* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 18 PowerPoint
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
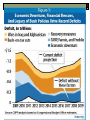
Chapter 18 Economic Policy US Government AP The Economy Hard to predict how policy will impact the economy over the long term Natural business cycle The Business Cycle Over time a business gains and loses This is normal The Impact of Government Policy goal is to keep the line as straight as possible, with steady growth Becomes a valence issue The Debt To eliminate it: Raise taxes or Reduce spending Or a combination of both Enter valance—Dem’s vs Rep’s 1990’s We had a budget surplus Dems -start new programs Had to compromise (did both) Rep’s -give a tax cut The players in Fiscal Policy OMB CBO Congress President Cabinet Departments Agencies (GAO) Interest groups Other Players-Monetary Policy 1. The Federal Reserve Board Sets interest rates Is independent Congress Approves taxes Approves the budget (CBO) Foreign policy laws (NAFTA) 2. Triple play……. 1. 2. 3. OMB Director Chair of the Council of Economic Advisors Treasury Secretary These 3 offices are the closest advisors to the President on the economy Economy and Elections “Pocket Book” issues during an election help/hurt incumbents (2008) 1. Unemployment 2. Inflation 3. Older voters/Fixed income Econ and Elections II Makes politicians tempted to look at short term policy Try to improve it at election time IMPOSSIBLE TO DO D= ↓ unemployment R= ↓ inflation The “Perfect” Policy 1. 2. 3. Have nice Govt. programs Have less debt (Lower spending) Keep taxes low mission: impossible 5 Economic theories 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Monetarism Keynesianism Planning Supply Side tax cuts Reaganomics 5 theories Each President chooses advisors who have his point of view on policies Monetary policy a. b. Govt. focus on the supply of money Control the supply by: Deposit requirements (reserve req.) Interest rates (prime) Fiscal Policy a. b. Government spending policy The budget The tax rate The Budget 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. October 1 to September 30 Executive branch and Congress President/OMB put it out Congress (H/S) go over it—put ceilings in place Changes are usually small Entitlements Most of the Budget is money that must be spent (66%) Social Security Medicare Bond payments The Budget-The End Is out of control Deficit spending allows the budget to be whatever it “needs” to be Current deficit: $15 trillion (Growing at $1.3 million a minute today) (your share?-$50,000) The “Perfect” Policy 1. 2. 3. Have nice Govt. programs Have less debt (Lower spending) Keep taxes low mission: impossible 3 Things that Matter in Economic Policy a. The economic health of the nation (real vs. perceived) (interest group) (Consumer confidence) b. The types of govt. spending (client, interest group) c. Taxes- rates and distribution of benefits (majoritarian or client)