pharmacy Services
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
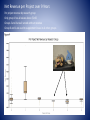
Introduction to Research Pharmacy Investigational Drug Control and Patient Safety CUMC RP Robert B. MacArthur, Pharm.D. “ Why does it take so long and cost so much for me to get my study pills ? “ Topics What, Why, and How about CUMCRP Labeling Some FDA and ISMP Standards and Requirements CPOE Revenue and Expenses What Do We Do ? • Investigational Drug Management and Dispensing • Compounding • Clinical Trial Kits • Pharmacokinetic Study Design and Support • Interactive Voice Response System (IVRS) • Multicenter clinical trial drug distribution CUMC Research Pharmacy – Locations • CUMC/NYPH Campus – Irving Pavilion IP-749 – Black Building, Basement B-30, • New Jersey – 17 Smith Street, Englewood NJ • Website: www.researchpharmacy.org • Email: [email protected] CUMC Research Pharmacy – Production • • • • • • Active Studies - ≈ 200 - 280 New projects/month ≈ 10 - 15 Dispensed products/month ≈ 300 Destroyed products/month ≈ 125 Kits/month ≈ 360 Shipments/month ≈ 160 Why? • Adds value to the clinical research capabilities offered by the medical center • Gives Investigators the ability to adhere to GCPs in a simple, cost-effective manner • Adds an additional level of quality control to drug storage and dispensing Research – Early Days “…I combed the Eastman Chemical Company Catalog and other price lists for suitable phenyl compounds…They wrote back to me that they had on hand 19 different compounds analogous to Phenobarbital, and that I was welcome to them…” 1937 Putnam “…142 patients received dilantin therapy for two to 11 months… was effective in controlling convulsive seizures in a great majority of a select group of patients who were not helped by other methods or therapy…without a doubt considerably more toxic than bromides and barbituric compounds…” 1938 Merritt and Putnam Multiple Regulatory Agencies Involved Regulatory Issues • 21 CFR 312.57 – A sponsor shall maintain adequate records showing receipt, shipment, or other disposition of investigational drug… • 21 CFR 312.59 – …sponsor shall assure the return of all unused drug supplies from each investigator… and maintain written records… • 21 CFR 312.62 – An investigator is required to maintain adequate records of the disposition of the drug, including dates, quantity, and use by subjects…investigator shall return the unused drug supplies to the sponsor Routine FDA Inspection Findings 1977 - 1990, 2308 inspections • Most Common Deficiencies – consent form problems – protocol non-adherence – drug accountability problems 54% 26% 25% » J Clin Pharmacol 1990;30:296-302 FDA Inspection Findings Drug Accountability • • • • • • On-going accountability does not match CRF Medication started before IRB approval Poorly maintained on-going drug accountability Maintained only in CRF, not independently Test drug not dispensed in sequential order Diversion of drug to animal studies without PI or sponsor approval Investigational Drug Accountability Report Product Expiration Report Labeling Prescription Product Patent Medicines 1906 Legislation Food and Drug Act Prohibited interstate commerce of adulterated or misbranded food and drugs, unlawful to add ingredients that would represent a health hazard, Food and drug labeling cannot be misleading 1937 Tragedy S.E. Massengill Company DIETHYLENE GLYCOL markets an oral liquid sulfanilamide preparation using diethylene glycol as a solvent. Several deaths result 1938 Legislation Federal Food, Drug and Cosmetic Act includes FDA authority to inspect sponsors, CROs, Investigators, IRBs 1941 Legislation Agency batch approval of insulin and antibiotics. Brought medical devices and cosmetics under FDA perview. Prohibited false therapeutic claims on labeling, drugs had to be labeled with adequate instructions, FDA inspections of factories were authorized, drug manufacturing and controls, drugs had to be shown to be safe before they could be marketed, birth of the NDA [505(b)(1)] 1955 Tragedy Cutter Laboratories polio vaccine causes 260 cases of polio, including 192 cases of paralytic polio 1965 Legislation Drug Abuse and Control Amendments 1960 Tragedy Thalidomide British Medical Journal publishes about neurotoxicity Withdrawan in Germany for causing congenital abnormalities. Complete US drug recall, 25000 doses unaccounted for, 17 cases of thalidomide-induced phocomelia identified 1962 Legislation Kefauver, Kelsey Amendments Signed Manufacturers had to prove that drugs were effective, as well as safe, going back to 1938. Experimental subjects to be given informed consent, FDA regulation of clinical investigations, GMP requirements, new drugs could only be marketed with FDA assent, with no limitation on approval time. FDA inspectors have access to establishment records FDA-IND Labeling Regulations Sec. 312.6 Labeling of an investigational new drug • (a) On the immediate package… "Caution: New Drug--Limited by Federal (or United States) law to investigational use.“ • (b) The label or labeling of an investigational new drug shall not bear any statement that is false or misleading in any particular and shall not represent that the investigational new drug is safe or effective for the purposes for which it is being investigated. • (c) The appropriate FDA Center Director, according to the procedures set forth in 201.26 or 610.68 of this chapter, may grant an exception or alternative to the provision in paragraph…. (a) of this section, to the extent that this provision is not explicitly required by statute, for specified lots, batches, or other units of a human drug product that is or will be included in the Strategic National Stockpile. FDA-NDA Labeling Regulations The United States Pharmacopeial Convention has established requirements for containers which are described in many of the drug product monographs in The United States Pharmacopeia/National Formulary (USP/NF)….. These requirements are defined in the "General Notices and Requirements" (Preservation, Packaging, Storage, and Labeling) section of the USP. Labeling Investigational Drugs No patient instructions No expiration date, retest date only What does one do with a retest date? Labeling Investigational Drugs Detailed instructions about how to push tablets through blister pack… in 11 languages Font too small to read Not Childproof Minimal product labeling Beautiful syringe labeling in French Storing Investigational Drugs One Study of 2 Active Drugs 5 Dosage Forms Drug A, Drug A Placebo Drug B, Drug B Placebo Drug A or B (blinded active) 4 Dosing Phases each with a Separate Drug Supply Titration Maintenance Conversion Adjustment 2 shelves per study Over 30,000 Dispensing Errors Have Been Voluntarily Reported In The Last 3 Years From Outpatient Pharmacies in Hospitals To U.S. Pharmacopeia 5 Most Frequent Types of Prescription Drug Dispensing Errors (As Voluntarily Reported to U.S. Pharmacopeia by Outpatient Pharmacies at Hospitals from 2004-2006) Error Type Improper Dose/Quantity Unauthorized/Wrong Drug Wrong Patient Drug Prepared Incorrectly Wrong Dosage Form Total Number % of Total Errors 10,642 35% 7,304 24% 3,976 13% 2,707 9% 2,513 8% What pharmacists need to focus on Senator J D. Klein About 1 in 184 Dispensing Errors Reported by Outpatient Pharmacies in Hospitals Caused Harm to Patients Nationwide Prescription Drug Dispensing Errors By Level of Severity (As Voluntarily Reported to U.S. Pharmacopeia by Outpatient Pharmacies at Hospitals from 2004-2006) Error Severity Code A B C D E F G H I Total Errors Total Harmful Errors Number 0 15811 13494 536 130 30 2 0 1 30004 163 Percentage of Overall Errors 0% 53% 45% 1.79% 0.43% 0.1% 0.007% 0% 0.003% 1 in 184 errors are harmful 0.54% E= temporary harm to the patient and required intervention F= temporary harm to the patient and required prolonged hospitalization G= permanent patient harm H= required intervention necessary to sustain life I= contributed to or resulted in a patient's death ISMP errors with investigational drugs “…syringes are labeled with an identification number [only]. “Once the syringes are removed from the box, the carton label containing important information is lost….” “…license plate-type code name changes name to generic name. The code name remains on the product label, but the research team refers to and orders the drug by its new generic name. ..” Pharmaceutical Industry estimates of in hospital investigational drug dispensing error rates are typically 4 – 6 % Pharmacist training programs are improving, via pharmacy manuals, on-line training, pictogram drug preparation instructions ISMP error potential investigational drugs “…Many investigational drugs are labeled using a very small font size;… drug packages for active and placebo look remarkably similar…” “…drugs are not supplied in unit-dose packages. Additionally, vial sizes of parenteral drugs are sometimes inappropriate…” 5 ml dose, 50 ml vial Standard Labeling • Agent dispensed to study subjects should be clearly labeled as an investigation drug. • Caution: Drug Limited by Federal Law to Investigational Use Only • Warning Labels – – – – – – – – – – Subject Name / Hospital MRN Subject Study Number Hospital or Clinic Name Administration instructions Accepted name of drug and dose Number of units or total volume Date agent prepared and expiration date IRB number Ordering physician name and pharmacist name Name, address and phone number of dispensing pharmacy Blinded Inv Drug Kit Labels Sample Kit Box Label Sample Tube/Vial Label CPOE and EPRESCRIBING The first national e-prescribing conference following the release of new rules and regulations borne from the Medicare Improvements for Patients and Providers Act of 2008 (MIPPA) The World Health Care Congress Leadership Summit on – ePrescribing & Medication Management Nov. 17, 2008 Westin Tyson's Corner – Falls Church, VA Computerized Physician Order Entry • • • • • • • • • • • • • RPH Assigned, 1st Draft Draft completed RPh, Reviewed Sent to nursing for review Returned to RPh for edits Sent to Eclypsis IT Received back from Eclypsis IT Screen Shot in Review by RPh Screen Shot sent to nursing Screen Shot sent to Eclypsis IT Order set not finalized by PI Order set approved by PI All signatures CPOE Example CUMC and NYPH Investigational Drug Policies JCAHO Requirement Distribution of investigational drugs administered to patients cared for within a health care organization be under the central control of the hospital pharmacy department NYPH Policy CUMC Policy • Any use of an investigational drug must be approved by the Columbia University Institutional Review Board • Any use of an investigational drug must be approved by the Columbia University Institutional Review Board • All research protocols using investigational drugs must contain the investigational drug information required to be provided in a Columbia University IRB submission. • All research protocols using investigational drugs must contain the investigational drug information required to be provided in a Columbia University IRB submission. CUMC and NYPH Investigational Drug Policies JCAHO Requirement Distribution of investigational drugs administered to patients cared for within a health care organization be under the central control of the hospital pharmacy department. NYPH Policy • Orders in Hospital medication profiling system CUMC Policy • Orders must be written and made available in the patient’s medical record and pharmacy medication profiling system. CUMC and NYPH Investigational Drug Policies JCAHO Requirement Distribution of investigational drugs administered to patients cared for within a health care organization be under the central control of the hospital pharmacy department. NYPH Policy • Pharmacy Dept will order, store, inventory, dispense, destroy/return all investigational drug. CUMC Policy • The RP will order, store, inventory, dispense and destroy/ return all investigational drug. CUMC and NYPH Investigational Drug Policies JCAHO Requirement Distribution of investigational drugs administered to patients cared for within a health care organization be under the central control of the hospital pharmacy department. NYPH Policy • Pharmacy Department will only dispense with a valid order. CUMC Policy • The RP will only dispense an investigational drug subsequent to a valid order by an authorized investigator. Net Revenue per Project over 9 Years Per project revenue by research group Only group 1 has all values above $0.00 Groups 3 and 4 are all served without revenue Group 0 and 1 are used to supplement losses in all other groups Revenue:Expense Ratios over 9 years Close to 1.0 “That Research Pharmacy sure does a great job ! “ Thanks for listening, and for supporting safe dispensing practices!